UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission file number: 0-20293
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| VIRGINIA | 54-1598552 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
211 North Main Street, P.O. Box 446, Bowling Green, Virginia 22427
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code is (804) 633-5031
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, par value $1.33 per share | The NASDAQ Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | x | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act).
Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2008 was approximately $184,200,283.
The number of shares of common stock outstanding as of March 2, 2009 was 13,594,125.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement to be used in conjunction with the registrant’s 2009 Annual Meeting of Shareholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Form 10-K.
FORM 10-K
INDEX
| PAGE | ||||
| ITEM |
||||
| PART I | ||||
| Item 1. |
1 | |||
| Item 1A. |
11 | |||
| Item 1B. |
16 | |||
| Item 2. |
16 | |||
| Item 3. |
16 | |||
| Item 4. |
16 | |||
| PART II | ||||
| Item 5. |
16 | |||
| Item 6. |
19 | |||
| Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
20 | ||
| Item 7A. |
40 | |||
| Item 8. |
41 | |||
| Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
82 | ||
| Item 9A. |
83 | |||
| Item 9B. |
83 | |||
| PART III | ||||
| Item 10. |
84 | |||
| Item 11. |
84 | |||
| Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
84 | ||
| Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
85 | ||
| Item 14. |
85 | |||
| PART IV | ||||
| Item 15. |
85 | |||
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Certain statements in this report may constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are statements that include projections, predictions, expectations or beliefs about future events or results or otherwise are not statements of historical fact. Such statements are often characterized by the use of qualified words (and their derivatives) such as “expect,” “believe,” “estimate,” “plan,” “project,” “anticipate” or other statements concerning opinions or judgment of the Company and its management about future events. Although the Company believes that its expectations with respect to forward-looking statements are based upon reasonable assumptions within the bounds of its existing knowledge of its business and operations, there can be no assurance that actual results, performance or achievements of the Company will not differ materially from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by such forward-looking statements. Actual future results and trends may differ materially from historical results or those anticipated depending on a variety of factors, including, but not limited to, the effects of and changes in: general economic conditions, the interest rate environment, legislative and regulatory requirements, competitive pressures, new products and delivery systems, inflation, changes in the stock and bond markets, technology, and consumer spending and savings habits. The Company does not update any forward-looking statements that may be made from time to time by or on behalf of the Company.
GENERAL
Union Bankshares Corporation (the “Company”) is a multi-bank holding company organized under Virginia law and registered under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956. The Company is headquartered in Bowling Green, Virginia. The Company is committed to the delivery of financial services through its three community bank subsidiaries (the “Community Banks”) and three non-bank financial services affiliates. The Company’s Community Banks and non-bank financial services affiliates are:
| Community Banks | ||||||
| Union Bank & Trust Company |
Bowling Green, Virginia | |||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
Warsaw, Virginia | |||||
| Rappahannock National Bank |
Washington, Virginia | |||||
| Financial Services Affiliates | ||||||
| Union Mortgage Group, Inc. |
Annandale, Virginia | |||||
| Union Investment Services, Inc. |
Ashland, Virginia | |||||
| Union Insurance Group, LLC |
Bowling Green, Virginia | |||||
History
The Company was formed in connection with the July 1993 merger of Northern Neck Bankshares Corporation and Union Bancorp, Inc. In connection with the merger, Union Bank and Trust Company (“Union Bank”) and Northern Neck State Bank became wholly- owned bank subsidiaries of the Company. Although the Company was formed in 1993, the Community Banks are among the oldest in Virginia. Union Bank and Rappahannock National Bank began business in 1902 and Northern Neck State Bank dates back to 1909. On September 1, 1996, King George State Bank and on July 1, 1998, Rappahannock National Bank became wholly-owned subsidiaries of the Company. On February 22, 1999, Bay Community Bank (formerly Bank of Williamsburg) began business as a newly organized bank. In June
1
1999, King George State Bank was merged into Union Bank, the Company’s largest subsidiary. The Company acquired Guaranty Financial Corporation and its wholly owned subsidiary, Guaranty Bank (“Guaranty”), on May 1, 2004, and operated Guaranty as a separate subsidiary until September 13, 2004, when Guaranty was merged into Union Bank. The Company acquired Prosperity Bank & Trust Company (“Prosperity”) on April 1, 2006 and operated Prosperity as a separate subsidiary until March 15, 2008, when Prosperity was also merged into Union Bank. On October 31, 2008, the Company merged its Bay Community Bank affiliate into Union Bank.
Product Offerings and Market Distribution
The Company is one of the largest community banking organizations based in Virginia, providing full service banking to the Northern, Central, Rappahannock, Tidewater and Northern Neck regions of Virginia through 59 locations of its bank subsidiaries. Union Bank currently has 43 locations in the counties of Albemarle, Caroline, Chesterfield, Fluvanna, Hanover, Henrico, King George, King William, Nelson, Spotsylvania, Stafford, Westmoreland and the Cities of Williamsburg, Newport News, Grafton, Charlottesville and Fredericksburg; Northern Neck State Bank has nine locations in the counties of Essex, Lancaster, Northumberland, Richmond and Westmoreland; Rappahannock National Bank has seven locations in Washington, Warrenton, Middleburg, Winchester and Front Royal.
Each of the Community Banks is a full service retail commercial bank offering consumers and businesses a wide range of banking and related financial services, including checking, savings, certificates of deposit and other depository services, as well as loans for commercial, industrial, residential mortgage and consumer purposes. The Community Banks issue credit cards and deliver automated teller machine (“ATM”) services through the use of reciprocally shared ATMs in the major ATM networks as well as remote ATMs for the convenience of customers and other consumers. Each of the Community Banks also offers internet banking services and online bill payment for all customers, whether consumer or commercial.
The Company provides other financial services through its non-bank affiliates, Union Investment Services, Inc., Union Mortgage Group, Inc. (“Union Mortgage”) and Union Insurance Group, LLC. Union Bank owns a non-controlling interest in Johnson Mortgage Company, LLC.
Union Investment Services, Inc. has provided securities, brokerage and investment advisory services since its formation in February 1993. It has six offices within the Community Banks’ trade areas and is a full service investment company handling all aspects of wealth management including stocks, bonds, annuities, mutual funds and financial planning.
Union Mortgage has thirteen offices in the following locations: Virginia (nine), Maryland (three) and South Carolina (one). Union Mortgage is also licensed to do business in selected states throughout the Mid-Atlantic and Southeast, as well as Washington, D.C. It provides a variety of mortgage products to customers in those areas. The mortgage loans originated by Union Mortgage are generally sold in the secondary market through purchase agreements with institutional investors.
On August 31, 2003, the Company formed Union Insurance Group, LLC (“UIG”), an insurance agency, in which each of the subsidiary banks and Union Mortgage has an ownership interest. This agency operates in a joint venture with Bankers Insurance, LLC, a large insurance agency owned by community banks across Virginia and managed by the Virginia Bankers Association. UIG generates revenue through sales of various insurance products, including long term care insurance and business owner policies.
2
SEGMENTS
The Company has two reportable segments: its traditional full service community banking business and its mortgage loan origination business. For more financial data and other information about each of the Company’s operating segments, refer to the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” section, “Community Bank Segment,” and to Note 18 “Segment Reporting” in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.”
EXPANSION AND STRATEGIC ACQUISITIONS
The Company expands its market area and increases its market share through internal growth, de novo expansion and strategic acquisitions. Strategic acquisitions by the Company to date have included whole bank acquisitions branch and deposit acquisitions and purchases of existing branches from other banks. The Company generally considers acquisitions of companies in strong growth markets or with unique products or services that will benefit the entire organization. Targeted acquisitions are priced to be economically feasible with minimal short-term drag to achieve positive long-term benefits. These acquisitions may be paid for in the form of cash, stock, debt or a combination thereof. The amount and type of consideration and deal charges paid could have a short-term dilutive effect on the Company’s earnings per share or book value. However, cost savings and revenue enhancements in such transactions are anticipated to provide long-term economic benefit to the Company.
In September 2007, the Company announced it had completed the acquisition of the deposits and facilities of six bank branches (“Acquired Bank Branches”) in Virginia from Provident Bank. The branches acquired are located in the communities of Charlottesville, Middleburg, Warrenton (two) and Winchester (two). They became part of two of the Company’s banking subsidiaries, Union Bank (Charlottesville branch) and Rappahannock National Bank (remaining five branches). The Acquired Bank Branches’ deposits were approximately $43.3 million.
The Company’s de novo expansion consists of opening five new branches in Virginia during the last three years:
| • | Cosner’s Corner, Union Bank branch located in Spotsylvania County (October 2008) |
| • | Harrison Crossing, Union Bank branch located in Spotsylvania County (December 2007) |
| • | Twin Hickory, Union Bank branch located in Henrico County (December 2006) |
| • | Front Royal, Rappahannock National Bank branch located in Warren County (December 2006) |
| • | Grafton, Bay Community Bank branch located in York County (March 2006) |
In May 2007, the Company completed construction of a new 70,000 square foot operations center in Caroline County, Virginia at a cost of approximately $13 million. The facility is located just west of Interstate 95 near the intersection of U.S. Route 1 and State Route 207; it is approximately twelve miles west of the Company’s corporate offices in Bowling Green, Virginia. The new facility will accommodate the Company’s anticipated growth and provide improved access to the Greater Richmond and Fredericksburg workforce. The Company sold its former operations center in the third quarter of 2007.
EMPLOYEES
As of December 31, 2008, the Company had approximately 670 full-time equivalent employees, including executive officers, loan and other banking officers, branch personnel, operations personnel and other support personnel. Of this total, 93 were mortgage segment personnel. None of the Company’s employees is represented by a union or covered under a collective bargaining agreement. Management of the Company considers its employee relations to be excellent.
3
COMPETITION
The financial services industry remains highly competitive and is constantly evolving. The Company experiences strong competition in all aspects of its business. In its market areas, the Company competes with large national and regional financial institutions, credit unions, other independent community banks, as well as consumer finance companies, mortgage companies, loan production offices, mutual funds and life insurance companies. Competition has increasingly come from out-of-state banks through their acquisitions of Virginia-based banks. Competition for deposits and loans is affected by various factors including interest rates offered, the number and location of branches and types of products offered, and the reputation of the institution. Because they enjoy a favorable tax status, credit unions have been allowed to increasingly expand their membership definitions and to offer more attractive loan and deposit pricing. The Company’s non-bank affiliates also operate in highly competitive environments.
The Company is headquartered in Bowling Green, Virginia and is one of the largest independent bank holding companies based in Virginia. The Company believes its community bank framework and philosophy provide a competitive advantage, particularly with regard to larger national and regional institutions, allowing the Company to compete effectively. The Company’s Community Banks generally have strong market shares within the markets they serve. The Company’s deposit market share in Virginia was 1.26% and 1.31% as of June 30, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
ECONOMY
The current recession, which economists suggest began in late 2007 or early 2008, became a major recognizable force in the late summer or early fall of 2008 in the United States of America (“U.S.”) and around the world. Since then, stock markets in most nations have dropped sharply, foreclosures have increased dramatically, unemployment has risen significantly, the capital and liquidity of financial institutions have been severely challenged and credit markets have been greatly reduced. In the U.S. and other industrialized nations, governments have provided support for financial institutions in order to strengthen capital, increase liquidity and ease the credit markets. In the U.S., these actions have provided capital for banks and other financial institutions and increased regulations, oversight on banks, including the Company.
SUPERVISION AND REGULATION
Bank holding companies and banks are extensively and increasingly regulated under both federal and state laws. The following description briefly addresses certain historic and current provisions of federal and state laws and certain regulations, proposed regulations, and the potential impacts on the Company and its Community Banks. To the extent statutory or regulatory provisions or proposals are described herein, the description is qualified in its entirety by reference to the particular statutory or regulatory provisions or proposals.
Bank Holding Companies
As a bank holding company registered under the Bank Holding Company Act of 1956 (the “BHCA”), the Company is subject to regulation by the Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System (the “Federal Reserve”). The Federal Reserve has jurisdiction under the BHCA to approve any bank or non-bank acquisition, merger or consolidation proposed by a bank holding company. The BHCA generally limits the activities of a bank holding company and its subsidiaries to that of banking, managing or controlling banks, or any other activity that is so closely related to banking or to managing or controlling banks as to be a proper incident thereto.
4
Since September 1995, the BHCA has permitted bank holding companies from any state to acquire banks and bank holding companies located in any other state, subject to certain conditions, including nationwide and state imposed concentration limits. Banks are also able to branch across state lines provided certain conditions are met, including that applicable state law must expressly permit interstate branching. Virginia law permits branching across state lines if there is reciprocity with the state law where the out-of-state bank is based. The Company currently has no plans to branch outside of the Commonwealth of Virginia.
There are a number of obligations and restrictions imposed on bank holding companies and their depository institution subsidiaries by federal law and regulatory policy. Collectively, these are designed to reduce potential loss exposure to the depositors of such depository institutions and to the Deposit Insurance Fund (the “DIF”) of the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation (the “FDIC”) if the depository institution is either in danger of default or is in default. For example, under a Federal Reserve policy relating to bank holding company operations, a bank holding company is required to serve as a source of financial strength to its subsidiary depository institutions and to commit resources to support such institutions in circumstances where it might not do so absent such policy. In addition, the “cross-guarantee” provisions of federal law require insured depository institutions under common control to reimburse the FDIC for any loss suffered or reasonably anticipated by the DIF as a result of the default of a commonly controlled insured depository institution. The FDIC may decline to enforce the cross-guarantee provisions if it determines that a waiver is in the best interest of the DIF. The FDIC’s claim for damages is superior to claims of stockholders of the insured depository institution or its holding company, but is subordinate to claims of depositors, secured creditors and holders of subordinated debt (other than affiliates) of the commonly controlled insured depository institutions.
The Federal Deposit Insurance Act (the “FDIA”) also provides that amounts received from the liquidation or other resolution of any insured depository institution by any receiver must be distributed (after payment of secured claims) to pay the deposit liabilities of the institution prior to payment of any other general creditor or stockholder. This provision would give depositors a preference over general and subordinated creditors and stockholders in the event a receiver is appointed to distribute the assets of such depository institutions.
The Company is registered under the bank holding company laws of Virginia. The Company and the Community Banks, other than Rappahannock National Bank, which is regulated and supervised by the Office of the Comptroller of the Currency (the “OCC”), are subject to regulation and supervision by the State Corporation Commission of Virginia (the “SCC”) and the Federal Reserve.
Capital Requirements
The Federal Reserve, the OCC and the FDIC have issued substantially similar risk-based and leverage capital guidelines applicable to United States banking organizations. In addition, those regulatory agencies may from time to time require that a banking organization maintain capital above the minimum levels because of its financial condition or actual or anticipated growth. Under the risk-based capital requirements of these federal bank regulatory agencies, the Company and each of the Community Banks are required to maintain a minimum ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets of at least 8.0%. At least half of the total capital is required to be “Tier 1 capital,” which consists principally of common and certain qualifying preferred shareholders’ equity (including Trust Preferred Securities), less certain intangibles and other adjustments. The remainder (“Tier 2 capital”) consists of a limited amount of subordinated and other qualifying debt (including certain hybrid capital instruments) and a limited amount of the general loan loss allowance. The Tier 1 and total capital to risk-weighted asset ratios of the Company were 13.31% and 14.56%, respectively, as of December 31, 2008, thus exceeding the minimum requirements.
Each of the federal regulatory agencies has established a minimum leverage capital ratio (Tier 1 capital to average adjusted assets) (“Tier 1 leverage ratio”). These guidelines provide for a minimum Tier 1
5
leverage ratio of 4% for banks and bank holding companies that meet certain specified criteria, including having the highest regulatory examination rating and are not contemplating significant growth or expansion. The Tier 1 leverage ratio of the Company as of December 31, 2008 was 11.14%, which is above the minimum requirements. The guidelines also provide that banking organizations experiencing internal growth or making acquisitions will be expected to maintain strong capital positions substantially above the minimum supervisory levels without significant reliance on intangible assets.
6
Limits on Dividends and Other Payments
The Company is a legal entity, separate and distinct from its subsidiaries. A significant portion of the revenues of the Company result from dividends paid to it by the Community Banks. There are various legal limitations applicable to the payment of dividends by the Community Banks to the Company and to the payment of dividends by the Company to its respective shareholders. The Community Banks are subject to various statutory restrictions on their ability to pay dividends to the Company. Under the current supervisory practices of the Community Banks’ regulatory agencies, prior approval from those agencies is required if cash dividends declared in any given year exceed net income for that year, plus retained net profits of the two preceding years. The payment of dividends by the Community Banks or the Company may be limited by other factors, such as requirements to maintain capital above regulatory guidelines. Bank regulatory agencies have the authority to prohibit the Community Banks or the Company from engaging in an unsafe or unsound practice in conducting their business. The payment of dividends, depending on the financial condition of the Community Banks, or the Company, could be deemed to constitute such an unsafe or unsound practice.
Under the FDIA, insured depository institutions such as the Community Banks are prohibited from making capital distributions, including the payment of dividends, if, after making such distribution, the institution would become “undercapitalized” (as such term is used in the statute). Based on the Community Banks’ current financial condition, the Company does not expect this provision will have any impact on its ability to receive dividends from the Community Banks. Non-bank subsidiaries pay the parent company dividends periodically on a non-regulated basis.
In addition to dividends it receives from the Community Banks, the Company receives management fees from its affiliated companies for various services provided to them including: data processing, item processing, loan operations, deposit operations, financial accounting, human resources, funds management, credit administration, credit support, sales and marketing, collections, facilities management, call center, legal, compliance and internal audit. These fees are charged to each subsidiary based upon various specific allocation methods measuring the estimated usage of such services by that subsidiary. The fees are eliminated from the financial statements in the consolidation process.
Under federal law, the Community Banks may not, subject to certain limited exceptions, make loans or extensions of credit to, or investments in the securities of, the Company or take securities of the Company as collateral for loans to any borrower. The Community Banks are also subject to collateral security requirements for any loans or extensions of credit permitted by such exceptions.
On December 19, 2008, the Company entered into a Letter Agreement (the “Purchase Agreement”) with the United States Department of the Treasury (“Treasury”), pursuant to which it issued 59,000 shares of the Company’s Fixed Rate Cumulative Perpetual Preferred Stock, Series A (the “Preferred Stock”) for $59 million. The issuance was made pursuant to the Treasury’s Capital Purchase Program (“CPP”) under the Troubled Asset Relief Program (“TARP”). For so long as the Company is a participant in the CPP, the Treasury’s consent will be required for any increase in common stock dividends beyond $.185 per share (the Company’s dividend level prior to the CPP transaction); the Treasury’s consent will also be required for any stock repurchases until the earlier of three years or redemption or transfer of all of the Preferred Stock.
Recent Legislative and Regulatory Initiatives to Address Financial and Economic Crises
Congress, Treasury, and the federal banking regulators, including the FDIC, have taken broad measures since early September 2008 to address the turmoil in the U. S. banking system.
On October 3, 2008, the Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 (“EESA”) was enacted. EESA authorizes the Treasury to purchase from financial institutions and their holding companies up to $700 billion in mortgage loans, mortgage-related securities and certain other financial instruments, including debt and equity securities issued by financial institutions and their holding companies in the TARP.
7
On February 17, 2009, President Obama signed into law the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (“ARRA”), establishing more limits on executive compensation for all current and future TARP recipients. The ARRA limits do not repeal or replace the rules discussed above but supplement the guidance issued by the Treasury. Under the ARRA, any TARP participant may not pay any bonus, retention award or incentive compensation to its five most highly paid executives, except for payments of long term restricted stock, the awards of which do not vest while the Preferred Stock is outstanding and do not have a value greater than one-third of the officer’s total annual compensation, unless the payments are required pursuant to a written agreement executed prior to February 11, 2009. In addition, the ARRA requires the Treasury to review bonuses, retention awards and other compensation paid to a TARP participant’s five most highly-compensated officers and the next 20 most highly compensated employees to determine if the payments were excessive or inconsistent with the purpose of the ARRA or TARP or were otherwise contrary to the public interest. If so, the Treasury is directed to negotiate the return of any such amounts to the government.
The purpose of TARP is to restore confidence and stability to the U. S. banking system and to encourage financial institutions to increase their lending to customers and to each other. The Treasury has allocated $250 billion to the TARP Capital Purchase Program. TARP also includes direct purchases or guarantees of troubled assets of financial institutions. Participants in the CPP are subject to certain executive compensation limits and are encouraged to expand their lending and mortgage loan modifications. Under CPP, the Treasury will purchase debt or equity securities from participating institutions. EESA also increased FDIC deposit insurance on most accounts from $100 thousand to $250 thousand. This increase is in place until the end of 2009 and is not covered by deposit insurance premiums paid by the banking industry.
The Community Banks
The Community Banks are supervised and regularly examined by the Federal Reserve and the SCC, except for Rappahannock National Bank, which is examined by the OCC. The various laws and regulations administered by the regulatory agencies affect corporate practices, such as the payment of dividends, incurrence of debt and acquisition of financial institutions and other companies; they also affect business practices, such as the payment of interest on deposits, the charging of interest on loans, types of business conducted and location of offices.
The Community Banks are subject to the requirements of the Community Reinvestment Act (the “CRA”). The CRA imposes on financial institutions an affirmative and ongoing obligation to meet the credit needs of the local communities, including low and moderate income neighborhoods, consistent with the safe and sound operation of those institutions. Each financial institution’s efforts in meeting community credit needs are evaluated regularly as part of the examination process pursuant to up to ten assessment factors. These factors also are considered in evaluating mergers, acquisitions and applications to open a branch or facility. Many of the banks’ competitors, such as credit unions, are not subject to the requirements of CRA.
Deposit accounts with the Community Banks are insured by the FDIC and the banks are subject to insurance assessments imposed by the FDIC. On February 15, 2006, federal legislation to reform federal deposit insurance was enacted. This legislation required, among other things, that the FDIC adopt regulations increasing the maximum amount of federal deposit insurance coverage per separately insured individual retirement savings account depositor to $250 thousand (with a cost of living adjustment to become effective in five years). The legislation also gave the FDIC greater discretion to identify the relative risks all institutions present to the DIF and set risk-based premiums.
8
On November 2, 2006, the FDIC adopted final regulations establishing a risk-based assessment system that is intended to tie more closely each bank’s deposit insurance assessments to the risk it poses to the DIF. Under the new risk-based assessment system, effective January 1, 2007, the FDIC evaluates each bank’s risk based on three primary factors: (1) its supervisory rating, (2) its financial ratios, and (3) its long-term debt issuer rating, if the bank has one. The new rates for most banks will vary between five and seven cents for every $100 of domestic deposits. In 2007 and 2008, under prior regulations, the Company paid only the base assessment rate for “well capitalized” institutions, which equaled $834 thousand and $1.2 million, respectively, in deposit insurance premiums. These totals included partial offsets of assessment credits of approximately $796 thousand for the two year period.
Legislation
On October 3, 2008, the FDIC’s deposit insurance temporarily increased from $100 thousand to $250 thousand per depositor. Checking, savings, certificates of deposit, money market accounts, and other interest-bearing deposit accounts, when combined, are now FDIC insured up to $250 thousand per depositor through December 31, 2009. Joint accounts may be insured up to $250 thousand per owner in addition to the $250 thousand of insurance available on those same owner’s individual accounts. On January 1, 2010, the standard coverage limit is scheduled to return to $100 thousand for all deposit categories except IRAs and certain retirement accounts mentioned above, which will continue to be insured up to $250 thousand per owner.
On October 14, 2008, the FDIC announced the Temporary Liquidity Guarantee Program to strengthen confidence and increase liquidity in the banking system. The new program guarantees newly issued senior unsecured debt of eligible institutions and provides full deposit insurance coverage for non-interest bearing transaction accounts in FDIC-insured institutions, regardless of the dollar amount, for participating entities. The Temporary Liquidity Guarantee Program has two primary components: the Debt Guarantee Program (FDIC will guarantee the payment of certain newly issued senior unsecured debt), and the Transaction Account Guarantee Program (the FDIC will guarantee certain noninterest-bearing transaction accounts).
Effective January 1, 2009, the FDIC increased assessment rates uniformly by 7 basis points (annual rate) for the first quarter 2009 assessment period only. The FDIC will issue another final rule early in 2009, effective April 1, 2009, to change the way the FDIC’s assessment system differentiates for risk, make corresponding changes to assessment rates beginning with the second quarter of 2009, and make certain technical and other changes to the assessment rules. These increases in insurance premiums are estimated to increase the Company’s pretax noninterest expense by an additional $1.1 million for 2009.
The Community Banks are participating in the FDIC’s Transaction Account Guarantee Program and the Debt Guarantee Program. Under the Transaction Account Guarantee Program, through December 31, 2009, all noninterest-bearing transaction accounts are fully guaranteed by the FDIC for the entire amount in the account. Coverage under the Transaction Account Guarantee Program is in addition to and separate from the coverage available under the FDIC’s general deposit insurance rules. The Company is assessed a 10 basis points fee (annualized) on the balance of each covered account in excess of $250 thousand. The Company does not expect this cost to be material.
Also consistent with EESA requirements, so long as Treasury is an equity holder, the Company is subject to more stringent executive compensation rules. The Company must satisfy certain guidelines, such as: (1) ensuring that incentive compensation for senior executives does not encourage unnecessary and excessive risks that threaten the value of the financial institution; (2) required clawback of any bonus or incentive compensation paid to a senior executive based on statements of earnings, gains, or other criteria that are later proven to be materially inaccurate; (3) the financial institution is prohibited from making any “golden
9
parachute” payment to a senior executive, as that term is defined in the Internal Revenue Code; and (4) agreement not to deduct for tax purposes executive compensation in excess of $500 thousand for each senior executive.
New regulations and statutes are regularly proposed that contain wide-ranging proposals that may or will alter the structures, regulations, and competitive relationships of the nation’s financial institutions. The Company cannot predict whether or in what form any proposed regulation or statute will be adopted or the extent to which the Company’s business may be affected by any new regulation or statute.
Other Safety and Soundness Regulations
The federal banking agencies have broad powers under current federal law to make prompt corrective action to resolve problems of insured depository institutions. The extent of these powers depends upon whether the institutions in question are “well capitalized,” “adequately capitalized,” “undercapitalized,” “significantly undercapitalized,” or “critically undercapitalized.” All such terms are defined under uniform regulations issued by each of the federal banking agencies. Each of the Community Banks meets the definition of being “well capitalized” as of December 31, 2008.
The Gramm-Leach-Bliley Act
Effective March 11, 2001, the Gramm-Leach Bliley Act (the “GLB Act”) allows a bank holding company or other company to certify its status as a financial holding company, thereby allowing such company to engage in activities that are financial in nature, that are incidental to such activities, or are complementary to such activities. The GLB Act enumerates certain activities deemed financial in nature, such as underwriting insurance or acting as an insurance principal, agent or broker; underwriting; dealing in or making markets in securities; and engaging in merchant banking under certain restrictions. It also authorizes the Federal Reserve to determine by regulation what other activities are financial in nature, or incidental or complementary thereto.
USA Patriot Act of 2001
In October 2001, the USA Patriot Act of 2001 (“Patriot Act”) was enacted in response to the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks in New York, Pennsylvania and Northern Virginia. The Patriot Act is intended to strengthen U. S. law enforcement and the intelligence communities’ abilities to work cohesively to combat terrorism. The continuing impact on financial institutions of the Patriot Act and related regulations and policies is significant and wide ranging. The Patriot Act contains sweeping anti-money laundering and financial transparency laws, and imposes various regulations, including standards for verifying customer identification at account opening, and rules to promote cooperation among financial institutions, regulators and law enforcement entities to identify persons whomay be involved in terrorism or money laundering.
Check 21
In October 2003, the Check Clearing for the 21st Century Act, also known as Check 21, became law. Check 21 gives “substitute checks,” such as a digital image of a check and copies made from that image, the same legal standing as the original paper check. Some major provisions of Check 21 include:
| • | allowing check truncation without making it mandatory; |
| • | demanding that every financial institution communicate to accountholders in writing a description of its substitute check processing program and their rights under the law; |
| • | legalizing substitutions for and replacements of paper checks without agreement from consumers; |
| • | retaining in place the previously mandated electronic collection and return of checks between financial institutions only when individual agreements are in place; |
10
| • | requiring that when accountholders request verification, financial institutions produce the original check (or a copy that accurately represents the original) and demonstrate that the account debit was accurate and valid; and |
| • | requiring recrediting of funds to an individual’s account on the next business day after a consumer proves the financial institution has erred. |
Effect of Governmental Monetary Policies
The Company’s operations are affected not only by general economic conditions, but also by the policies of various regulatory authorities. In particular, the Federal Reserve regulates money and credit conditions and interest rates to influence general economic conditions. These policies have a significant impact on overall growth and distribution of loans, investments and deposits; they affect interest rates charged on loans or paid for time and savings deposits. Federal Reserve monetary policies have had a significant effect on the operating results of commercial banks, including the Company, in the past and are expected to do so in the future. As part of EESA, Treasury is granted authority to implement policies and programs to help restore stability and liquidity to the U. S. financial markets. There can be no assurances that any programs initiated in the future will be effective in restoring stability and providing sufficient liquidity to the U. S financial markets. As a result, we are unable to predict the effects of possible changes in monetary policies upon the future operating results of the Company.
Filings with the SEC
The Company files annual, quarterly and other reports under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). These reports are posted and are available at no cost on the Company’s website, www.ubsh.com, through the Investor Relations link, as soon as reasonably practicable after the Company files such documents with the SEC. This Form 10-K is directly available at http://www.ubsh.com/site/2008AnnualReport_10-K.pdf. The Company’s filings are also available through the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
General economic conditions, either national or within the Company’s local markets, could materially impact the Company’s financial condition and performance.
The Company is affected by general economic conditions in the U.S. and the local markets within which it operates. A significant decline in general economic conditions caused by inflation, recession, unemployment or other factors beyond the Company’s control could negatively impact the growth rate of loans (including mortgage originations) and deposits, the quality of the loan portfolio, loan and deposit pricing, and other key drivers of the Company’s business. Such negative developments could adversely impact the Company’s financial condition and performance.
Changes in interest rates could adversely affect the Company’s income and cash flows.
The Company’s income and cash flows depend to a great extent on the difference between the interest rates earned on interest-earning assets, such as loans and investment securities, and the interest rates paid on interest-bearing liabilities, such as deposits and borrowings. These rates are highly sensitive to many factors beyond the Company’s control, including general economic conditions and the policies of the Federal Reserve and other governmental and regulatory agencies. Changes in monetary policy, including changes in interest rates, will influence the origination of loans, the prepayment of loans, the purchase of investments, the generation of deposits, and the rates received on loans and investment securities and paid on deposits or other sources of funding. The impact of these changes may be magnified if the Company does not effectively manage the relative sensitivity of its assets and liabilities to changes in market interest rates. In addition, the Company’s ability to reflect such interest rate changes in pricing its products is influenced by competitive pressures. Fluctuations in these areas may adversely affect the Company and its shareholders. Community banks are often at a competitive disadvantage in managing their costs of funds compared to the large regional, super-regional or national banks that have access to the national and international capital markets.
11
The Company generally seeks to maintain a neutral position in terms of the volume of assets and liabilities that mature or re-price during any period so that it may reasonably maintain its net interest margin; however, interest rate fluctuations, loan prepayments, loan production, deposit flows and competitive pressures are constantly changing and influence the ability to maintain a neutral position. Generally, the Company’s earnings will be more sensitive to fluctuations in interest rates depending upon the variance in volume of assets and liabilities that mature and re-price in any period. The extent and duration of the sensitivity will depend on the cumulative variance over time, the velocity and direction of interest rates, shape and slope of the yield curve, and whether the Company is more asset sensitive or liability sensitive. Accordingly, the Company may not be successful in maintaining a neutral position and, as a result, the Company’s net interest margin may be impacted.
The Company faces substantial competition that could adversely affect the Company’s growth and/or operating results.
The Company operates in a competitive market for financial services and faces intense competition from other financial institutions both in making loans and attracting deposits. Many of these financial institutions have been in business for many years, are significantly larger, have established customer bases, and have greater financial resources and higher lending limits.
The inability of the Company to successfully manage its growth or implement its growth strategy may adversely affect the results of operations and financial conditions.
The Company may not be able to successfully implement its growth strategy if it is unable to identify attractive markets, locations or opportunities to expand in the future. The ability to manage growth successfully depends on whether the Company can maintain adequate capital levels, maintain cost controls, asset quality and successfully integrate any businesses acquired into the organization.
As the Company continues to implement its growth strategy by opening new branches or acquiring branches or banks, it expects to incur increased personnel, occupancy and other operating expenses. In the case of new branches, the Company must absorb those higher expenses while it begins to generate new deposits; there is also further time lag involved in redeploying new deposits into attractively priced loans and other higher yielding earning assets. Thus, the Company’s plans to branch could depress earnings in the short run, even if it efficiently executes a branching strategy leading to long-term financial benefits.
Difficulties in combining the operations of acquired entities with the Company’s own operations may prevent the Company from achieving the expected benefits from acquisitions.
The Company may not be able to achieve fully the strategic objectives and operating efficiencies in an acquisition. Inherent uncertainties exist in integrating the operations of an acquired entity. In addition, the markets and industries in which the Company and its potential acquisition targets operate are highly competitive. The Company may lose customers or the customers of acquired entities as a result of an acquisition; the Company also may lose key personnel, either from the acquired entity or from itself. These factors could contribute to the Company’s not achieving the expected benefits from its acquisitions within desired time frames, if at all. Future business acquisitions could be material to the Company and it may issue additional shares of common stock to pay for those acquisitions, which would dilute current shareholders’ ownership interests. Acquisitions also could require the Company to use substantial cash or other liquid assets or to incur debt; the Company could therefore become more susceptible to economic downturns and competitive pressures.
12
The Company’s exposure to operational, technological and organizational risk may adversely affect the Company.
Similar to other financial institutions, the Company is exposed to many types of operational and technological risk, including reputation, legal and compliance risk. The Company’s ability to grow and compete is dependent on its ability to build or acquire the necessary operational and technological infrastructure and to manage the cost of that infrastructure while it expands and integrates acquired businesses. Similar to other financial institutions, operational risk can manifest itself in many ways, such as errors related to failed or inadequate processes, faulty or disabled computer systems, fraud by employees or persons outside of the Company and exposure to external events. We are dependent on our operational infrastructure to help manage these risks. From time to time, we may need to change or upgrade our technology infrastructure. We may experience disruption, and we may face additional exposure to these risks during the course of making such changes. As the Company acquires other financial institutions, it faces additional challenges when integrating different operational platforms. Such integration efforts may be more disruptive to the business and/or more costly than anticipated.
The Company’s dependency on its management team and the unexpected loss of any of those personnel could adversely affect operations.
The Company is a customer-focused and relationship-driven organization. Future growth is expected to be driven in large part by the relationships maintained with customers. While the Company has assembled an experienced management team, is building the depth of that team, and has management development plans in place, the unexpected loss of key employees could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business and may result in lower revenues.
The Company’s concentration in loans secured by real estate may adversely impact earnings due to changes in the real estate markets.
The Company offers a variety of secured loans, including commercial lines of credit, commercial term loans, real estate, construction, home equity, consumer and other loans. Many of the Company’s loans are secured by real estate (both residential and commercial) in the Company’s market areas. A major change in the real estate markets, resulting in deterioration in the value of this collateral, or in the local or national economy, could adversely affect customers’ ability to pay these loans, which in turn could impact the Company. Risks of loan defaults and foreclosures are unavoidable in the banking industry; the Company tries to limit its exposure to these risks by monitoring carefully extensions of credit. The Company cannot fully eliminate credit risk; thus, credit losses may occur in the future.
If the Company’s allowance for loan losses becomes inadequate, the results of operations may be adversely affected.
The Company maintains an allowance for loan losses that it believes is a reasonable estimate of potential losses within the loan portfolio. Through a periodic review and consideration of the loan portfolio, management determines the amount of the allowance for loan losses by considering general market conditions, credit quality of the loan portfolio, the collateral supporting the loans and performance of customers relative to their financial obligations with the Company. The amount of future losses is susceptible to changes in economic, operating and other conditions, including changes in interest rates, which may be beyond the Company’s control, and these losses may exceed current estimates. Rapidly growing loan portfolios are, by their nature, unseasoned. As a result, estimating loan loss allowances is more difficult and may be more susceptible to changes in estimates, and to losses exceeding estimates, than more seasoned portfolios. Although the Company believes the allowance for loan losses is a reasonable estimate of known and inherent losses in the loan portfolio, it cannot fully predict such losses or that the loss allowance will be adequate in the future. Excessive loan losses could have a material impact on financial performance. Consistent with the loan loss reserve methodology, the Company expects to make additions to the allowance for loan losses as a result of its growth strategy, which may affect the Company’s short-term earnings.
13
Federal and state regulators periodically review the allowance for loan losses and may require the Company to increase its provision for loan losses or recognize further loan charge-offs, based on judgments that may be different than those of management. Any increase in the amount of the provision or loans charged-off as required by these regulatory agencies could have a negative effect on the Company’s operating results.
Legislative or regulatory changes or actions, or significant litigation, could adversely impact the Company or the businesses in which the Company is engaged.
The Company is subject to extensive state and federal regulation, supervision and legislation that govern almost all aspects of its operations. Laws and regulations may change from time to time and are primarily intended for the protection of consumers, depositors and the FDIC Deposit Insurance Funds. The impact of any changes to laws and regulations or other actions by regulatory agencies may negatively impact the Company or its ability to increase the value of its business. Actions by regulatory agencies or significant litigation against the Company could cause it to devote significant time and resources to defend itself and may lead to liability or penalties that materially affect the Company and its shareholders. Future changes in the laws or regulations or their interpretations or enforcement could be materially adverse to the Company and its shareholders.
Changes in accounting standards could impact reported earnings.
The bodies that promulgate accounting standards, including the Financial Accounting Standards Board, SEC, and other regulatory bodies, periodically change the financial accounting and reporting standards that govern the preparation of the Company’s consolidated financial statements. These changes are difficult to predict and can materially impact how the Company records and reports its financial condition and results of operations. In some cases, the Company could be required to apply a new or revised standard retroactively, resulting in the restatement of financial statements for prior periods.
Limited availability of financing or inability to raise capital could adversely impact the Company.
The amount, type, source, and cost of the Company’s funding directly impacts the ability to grow assets. The ability to raise capital in the future could become more difficult, more expensive, or altogether unavailable. A number of factors could make such financing more difficult, more expensive or unavailable including: the financial condition of the Company at any given time; rate disruptions in the capital markets; the reputation for soundness and security of the financial services industry as a whole; competition for funding from other banks or similar financial service companies, some of which could be substantially larger, or be more favorably rated.
Recent legislative regulatory initiatives to address difficult market and economic conditions may not stabilize the U.S. banking system.
Recently enacted EESA authorizes Treasury to purchase from financial institutions and their holding companies up to $700 billion in mortgage loans, mortgage-related securities and certain other financial instruments, including debt and equity securities issued by financial institutions and their holding companies, under TARP. The purpose of TARP is to restore confidence and stability to the U. S. banking system and to encourage financial institutions to increase their lending to customers and to each other. Treasury has allocated $250 billion towards the TARP Capital Purchase Program (“CPP”). Under the CPP, Treasury is purchasing equity securities from participating institutions. The Company participated in CPP and issued to Treasury $59 million in Preferred Stock and 422,636 shares in a related warrant. EESA also increased federal deposit insurance on most deposit accounts from $100 thousand to $250 thousand. This increase is in place until the end of 2009 and is not covered by deposit insurance premiums paid by the banking industry.
The Board of Governors of the Federal Reserve System, Congress, through EESA, Treasury, the FDIC, the SEC, and others continue to address the current liquidity and credit crisis that has followed the sub-prime meltdown that commenced in 2007. These measures include homeowner relief that encourage loan
14
restructuring and modification; the establishment of significant liquidity and credit facilities for financial institutions and investment banks; the lowering of the Federal Funds rate; emergency action against short selling practices; a temporary guaranty program for money market funds; the establishment of a commercial paper funding facility to provide back-stop liquidity to commercial paper issuers; and coordinated international efforts to address illiquidity and other weaknesses in the banking sector. The purpose of these legislative and regulatory actions is to stabilize the U. S. banking system. EESA and the other regulatory initiatives described above may not have their desired effects. If the volatility in the markets continues and economic conditions fail to improve or worsen, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
The Company’s Preferred Stock is equity and is subordinate to all of its existing and future indebtedness; regulatory and contractual restrictions may limit or prevent the Company from paying dividends on the Preferred Stock; and the Preferred Stock places no limitations on the amount of indebtedness the Company may incur in the future.
The shares of Preferred Stock are equity interests in the Company and do not constitute indebtedness. As such, the Preferred Stock, like the Company’s common stock, ranks junior to all indebtedness and other non-equity claims on the Company with respect to assets available to satisfy claims on the Company, including in a liquidation of the Company. Additionally, unlike indebtedness, where principal and interest would customarily be payable on specified due dates, in the case of preferred stock like the Preferred Stock, (a) dividends are payable only when, as and if authorized and declared by the Company’s Board of Directors (the “Board”) and depend on, among other things, the results of operations, financial condition, debt service requirements, other cash needs and any other factors the Company’s Board deems relevant, (b) as a Virginia corporation, the Company may not pay dividends if, after giving effect thereto, the Company would not be able to pay debts as they come due in the usual course of business, or total assets would be less than total liabilities and the amount needed to satisfy the liquidity preferences of any preferred stock, and (c) the Company may not pay dividends on capital stock if it is in default on certain indebtedness or elected to defer payments of interest on subordinated indebtedness.
The Company derives substantially all of its revenue in the form of dividends from its subsidiaries. The Company is and will be dependent upon dividends from its subsidiaries to pay the principal and interest on its indebtedness, to satisfy its other cash needs, and to pay dividends on the Preferred Stock and its common stock. The ability of each subsidiary to pay dividends is subject to its ability to earn net income and to meet certain regulatory requirements. In the event the subsidiaries are unable to pay dividends, the Company may not be able to pay dividends on the Preferred Stock. The Company’s right to participate in a distribution of assets upon a subsidiary’s liquidation or reorganization is subject to the prior claims of such subsidiary’s creditors.
The Preferred Stock does not limit the amount of debt or other obligations the Company may incur in the future. The Company may incur substantial amounts of additional debt and other obligations that will rank senior to the Preferred Stock or to which the Preferred Stock will be structurally subordinated.
If the Company is unable to redeem the Preferred Stock after five years, the cost of this capital to the Company will increase substantially.
If the Company is unable to redeem the Preferred Stock prior to February 15, 2014, the cost of this capital will increase substantially on that date, from 5.0% per annum to 9.0% per annum. Depending on the Company’s financial condition at the time, this increase in the annual dividend rate on the Preferred Stock could have a material negative effect on liquidity and the dividend available to common shareholders.
The Purchase Agreement between the Company and Treasury limits the Company’s ability to pay dividends on and repurchase its common stock.
The Purchase Agreement between the Company and Treasury provides that until the earlier of December 19, 2011 or the date on which all shares of the Preferred Stock have been redeemed by the Company or transferred by Treasury to third parties, the Company may not, without the consent of
15
Treasury, (a) increase the cash dividend on the Company’s common stock beyond $.185 per share or (b) subject to limited exceptions, redeem, repurchase or otherwise acquire shares of the Company’s common stock or preferred stock (other than the Preferred Stock) or trust preferred securities. The Company is also unable to pay any dividends on common stock unless it is current on its dividend payments on the Preferred Stock. These restrictions could have a negative effect on the value of the Company’s common stock.
ITEM 1B. – UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
The Company does not have any unresolved staff comments to report for the year ended December 31, 2008.
The Company, through its subsidiaries, owns or leases buildings that are used in the normal course of business. The corporate headquarters is located at 211 North Main Street, Bowling Green, Virginia, in a building owned by Union Bank. The Company’s subsidiaries own or lease various other offices in the counties and cities in which they operate. At December 31, 2008, the Company’s subsidiary banks operated 59 branches throughout Virginia. Some of the Company’s non-banking subsidiaries include Union Mortgage and Union Investment Services, Inc. All of the offices of Union Mortgage are leased. The vast majority of the offices for Union Investment Services, Inc. are also used for branch banking operations. In May 2007, the Company completed construction of its new 70,000 square foot operations center in Caroline County, Virginia. The Company sold its former operations center in the third quarter of 2007. See the Note 1 “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” and Note 5 “Bank Premises and Equipment” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements” of this Form 10-K for information with respect to the amounts at which bank premises and equipment are carried and commitments under long-term leases.
In the ordinary course of its operations, the Company and its subsidiaries are parties to various legal proceedings. Based on the information presently available, and after consultation with legal counsel, management believes that the ultimate outcome in such proceedings, in the aggregate, will not have a material adverse effect on the business or the financial condition or results of operations of the Company.
ITEM 4. – SUBMISSION OF MATTERS TO A VOTE OF SECURITY HOLDERS.
No matters were submitted to a vote of security holders during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2008.
ITEM 5. – MARKET FOR REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES.
The following performance graph does not constitute soliciting material and should not be deemed filed or incorporated by reference into any other Company filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, except to the extent the Company specifically incorporates the performance graph by reference therein.
16
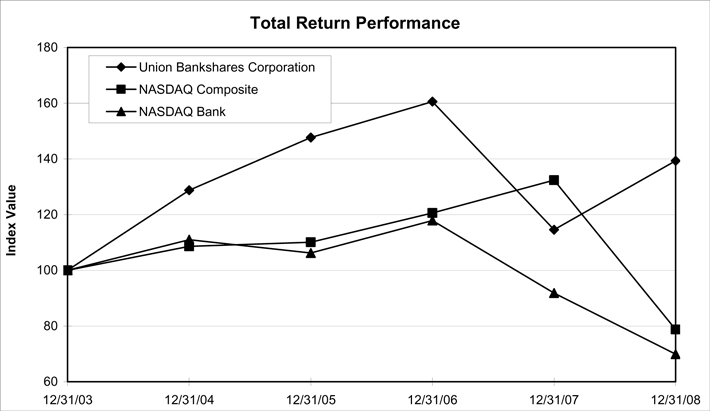
Five-Year Stock Performance Graph
The following chart compares the yearly percentage change in the cumulative shareholder return on the Company’s common stock during the five years ended December 31, 2008, with (1) the Total Return Index for the NASDAQ Stock Market (U. S. Companies) and (2) the Total Return Index for NASDAQ Bank Stocks. This comparison assumes $100 was invested on December 31, 2003, in the common stock and the comparison groups and assumes the reinvestment of all cash dividends prior to any tax effect and retention of all stock dividends. The Company’s total cumulative return was 39.29% over the five year period ending December 31, 2008 compared to a cumulative decline of 21.3% and 30.1% for the NASDAQ Composite and NASDAQ Bank Stocks, respectively:

| Period Ending | ||||||||||||
| Index |
12/31/03 | 12/31/04 | 12/31/05 | 12/31/06 | 12/31/07 | 12/31/08 | ||||||
| Union Bankshares Corporation |
100.00 | 128.78 | 147.66 | 160.56 | 114.53 | 139.29 | ||||||
| NASDAQ Composite |
100.00 | 108.59 | 110.08 | 120.56 | 132.39 | 78.72 | ||||||
| NASDAQ Bank |
100.00 | 110.99 | 106.18 | 117.87 | 91.85 | 69.88 | ||||||
Information on Common Stock, Market Prices and Dividends
There were 13,570,970 shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding at the close of business on December 31, 2008, which were held by 2,406 shareholders of record. The closing price of the Company’s stock on December 31, 2008 was $24.80 per share compared to $21.14 on December 31, 2007.
On September 7, 2006, the Company’s Board declared a three-for-two stock split to shareholders of record as of the close of business on October 2, 2006. Share and per share amounts for periods prior to the stock split have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the effect of the three-for-two split.
The following table summarizes the high and low closing sales prices and dividends declared for quarterly periods during the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007.
17
| Market Values | Dividends Declared | |||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 21.90 | $ | 16.05 | $ | 30.00 | $ | 24.05 | $ | 0.185 | $ | 0.175 | ||||||
| Second Quarter |
20.38 | 14.89 | 27.01 | 22.88 | 0.185 | 0.180 | ||||||||||||
| Third Quarter |
29.20 | 14.25 | 24.93 | 19.40 | 0.185 | 0.185 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth Quarter |
25.00 | 16.02 | 24.35 | 18.04 | 0.185 | 0.185 | ||||||||||||
| $ | 0.740 | $ | 0.725 | |||||||||||||||
Regulatory restrictions on the ability of the Community Banks to transfer funds to the Company at December 31, 2008 are set forth in Note 17, “Parent Company Financial Information”, contained in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements” of this Form 10-K. A discussion of certain limitations on the ability of the Community Banks to pay dividends to the Company and the ability of the Company to pay dividends on its common stock, is set forth in Part I. Business, of this Form 10-K under the headings “Supervision and Regulation - Limits on Dividends and Other Payments” and “Supervision and Regulation - The Community Banks.”
In 2006, the Company began paying its dividend on a quarterly basis instead of semi-annually. It is anticipated the dividends will continue to be paid near the end of February, May, August and November. In making its decision on the payment of dividends on the Company’s common stock, the Board considers operating results, financial condition, capital adequacy, regulatory requirements, shareholder returns and other factors.
Stock Repurchase Program
The Board has authorized management of the Company to buy up to 150,000 shares of its outstanding common stock in the open market at prices that management determines to be prudent. This authorization expires May 31, 2009. The Company considers current market conditions and the Company’s current capital level, in addition to other factors, when deciding whether to repurchase stock. It is anticipated that any repurchased shares will be used primarily for general corporate purposes, including the dividend reinvestment and stock purchase plan, the 2003 Stock Incentive Plan and other employee benefit plans. In March 2008, management repurchased 15,000 shares at a price of $16.87 per share. No shares were repurchased during the remainder of 2008. In addition, under the terms of CPP, such repurchases are not permissible without the consent of Treasury until the Preferred Stock is redeemed.
18
ITEM 6. – SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
The following table sets forth selected financial data for the Company over the past five years ended December 31 (dollars in thousands, except per share amounts):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||
| Results of Operations |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest and dividend income |
$ | 135,095 | $ | 140,996 | $ | 129,156 | $ | 102,317 | $ | 80,544 | ||||||||||
| Interest expense |
57,222 | 65,251 | 52,441 | 32,967 | 25,652 | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
77,873 | 75,745 | 76,715 | 69,350 | 54,892 | |||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
10,020 | 1,060 | 1,450 | 1,172 | 2,154 | |||||||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
67,853 | 74,685 | 75,265 | 68,178 | 52,738 | |||||||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
30,555 | 25,105 | 28,245 | 25,510 | 23,302 | |||||||||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
79,636 | 73,550 | 67,567 | 58,275 | 51,221 | |||||||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
18,772 | 26,240 | 35,943 | 35,413 | 24,819 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
4,258 | 6,484 | 9,951 | 10,591 | 6,894 | |||||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,514 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | $ | 24,822 | $ | 17,925 | ||||||||||
| Financial Condition |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
$ | 2,551,932 | $ | 2,301,397 | $ | 2,092,891 | $ | 1,824,958 | $ | 1,672,210 | ||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
1,874,088 | 1,747,820 | 1,549,445 | 1,362,254 | 1,264,841 | |||||||||||||||
| Deposits |
1,926,999 | 1,659,578 | 1,665,908 | 1,456,515 | 1,314,317 | |||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
273,798 | 212,082 | 199,416 | 179,358 | 162,758 | |||||||||||||||
| Ratios |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Return on average assets |
0.61 | % | 0.91 | % | 1.30 | % | 1.43 | % | 1.19 | % | ||||||||||
| Return on average equity |
6.70 | % | 9.61 | % | 13.64 | % | 14.49 | % | 12.18 | % | ||||||||||
| Cash basis return on average assets (1) |
0.68 | % | 1.00 | % | 1.40 | % | 1.51 | % | 1.26 | % | ||||||||||
| Cash basis return on average tangible common equity (1) |
10.69 | % | 14.88 | % | 20.31 | % | 19.57 | % | 15.78 | % | ||||||||||
| Efficiency ratio (2) |
73.45 | % | 72.93 | % | 64.37 | % | 61.43 | % | 65.51 | % | ||||||||||
| Equity to assets |
10.73 | % | 9.22 | % | 9.53 | % | 9.82 | % | 9.73 | % | ||||||||||
| Asset Quality |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
$ | 25,496 | $ | 19,336 | $ | 19,148 | $ | 17,116 | $ | 16,384 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses / total outstanding loans |
1.36 | % | 1.11 | % | 1.24 | % | 1.26 | % | 1.30 | % | ||||||||||
| Per Share Data |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Earnings per share, basic |
$ | 1.08 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.97 | $ | 1.89 | $ | 1.42 | ||||||||||
| Earnings per share, diluted |
1.07 | 1.47 | 1.94 | 1.87 | 1.41 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash basis earnings per share, diluted (1) |
1.16 | 1.56 | 2.03 | 1.93 | 1.46 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends paid |
0.740 | 0.725 | 0.630 | 0.520 | 0.453 | |||||||||||||||
| Market value per share |
24.80 | 21.14 | 30.59 | 28.73 | 25.62 | |||||||||||||||
| Book value per common share |
16.03 | 15.82 | 14.99 | 13.59 | 12.41 | |||||||||||||||
| Price to earnings ratio, diluted |
23.18 | 14.38 | 15.77 | 15.34 | 18.21 | |||||||||||||||
| Price to book value ratio |
1.55 | 1.34 | 2.04 | 2.11 | 2.07 | |||||||||||||||
| Dividend payout ratio |
69.16 | % | 49.32 | % | 31.98 | % | 27.21 | % | 31.92 | % | ||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding, basic |
13,477,760 | 13,341,741 | 13,233,101 | 13,142,999 | 12,604,187 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding, diluted |
13,542,948 | 13,422,139 | 13,361,773 | 13,275,074 | 12,723,213 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Refer to “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operation”, section “Non GAAP Measures” for a reconciliation. |
| (2) | The efficiency ratio is calculated by dividing noninterest expense over the sum of net interest income plus noninterest income. |
19
ITEM 7. – MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS.
The following discussion and analysis provides information about the major components of the results of operations and financial condition, liquidity and capital resources of the Company and its subsidiaries. This discussion and analysis should be read in conjunction with the “Consolidated Financial Statements” and the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements” presented in Item 8 “Financial Statements and Supplementary Data” of this Form 10-K. In addition, share and per share amounts for periods prior to the stock split have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the effect of the three-for-two stock split in October 2006.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
General
The accounting and reporting policies of the Company and its subsidiaries are in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) and conform to general practices within the banking industry. The Company’s financial position and results of operations are affected by management’s application of accounting policies, including estimates, assumptions and judgments made to arrive at the carrying value of assets and liabilities and amounts reported for revenues, expenses and related disclosures. Different assumptions in the application of these policies could result in material changes in the Company’s consolidated financial position and/or results of operations.
The more critical accounting and reporting policies include the Company’s accounting for the allowance for loan losses, merger and acquisitions and goodwill and intangibles. The Company’s accounting policies are fundamental to understanding the Company’s consolidated financial position and consolidated results of operations. The Company’s significant accounting policies are discussed in detail in Note 1 “Summary of Significant Accounting Policies” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements”.
The following is a summary of the Company’s critical accounting policies that are highly dependent on estimates, assumptions and judgments.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses is an estimate of the losses that may be sustained in the loan portfolio. The allowance is based on two basic principles of accounting: (i) Statement of Financial Accounting Standard (“SFAS”) No. 5, Accounting for Contingencies (“SFAS No. 5”), which requires that losses be accrued when occurrence is probable and can be reasonably estimated and (ii) SFAS No. 114, Accounting by Creditors for Impairment of a Loan (“SFAS No. 114”), as amended, which requires that losses be accrued based on the differences between the value of collateral, present value of future cash flows or values that are observable in the secondary market and the loan balance.
The Company’s allowance for loan losses is the accumulation of various components that are calculated based on independent methodologies. All components of the allowance represent an estimation performed pursuant to either SFAS No. 5 or SFAS No. 114. Management’s estimate of each SFAS No. 5 component is based on certain observable data that management believes are most reflective of the underlying credit losses being estimated. This evaluation includes credit quality trends; collateral values; loan volumes; geographic, borrower and industry concentrations; seasoning of the loan portfolio; the findings of internal credit quality assessments and results from external bank regulatory examinations. These factors, as well as historical losses and current economic and business conditions, are used in developing estimated loss factors used in the calculations.
20
The Company adopted SFAS No. 114, which has been amended by SFAS No. 118, Accounting by Creditors for Impairment of a Loan – Income Recognition and Disclosures (“SFAS No. 118”). SFAS No. 114, as amended, requires that the impairment of loans that have been separately identified for evaluation is to be measured based on the present value of expected future cash flows or, alternatively, the observable market price of the loans or the fair value of the collateral. However, for those loans that are collateral dependent (that is, if repayment of those loans is expected to be provided solely by the underlying collateral) and for which management has determined foreclosure is probable, the measure of impairment is to be based on the net realizable value of the collateral. SFAS No. 114, as amended, also requires certain disclosures about investments in impaired loans and the allowance for loan losses and interest income recognized on loans.
Reserves for commercial loans are determined by applying estimated loss factors to the portfolio based on historical loss experience and management’s evaluation and “risk grading” of the commercial loan portfolio. Reserves are provided for noncommercial loan categories using historical loss factors applied to the total outstanding loan balance of each loan category. Additionally, environmental factors based on national and local economic conditions, as well as portfolio specific attributes, are considered in estimating the allowance for loan losses.
While management uses the best information available to establish the allowance for loan and lease losses, future adjustments to the allowance may be necessary if future economic conditions differ substantially from the assumptions used in making the valuations or, if required by regulators, based upon information available to them at the time of their examinations. Such adjustments to original estimates, as necessary, are made in the period in which these factors and other relevant considerations indicate that loss levels may vary from previous estimates.
Mergers and Acquisitions
The Company’s merger and acquisition strategy focuses on high growth areas with strong market demographics and targets organizations that have a comparable corporate culture, strong performance and good asset quality, among other factors.
The Company has accounted for its previous acquisitions under the purchase method of accounting and was required to record the assets acquired, including identified intangible assets and liabilities assumed at their fair value, which often involved estimates based on third party valuations, such as appraisals, or internal valuations based on discounted cash flow analyses or other valuation techniques, which are inherently subjective. The amortization of identified intangible assets was based upon the estimated economic benefits to be received, which was also subjective. These estimates also included the establishment of various accruals and allowances based on planned facility dispositions and employee severance considerations, among other acquisition-related items. In addition, purchase acquisitions typically resulted in goodwill, which is subject to at least annual impairment testing, or more frequently if certain indicators are in evidence, based on the fair value of net assets acquired compared to the carrying value of goodwill.
The Company and the acquired entity also incurred merger-related costs during an acquisition. The Company capitalized direct costs of the acquisition, such as investment banker and attorneys’ fees and included them as part of the purchase price. Other merger-related internal costs associated with acquisitions were expensed as incurred. Some examples of these merger-related costs included systems conversions, integration planning consultants and advertising fees. These merger-related costs were included within the Consolidated Statement of Income classified within the noninterest expense line. The acquired entity records merger-related costs that result from a plan to exit an activity, involuntarily terminate or relocate employees and are recognized as liabilities assumed as of the consummation date of the acquisition.
21
On September 2007, the Company acquired the deposits and facilities of six bank branches in Virginia. The costs associated with the acquisition were principally related to system conversion costs.
After January 1, 2009, the Company will account for any future business combinations using SFAS 141(R), Business Combinations (“SFAS No. 141(R)”).
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations (“SFAS No. 141”), required the purchase method of accounting be used for all business combinations initiated after June 30, 2001 through December 31, 2008. For purchase acquisitions, the Company was required to record assets acquired, including identifiable intangible assets, and liabilities assumed at their fair value, which in many instances involved estimates based on third party valuations, such as appraisals, or internal valuations based on discounted cash flow analysis or other valuation techniques. Effective January 1, 2001, the Company adopted SFAS No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Asset (“SFAS 142”), which prescribes the accounting for goodwill and intangible assets subsequent to initial recognition. The provisions of SFAS No. 142 discontinue the amortization of goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives, but require at least an annual impairment review and more frequently if certain impairment indicators are in evidence. Additionally, the Company adopted SFAS No. 147, Acquisitions of Certain Financial Institutions (“SFAS No. 147”), on January 1, 2002 and determined that core deposit intangibles will continue to be amortized over their estimated useful lives. Beginning in 2009, SFAS No. 141(R), supersedes SFAS No. 141 and SFAS No. 147, amends SFAS No. 142, and significantly changes the financial accounting and reporting of business combination transactions.
Goodwill totaled $56.5 million for both years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007. Based on the testing of goodwill for impairment, there were no impairment charges for 2008, 2007 or 2006. Core deposit intangible assets are being amortized over the periods of expected benefit, which range from 5 to 15 years. Core deposit intangibles, net of amortization, amounted to $9.6 million and $11.6 million at the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Amortization expense of core deposit intangibles for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 totaled $2.0 million, $1.9 million and $1.7 million, respectively.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Net Income
For the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to the year ended December 31, 2007, net income decreased $5.3 million, or 26.5%, from $19.8 million to $14.5 million, which represented a decrease in earnings per share, on a diluted basis, of $.40, or 27.2%, from $1.47 to $1.07. Return on average equity for the year ended December 31, 2008 was 6.70%, while return on average assets was .61%, compared to 9.61% and .91%, respectively, for the same period in 2007.
The decrease was driven by declines in the net interest margin, increased provisions for loan losses and noninterest expenses associated with acquired bank branches. These expense increases were partially offset by gains from the sale of bank owned property, growth in service charge income on deposit accounts and increased profitability in the mortgage segment.
Net Interest Income
Net interest income, which represents the principal source of earnings for the Company, is the amount by which interest income exceeds interest expense. The net interest margin is net interest income expressed as a percentage of average earning assets. Changes in the volume and mix of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities, as well as their respective yields and rates, have a significant impact on the level of net interest income, the net interest margin and net income.
22
The Federal Open Market Committee (“FOMC”) of the Federal Reserve Board of Governors began the year with a target Federal Funds rate of 4.25%. Throughout 2008, the target Federal Funds rate was reduced seven times for a total reduction of 400 basis points. At the last meeting of the FOMC, the target Federal Funds rate was converted to a target range of 0% to 25 basis points. Their decisions to lower the target Federal Funds rate during the year stemmed from a series of factors, such as weakening economic outlooks, tightening credit conditions, softening labor markets, lower household spending to declines in business investment, consumer spending and industrial production. These economic events, together with targeted Federal Funds rate cuts, have placed stress on deposit pricing and competition for those deposits, both having an impact on the Company’s net interest margin.
For the year ended December 31, 2008, net interest income, on a tax-equivalent basis, increased by $2.5 million, or 3.2%, to $81.3 million compared to the same period last year. The increase in net interest income was achieved despite a decline in the net interest margin of 27 basis points, from 4.06% to 3.79%. The net interest margin decline was partially attributable to a steeper decline in yields on interest-earning assets as compared to costs of interest-bearing liabilities. Yields on interest-earning assets declined 96 basis points and the cost of interest-bearing liabilities declined 87 basis points. The increase in net interest income was achieved principally as a result of lower interest expenses associated with certificates of deposit and borrowings and increased interest income from increased loan volume, despite lower yields.
23
The following table shows interest income on earning assets and related average yields, as well as interest expense on interest-bearing liabilities and related average rates paid for the years ended December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average Balance |
Interest Income / Expense |
Yield / Rate |
Average Balance |
Interest Income / Expense |
Yield / Rate |
Average Balance |
Interest Income / Expense |
Yield / Rate |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxable |
$ | 178,221 | $ | 9,068 | 5.09 | % | $ | 173,942 | $ | 8,945 | 5.14 | % | $ | 188,461 | $ | 9,883 | 5.24 | % | ||||||||||||
| Tax-exempt |
111,027 | 7,997 | 7.20 | % | 100,944 | 7,272 | 7.20 | % | 89,407 | 6,546 | 7.32 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total securities |
289,248 | 17,065 | 5.90 | % | 274,886 | 16,217 | 5.90 | % | 277,868 | 16,429 | 5.91 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net (1) (2) |
1,817,755 | 119,898 | 6.60 | % | 1,637,573 | 125,628 | 7.67 | % | 1,489,794 | 111,771 | 7.50 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
24,320 | 1,370 | 5.63 | % | 21,991 | 1,346 | 6.12 | % | 25,129 | 1,572 | 6.26 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
8,217 | 98 | 1.19 | % | 2,852 | 614 | 5.53 | % | 8,837 | 1,438 | 5.35 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Money market investments |
153 | 1 | 0.40 | % | 217 | 4 | 1.94 | % | 151 | 3 | 2.24 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits in other banks |
1,355 | 39 | 1.73 | % | 1,116 | 57 | 5.12 | % | 1,104 | 57 | 5.13 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other interest-bearing deposits |
2,598 | 49 | 1.87 | % | 2,596 | 135 | 5.18 | % | 2,598 | 129 | 4.96 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total earning assets |
2,143,646 | 138,520 | 6.46 | % | 1,941,231 | 144,001 | 7.42 | % | 1,805,481 | 131,399 | 7.28 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
(21,830 | ) | (18,666 | ) | (18,468 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total non-earning assets |
257,587 | 244,558 | 211,055 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,379,403 | $ | 2,167,123 | $ | 1,998,068 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Checking |
$ | 218,349 | 1,352 | 0.62 | % | $ | 206,748 | $ | 1,316 | 0.64 | % | $ | 204,023 | $ | 911 | 0.45 | % | |||||||||||||
| Money market savings |
238,540 | 5,708 | 2.39 | % | 158,461 | 3,708 | 2.34 | % | 175,163 | 3,945 | 2.25 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Regular savings |
100,782 | 584 | 0.58 | % | 104,507 | 820 | 0.78 | % | 116,569 | 1,061 | 0.91 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposit: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $100,000 and over |
435,807 | 17,363 | 3.98 | % | 446,662 | 22,024 | 4.93 | % | 387,023 | 17,603 | 4.55 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Under $100,000 |
499,591 | 19,291 | 3.86 | % | 451,224 | 20,366 | 4.51 | % | 405,930 | 16,210 | 3.99 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
1,493,069 | 44,298 | 2.97 | % | 1,367,602 | 48,234 | 3.53 | % | 1,288,708 | 39,730 | 3.08 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other borrowings |
377,601 | 12,924 | 3.42 | % | 291,742 | 17,017 | 5.83 | % | 220,632 | 12,711 | 5.85 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing liabilities |
1,870,670 | 57,222 | 3.06 | % | 1,659,344 | 65,251 | 3.93 | % | 1,509,340 | 52,441 | 3.47 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Demand deposits |
272,764 | 283,877 | 284,094 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other liabilities |
19,347 | 18,377 | 14,074 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities |
2,162,781 | 1,961,598 | 1,807,508 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
216,622 | 205,525 | 190,560 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 2,379,403 | $ | 2,167,123 | $ | 1,998,068 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
$ | 81,298 | $ | 78,750 | $ | 78,958 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest rate spread (3) |
3.40 | % | 3.49 | % | 3.81 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense as a percent of average earning assets |
2.67 | % | 3.36 | % | 2.90 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net interest margin |
3.79 | % | 4.06 | % | 4.37 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Nonaccrual loans are included in average loans outstanding. |
| (2) | Foregone interest on previously charged off credits of $464 thousand has been excluded for 2006. |
| (3) | Income and yields are reported on a taxable equivalent basis using the statutory federal corporate tax rate of 35%. |
The Volume Rate Analysis table presents changes in interest income and interest expense, and distinguishes between the changes related to increases or decreases in average outstanding balances of
24
interest-earning assets and interest-bearing liabilities (volume), and the changes related to increases or decreases in average interest rates on such assets and liabilities (rate). Changes attributable to both volume and rate have been allocated proportionately. Results, on a taxable equivalent basis, are as follows in this Volume Rate Analysis table for the years ended December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 vs. 2007 Increase (Decrease) Due to Change in: | 2007 vs. 2006 Increase (Decrease) Due to Change in: | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | Rate | Total | Volume | Rate | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Earning Assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Securities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxable |
$ | 214 | $ | (91 | ) | $ | 123 | $ | (751 | ) | $ | (187 | ) | $ | (938 | ) | ||||||||
| Tax-exempt |
725 | — | 725 | 833 | (107 | ) | 726 | |||||||||||||||||
| Total securities |
939 | (91 | ) | 848 | 82 | (294 | ) | (212 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Loans, net |
12,925 | (18,639 | ) | (5,714 | ) | 11,283 | 2,574 | 13,857 | ||||||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
136 | (112 | ) | 24 | (191 | ) | (35 | ) | (226 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Federal funds sold |
266 | (782 | ) | (516 | ) | (815 | ) | (9 | ) | (824 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Money market investments |
— | (3 | ) | (3 | ) | 1 | — | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits in other banks |
10 | (44 | ) | (34 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Other interest-bearing deposits |
— | (86 | ) | (86 | ) | — | 6 | 6 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total earning assets |
$ | 14,276 | $ | (19,757 | ) | $ | (5,481 | ) | $ | 10,360 | $ | 2,242 | $ | 12,602 | ||||||||||
| Interest Bearing Liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Checking |
$ | 75 | $ | (39 | ) | $ | 36 | $ | 13 | $ | 392 | $ | 405 | |||||||||||
| Money market savings |
1,916 | 84 | 2,000 | (388 | ) | 151 | (237 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Regular savings |
(31 | ) | (205 | ) | (236 | ) | (101 | ) | (140 | ) | (241 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Certificates of deposit: |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| $100,000 and over |
(516 | ) | (4,145 | ) | (4,661 | ) | 2,865 | 1,556 | 4,421 | |||||||||||||||
| Under $100,000 |
2,043 | (3,118 | ) | (1,075 | ) | 1,917 | 2,239 | 4,156 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
3,487 | (7,423 | ) | (3,936 | ) | 4,306 | 4,198 | 8,504 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other borrowings |
4,150 | (8,243 | ) | (4,093 | ) | 3,858 | 448 | 4,306 | ||||||||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing liabilities |
7,637 | (15,666 | ) | (8,029 | ) | 8,164 | 4,646 | 12,810 | ||||||||||||||||
| Change in net interest income |
$ | 6,639 | $ | (4,091 | ) | $ | 2,548 | $ | 2,196 | $ | (2,404 | ) | $ | (208 | ) | |||||||||
Interest Sensitivity
An important element of earnings performance and the maintenance of sufficient liquidity is proper management of the interest sensitivity gap and liquidity gap. The interest sensitivity gap is the difference between interest sensitive assets and interest sensitive liabilities in a specific time interval. This gap can be managed by re-pricing assets or liabilities, which are variable rate instruments, by replacing an asset or liability at maturity or by adjusting the interest rate during the life of the asset or liability. Matching the amounts of assets and liabilities maturing in the same time interval helps to hedge interest rate risk and to minimize the impact of rising or falling interest rates on net interest income.
The Company determines the overall magnitude of interest sensitivity risk and then formulates policies and practices governing asset generation and pricing, funding sources and pricing, and off-balance sheet commitments. These decisions are based on management’s expectations regarding future interest rate movements, the state of the national, regional and local economy, and other financial and business risk factors. The Company uses computer simulation modeling to measure and monitor the effect of various interest rate scenarios and business strategies on net interest income. This modeling reflects interest rate changes and the related impact on net interest income and net income over specified time horizons.
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company was in an asset sensitive position. As described in the table below, management’s earnings simulation model indicates net interest income will increase as rates increase. An asset sensitive company generally will be impacted favorably by increasing interest rates
25
while a liability sensitive company’s net interest margin and net interest income generally will be impacted favorably by declining interest rates. Although the static gap report indicates $86.2 million and $540.8 million more liabilities than assets re-pricing within one year at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, computer simulation modeling shows the Company’s net interest income tends to increase when interest rates rise and fall when interest rates decline. The explanation for this is that interest rate changes affect bank products differently. For example, if the prime rate changes by 1.00% (100 basis points or bps), the change on certificates of deposit may only be 0.75% (75 bps), while other interest bearing deposit accounts may only change 0.10% (10 bps). Despite their fixed terms, loan products are often refinanced as rates decline, but rarely refinanced as rates rise. Assets and liabilities re-price throughout the year resulting in changes in the earning asset rate, the cost of funds rate, and the net interest margin.
Earnings Simulation Analysis
Management uses simulation analysis to measure the sensitivity of net interest income to changes in interest rates. The model calculates an earnings estimate based on current and projected balances and rates. This method is subject to the accuracy of the assumptions that underlie the process, but it provides a better analysis of the sensitivity of earnings to changes in interest rates than other analysis, such as the static gap analysis discussed above.
Assumptions used in the model are derived from historical trends and management’s outlook and include loan and deposit growth rates and projected yields and rates. Such assumptions are monitored and periodically adjusted as appropriate. All maturities, calls and prepayments in the securities portfolio are assumed to be reinvested in like instruments. Mortgage loans and mortgage backed securities prepayment assumptions are based on industry estimates of prepayment speeds for portfolios with similar coupon ranges and seasoning. Different interest rate scenarios and yield curves are used to measure the sensitivity of earnings to changing interest rates. Interest rates on different asset and liability accounts move differently when the prime rate changes and are reflected in the different rate scenarios.
The Company uses its simulation model to estimate earnings in rate environments where rates ramp up or down around a “most likely” rate scenario, based on implied forward rates. The analysis assesses the impact on net interest income over a 12 month time horizon by applying 12 month rate ramps, with interest rates rising gradually versus an immediate increase or “shock” in rates, of 100 basis points up to 200 basis points. The ramp down 200 basis points is not meaningful as interest rates are at historic lows and can not drop another 200 basis points. The model, under all scenarios, does not drop the index below zero. The following table represents the interest rate sensitivity on net interest income for the Company across the rate paths modeled for the year ended December 31, 2008 (dollars in thousands):
| Change In Net Interest Income | ||||||
| % | $ | |||||
| Change in Yield Curve: |
||||||
| +200 basis points |
5.30 | % | 4,222 | |||
| +100 basis points |
2.67 | % | 2,129 | |||
| Most likely rate scenario |
0.00 | % | — | |||
| -100 basis points |
-2.76 | % | (2,200 | ) | ||
| -200 basis points |
-6.25 | % | (4,978 | ) | ||
Economic Value Simulation
Economic value simulation is used to calculate the estimated fair value of assets and liabilities over different interest rate environments. Economic values are calculated based on discounted cash flow analysis. The net economic value of equity is the economic value of all assets minus the economic value
26
of all liabilities. The change in net economic value over different rate environments is an indication of the longer term earnings capability of the balance sheet. The same assumptions are used in the economic value simulation as in the earnings simulation. The economic value simulation uses instantaneous rate shocks to the balance sheet where the earnings simulation uses rate ramps over 12 months. The following chart reflects the estimated change in net economic value over different rate environments using economic value simulation (dollars in thousands):
| Change In Economic Value Of Equity | ||||||
| % | $ | |||||
| Change in Yield Curve: |
||||||
| +200 basis points |
-2.63 | % | (9,288 | ) | ||
| +100 basis points |
-1.22 | % | (4,319 | ) | ||
| Most likely rate scenario |
0.00 | % | — | |||
| -100 basis points |
-1.55 | % | (5,476 | ) | ||
| -200 basis points |
-10.00 | % | (35,337 | ) | ||
Noninterest Income
For the year ended December 31, 2008, noninterest income increased $5.5 million, or 21.7%, to $30.6 million from $25.1 million for the same period in 2007. This increase included increased gains on the sale of mortgage loans of approximately $2.3 million, increased revenue of $1.8 million from deposit account service charges and other fees and increases in gains from sales of bank owned real estate totaling approximately $1.6 million over 2007. These increases were partially offset by lower gains on securities transactions of $557 thousand related to securities that were called by the issuers in the prior year.
For the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to the same period in 2006, noninterest income decreased $3.1 million, or 11.1%, from $28.2 million to $25.1 million. The decrease was principally driven by lower gains on sales within the mortgage segment of $2.5 million. Deposit accounts and other service charge income increased $755 thousand, or 5.7%, compared to 2006. The prior year gains from the sale of real estate of approximately $837 thousand, insurance proceeds and bank owned life insurance commissions of approximately $617 thousand did not recur in 2007 thereby contributing to lower noninterest income.
Noninterest Expense
For the year ended December 31, 2008, noninterest expense increased $6.1 million, or 8.3 %, to $79.6 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2007. Increases in salaries and benefits of $4.4 million, or 11.2%, were primarily attributable to increased mortgage segment commissions of $1.5 million as well as costs associated with personnel in the new branches and normal compensation increases. Occupancy expenses increased $875 thousand, or 14.4%, and were principally attributable to increased facilities costs associated with the Company’s new operations center and the new branches. Some of these increased costs included depreciation, rental expenses, real estate taxes, and, to a lesser extent, utility costs. Other operating expenses increased $678 thousand, or 2.8%, and principally related to ongoing infrastructure enhancements to support the Company’s continued growth, conversion expenses related to merging affiliate banks, as well as higher FDIC insurance costs due to exhausting assessment credits. Infrastructure enhancements included Voice-over Internet Protocol and the associated hardware and software to support this technology. Approximately $515 thousand of operating expenses related to conversion costs incurred to combine two affiliate banks. Furniture and equipment expenses increased $172 thousand, or 3.6%, and were attributable to the related depreciation of the new branches and the new operations center.
For comparative purposes, noninterest expense for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 includes expense associated with the purchase of six bank branches acquired in September 2007, the opening of one de novo bank branch in December 2007 and one in October 2008. These new branches contributed
27
approximately $828 thousand of noninterest expense for 2007. During 2008, these new branches contributed $1.5 million toward the increase in salaries and benefits, $747 thousand in occupancy expenses, $429 thousand in other operating expenses and $315 thousand in furniture and equipments expenses. Absent the noninterest expense associated with the new branches, merger-related costs, and mortgage segment expenses, noninterest expense increased approximately $2.4 million, or 3.9%, over the year ended December 31, 2007.
The Company expects the higher FDIC insurance assessments to unfavorably impact future periods. The current estimate of the impact of the increased assessments is an additional $1.1 million in noninterest expenses for 2009.
For the year ended December 31, 2007 compared to 2006, noninterest expense increased $6.0 million, or 8.9%, from $67.6 million to $73.6 million. These figures include the acquisition of Prosperity on April 1, 2006; therefore, results of operations include twelve months of Prosperity activity for 2007 and only nine months for 2006. Excluding this year’s first quarter of noninterest expense related to Prosperity of $1.0 million, total noninterest expense increased $5.0 million, or 7.4%, when compared to the prior year.
The following increases exclude the first quarter 2007 noninterest expenses of Prosperity. Other operating expenses increased $3.1 million, or 15.0%, and principally related to telecommunications enhancements of approximately $1.2 million, the acquisition of six bank branches of approximately $428 thousand, bank franchise taxes of approximately $248 thousand and three additional bank branches of approximately $119 thousand. The telecommunications enhancements include the Company’s internet banking delivery channel (e.g., increased bandwidth), and improvements in data security and business continuity. Salary and benefits increased $741 thousand, or 2.0%, which was attributable to normal compensation adjustments, increased retail staff related to branch growth, equity based compensation and group insurance costs. This increase of $741 thousand was partially offset by lower commissions from the mortgage segment, as well as lower profit sharing expenses. Occupancy expense increased $967 thousand, or 19.3%, and was principally related to the Company’s fixed asset expansion that included new bank branches and operations center. These costs included depreciation, property insurance and, to a lesser extent, utility costs. Furniture and equipment expense increased $257 thousand, or 5.7%.
For the year ended December 31, 2007, total acquisition charges of approximately $211 thousand were charged to expense and currently are reflected in the caption “Other operating expenses” in the Company’s Consolidated Statements of Income. These costs primarily related to system conversion costs.
SEGMENT INFORMATION
Community Bank Segment
For the year ended December 31, 2008, net income for the community banking segment decreased approximately $6.1 million, or 29.6%, from $20.6 million to $14.5 million compared to the same period in 2007. Net interest income increased $1.8 million, or 2.3%, principally as a result of increased interest-earning asset volumes and declining cost of funds. Provision for loan loss increased $9.0 million during 2008. Net interest income after the provision for loan losses decreased $7.2 million, or 9.7%, from a year ago. Reflected in this net decrease are specific loan loss reserves of $750 thousand that were recaptured during the first quarter of 2007. See the “Asset Quality” section below for additional information regarding this loan loss provision recapture.
Noninterest income increased $3.2 million, or 19.2%, to $19.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. This increase included increased revenue of $1.8 million from deposit account service charges and other fees and increases in gains from sales of bank owned real estate totaling approximately $1.6 million. Additionally during 2008, the Company recorded a gain of $198 thousand relating to the mandatory redemption of certain classes of common stock to financial institution members of Visa U.S.A.
28
Noninterest expense increased $4.8 million, or 7.6 %, to $68.3 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to 2007. Increases in salaries and benefits of $3.1 million, or 9.8%, were primarily attributable to the costs associated with personnel in the new branches and normal compensation increases. Occupancy expenses increased $837 thousand, or 16.0%, and were largely related to increased facilities costs associated with the Company’s new operations center and the new branches. Some of these increased costs included depreciation, rental expenses, real estate taxes, and, to a lesser extent, utility costs. Other operating expenses increased $788 thousand, or 3.5%, and principally related to ongoing infrastructure enhancements to support the Company’s continued growth, conversion expenses related to merging affiliate banks, as well as higher FDIC insurance costs due to exhausting assessment credits. Infrastructure enhancements included Voice-over Internet Protocol and the associated hardware and software to support this technology. Approximately $515 thousand of other operating expenses related to conversion costs incurred to combine two affiliate banks. This will benefit the Company by building a common brand and providing customer access throughout the markets we serve. These combinations are expected to also achieve additional efficiencies that arise from enhanced product offerings and reduced back office redundancies. For comparative purposes, the Company incurred $212 thousand in conversion costs during 2007. Furniture and equipment expenses increased $162 thousand, or 3.6%, and were attributable to the related depreciation of the new branches and the new operations center. Excluding the conversion costs related to the affiliate mergers and new branches, noninterest expense increased $4.5 million, or 7.2%, when compared to the year ended December 31, 2007.
During the first half of 2007, proceeds from called investment securities were used to payoff higher rate FHLB advances in order to enhance the net interest margin in future periods. Approximately $513 thousand in penalties associated with the early payoff of FHLB advances are included in year end results for 2007. Additionally, for comparative purposes, during 2007 the Company recorded a gain of $508 thousand on sales of trust preferred securities called by the issuer and a gain of $324 thousand from the sale of its former operations center, partially offset by losses from the disposal of legacy telecommunications equipment of $121 thousand.
Mortgage Segment
For the year ended December 31, 2008, mortgage segment net income increased by $842 thousand from a net loss of $803 thousand to net income of $39 thousand. Gains on the sale of loans increased $2.3 million, or 26.2%, as a result of revised fee schedules, increased volume in government (FHA/VA) loans and an increase in originations of 14.2%. Expenses related to loan payoff and early payment defaults amounted to $503 thousand, which reduced the gain on sale of loans for the period due to the volatile state of residential mortgage lending. Salaries and benefits increased $1.3 million, principally due to commissions and other expenses related to increased loan originations. Occupancy and furniture and equipment costs increased $38 thousand and $9 thousand, respectively, largely driven by origination growth and additions to the branch office network. Other operating costs declined $62 thousand to $1.6 million, or 3.6%, and were principally related to lower loan related losses.
BALANCE SHEET
Balance Sheet Overview
On December 19, 2008, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement with the U. S Treasury pursuant to which it issued 59,000 shares of the Company’s Preferred Stock having a liquidation preference of $1,000 per share, for a total price of $59 million. The issuance was made pursuant to the Treasury’s Capital Purchase Plan under TARP. The Preferred Stock pays a cumulative dividend at a rate of 5% per year during the first five years and thereafter at 9% per year. The transaction closed on December 19,
29
2008. At the time of issuance, the Treasury also received a warrant to purchase 422,636 shares of the Company’s common stock at an initial per share exercise price of $20.94. The warrant expires ten years from the issuance date. The issuance and sale of these securities was a private placement exempt from registration pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933. Both the Preferred Stock and the warrant will be accounted for as components of the Company’s Tier 1 capital for regulatory purposes. See the Company’s Form 8-K filing dated December 19, 2008 for additional details about this transaction.
At December 31, 2008, total assets were approximately $2.6 billion compared to $2.3 billion at December 31, 2007. Net loans increased $120.1 million, or 6.9% from December 31, 2007. The year over year increase in loan growth was spread among the consumer and commercial loan portfolios. Total cash and cash equivalents increased $90.3 million from $58.3 million at December 31, 2007. This increase represented excess liquidity from an FHLB advance plus additional funds related to proceeds from the issuance of Preferred Stock. Deposits increased $267.4 million, or 16.1%, from December 31, 2007 primarily due to increases in money market accounts, the issuance of approximately $81.7 million in brokered certificates of deposit, of which $66.7 million remained at December 31, 2008. Proceeds of $59 million related to the Company’s Preferred Stock issuance added additional capital of $10 million to bank affiliates with the remaining $49 million held in a demand deposit account of the Company’s bank affiliate at December 31, 2008 and eliminated in consolidation. Total borrowings, including repurchase agreements, decreased $79.1 million from December 31, 2007 to $333.6 million at December 31, 2008. The Company’s equity to assets ratio was 10.73% and 9.22% at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
The Company remains focused on maintaining adequate levels of liquidity and capital during this challenging environment of weakening economic conditions, and believes sound risk management practices in underwriting and lending will enable it to successfully weather this period of economic uncertainty.
The following table presents the Company’s contractual obligations and scheduled payment amounts due at the various intervals over the next five years and beyond as of December 31, 2008 (dollar in thousands):
| Total | Less than 1 year |
1-3 years | 4-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
$ | 210,310 | $ | — | $ | 10,000 | $ | — | $ | 200,310 | |||||
| Operating leases |
9,465 | 1,853 | 2,868 | 1,693 | 3,051 | ||||||||||
| Other short-term borrowings |
55,000 | 55,000 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| Repurchase agreements |
68,282 | 68,282 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| Total contractual obligations |
$ | 343,057 | $ | 125,135 | $ | 12,868 | $ | 1,693 | $ | 203,361 | |||||
For more information pertaining to the previous table, reference Note 5 “Bank Premise and Equipment” and Note 8 “Borrowings” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements”.
Loan Portfolio
As of December 31, 2008 compared to December 31, 2007, loans, net of unearned income increased $126.3 million, or 7.2%, to $1.9 billion from $1.7 billion. At December 31, 2008, loans secured by real estate continue to represent the Company’s largest category, comprising 80.8% of the total loan portfolio. At December 31, 2008, residential 1-4 family loans, not including home equity lines, comprised 15.6% of total loans and increased $10.2 million, or 3.6% compared to the prior year. At December 31, 2008, mortgage loans secured by commercial real estate comprised 29.4% of the total loans, and increased $50.6 million, or 10.1% compared to the prior year. At December 31, 2008, real estate construction loans accounted for 21.5% of total loans. The Company also experienced increases in home equity lines of credit, up $33.8 million, or 26.3%.
30
Commercial business loan balances increased $10.5 million or 7.7% from the prior year. Commercial business loans composition remained unchanged at 7.8% of total loans for both 2008 and 2007. The Company’s consumer loan portfolio consists principally of installment loans. Such loans to individuals for household, family and other personal expenditures totaled 9.3% of total loans at December 31, 2008, down from 10.6% in 2007. Loans to the agricultural industry increased to 1.6% of total loans at December 31, 2008, up from 1.1% in 2007.
The following table presents the composition of the Company’s loans, net of unearned income and as a percentage of the Company’s total gross loans as of December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Residential 1-4 family |
$ | 292,003 | 15.6 | % | $ | 281,847 | 16.1 | % | $ | 263,770 | 17.0 | % | $ | 271,721 | 19.9 | % | $ | 270,341 | 21.4 | % | ||||||||||
| Commercial |
550,680 | 29.4 | % | 500,118 | 28.6 | % | 448,691 | 29.0 | % | 394,094 | 28.9 | % | 368,816 | 29.2 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Construction |
403,502 | 21.5 | % | 396,928 | 22.7 | % | 324,606 | 20.9 | % | 273,262 | 20.1 | % | 221,190 | 17.5 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Second mortgages |
38,060 | 2.0 | % | 37,875 | 2.2 | % | 35,584 | 2.3 | % | 24,088 | 1.8 | % | 18,017 | 1.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Equity lines of credit |
162,740 | 8.7 | % | 128,897 | 7.4 | % | 112,079 | 7.2 | % | 96,490 | 7.1 | % | 90,042 | 7.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Multifamily |
37,321 | 2.0 | % | 32,970 | 1.9 | % | 29,263 | 1.9 | % | 14,648 | 1.1 | % | 18,287 | 1.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Agriculture |
30,727 | 1.6 | % | 18,958 | 1.1 | % | 12,903 | 0.8 | % | 11,145 | 0.8 | % | 5,530 | 0.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total real estate loans |
1,515,033 | 80.8 | % | 1,397,593 | 80.0 | % | 1,226,896 | 79.2 | % | 1,085,448 | 79.7 | % | 992,223 | 78.4 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Commercial Loans |
146,827 | 7.8 | % | 136,317 | 7.8 | % | 136,617 | 8.8 | % | 127,048 | 9.3 | % | 135,907 | 10.7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer installment loans |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Personal |
160,161 | 8.5 | % | 173,650 | 9.9 | % | 153,865 | 9.9 | % | 126,174 | 9.3 | % | 113,841 | 9.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Credit cards |
15,723 | 0.8 | % | 13,108 | 0.7 | % | 9,963 | 0.6 | % | 9,388 | 0.7 | % | 8,655 | 0.7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total consumer installment loans |
175,884 | 9.3 | % | 186,758 | 10.6 | % | 163,828 | 10.6 | % | 135,562 | 10.0 | % | 122,496 | 9.7 | % | |||||||||||||||
| All other loans |
36,344 | 1.9 | % | 27,152 | 1.6 | % | 22,104 | 1.4 | % | 14,196 | 1.0 | % | 14,219 | 1.1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Gross loans |
1,874,088 | 100.0 | % | 1,747,820 | 100.0 | % | 1,549,445 | 100.0 | % | 1,362,254 | 100.0 | % | 1,264,845 | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Less unearned income on loans |
— | — | — | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
$ | 1,874,088 | $ | 1,747,820 | $ | 1,549,445 | $ | 1,362,254 | $ | 1,264,841 | ||||||||||||||||||||
The following table presents the remaining maturities and type of rate (variable or fixed) on commercial and real estate constructions loans as of December 31, 2008 (dollars in thousands):
| Variable Rate | Fixed Rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total Maturities |
Less than 1 year |
Total | 1-5 years | More than 5 years |
Total | 1-5 years | More than 5 years | |||||||||||||||||
| Real Estate Construction |
$ | 403,502 | $ | 348,905 | $ | 9,527 | $ | 9,527 | $ | — | $ | 45,070 | $ | 23,382 | $ | 21,688 | ||||||||
| Commercial |
$ | 146,827 | $ | 90,011 | $ | 5,836 | $ | 5,548 | $ | 288 | $ | 50,980 | $ | 42,128 | $ | 8,852 | ||||||||
While the current economic environment is challenging, the Company remains committed to originating soundly underwritten loans to qualifying borrowers within its markets. The Company is focused on providing community-based financial services and discourages the origination of portfolio loans outside of its principal trade areas. The Company maintains a policy not to originate or purchase loans to foreign entities or loans classified by regulators as highly leveraged transactions. To manage the growth of the real estate loans in the loan portfolio, facilitate asset/liability management and generate additional fee income, the Company sells a portion of conforming first mortgage residential real estate loans to the secondary market as they are originated. Union Mortgage serves as a mortgage brokerage operation, selling the majority of its loan production in the secondary market or selling loans to the Community Banks that meet the banks’ current asset/liability management needs. This venture has provided the Community Banks’ customers with enhanced mortgage products and the Company with improved efficiencies through the consolidation of this function.
Asset Quality
Industry concerns over asset quality, precipitated by subprime mortgage lending, declining real estate activity and general economic conditions, continued during the fourth quarter. These factors are impacting the markets in which the Company operates, principally through slowing real estate activity and general
31
economic uncertainty. The risk and performance of the Company’s loan portfolio is reflective of the relatively stable markets in which we operate and which we understand. While these markets have experienced slowing economic activity in the last year, they remain in much better condition than the well-publicized markets in Arizona, Florida, California and other states where the Company does not lend and does not have loan loss exposure. In addition, the Company’s loan portfolio does not include exposure to subprime mortgage loans.
During the fourth quarter, the Company experienced some deterioration in asset quality, including increased nonperforming assets and anticipates there may be additional softening in the near-term. The Company has a significant concentration in real estate loans and has experienced reduced activity in the real estate development and housing sector. Residential acquisition and development lending and builder/construction lending have been scaled back as housing activity across our markets has declined. While this slower activity may negatively impact delinquency and nonperforming asset levels, the collateralized nature of real estate loans serves to better protect the Company from loss.
Necessary resources are being devoted to the ongoing review of our portfolio and the workout of any problem assets to minimize any loss to the Company. Management will continue to monitor delinquencies, risk rating changes, charge-offs, market trends and other indicators of risk in the Company’s portfolio, particularly those tied to residential real estate and adjust the allowance for loan losses accordingly.
Net charge-offs were $2.0 million, or 0.42% of loans on an annualized basis, for the quarter ended December 31, 2008, compared to net charge-offs of $393 thousand, or 0.09%, in the same quarter last year and $897 thousand, or 0.19 %, for the quarter ended September 30, 2008. Net charge-offs in the current quarter included commercial loan charge-offs of $681 thousand, construction loans charge-offs of $634 thousand and indirect auto loan charge-offs of $294 thousand. Net charge-offs for the year were $3.9 million, or 0.21%, of total loans for 2008, as compared to $872 thousand, or 0.05% of total loans for 2007. At December 31, 2008, total past due loans were $29.4 million, or 1.57%, of total loans, up from 0.61% at December 31, 2007.
At December 31, 2008, nonperforming assets totaled $21.6 million, an increase of $11.4 million since December 31, 2007 and $4.4 million since September 30, 2008. The increases in 2008 relate principally to loans in the real estate development and housing sector, including construction-related businesses.
The largest nonperforming asset is a single credit relationship totaling $6.9 million dating to 2004. The Company entered into a workout agreement with that borrower in March 2004. Under the terms of the agreement, the Company extended further credit secured by additional property with significant equity. During the first quarter of 2007, such equity was extracted from this relationship, reducing nonperforming assets totals on this relationship from $10.6 million as of December 31, 2006 to $7.9 million, and resulting in the recapture of $750 thousand in specific reserves. In the second quarter of 2007, approximately $400 thousand of this relationship returned to accrual status, further reducing the nonperforming balance to $7.5 million as of the end of June 30, 2007. This balance has been further reduced, due to payments from the borrower, to $6.9 million at December 31, 2008. Despite the lengthy nature of this workout, the Company continues to work with the borrower toward a resolution of the affiliated loans and anticipates this workout will result in further reductions of the Company’s overall exposure to the borrower. The loans to this relationship continue to be secured by real estate (two assisted living facilities).
Nonperforming loans include commercial real estate loans of $7.2 million (including the aforementioned $6.9 million credit), commercial and industrial loans of $3.0 million, acquisition and development loans of $939 thousand, construction loans of $890 thousand, and other loans totaling $2.4 million. Historically and particularly in the current economic environment, we seek to work with our customers to work
32
through collection issues, while taking appropriate actions to minimize any loss to the Bank. These loans are closely monitored and evaluated for collection with appropriate loss reserves established where necessary. A special assets loan committee, including the Company’s CEO, Senior Credit Officer and other senior lenders has been formed to address significant potential problem loans and develop action plans related to such assets.
Nonperforming assets also includes $7.1 million in other real estate owned. This total includes foreclosures on three acquisition and development loans totaling approximately $4.2 million, construction loans of $2.4 million and $466 thousand in land left from the development of a bank branch site. These properties have been adjusted to their fair values at the time of foreclosure and any losses taken as loan charge-offs.
The following table summarizes activity in the allowance for loan losses over the past five years ended December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year |
$ | 19,336 | $ | 19,148 | $ | 17,116 | $ | 16,384 | $ | 11,519 | ||||||||||
| Allowance from acquired bank |
— | — | 785 | — | 2,040 | |||||||||||||||
| Loans charged-off: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial |
1,638 | 207 | 22 | 25 | 167 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate |
18 | — | — | 6 | 5 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
2,544 | 1,005 | 600 | 809 | 1,002 | |||||||||||||||
| Total loans charged-off |
4,200 | 1,212 | 622 | 840 | 1,174 | |||||||||||||||
| Recoveries: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial |
52 | 30 | 102 | 43 | 1,388 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate |
— | — | — | — | 42 | |||||||||||||||
| Consumer |
288 | 310 | 317 | 357 | 415 | |||||||||||||||
| Total recoveries |
340 | 340 | 419 | 400 | 1,845 | |||||||||||||||
| Net charge-offs (recoveries) |
3,860 | 872 | 203 | 440 | (671 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
10,020 | 1,060 | 1,450 | 1,172 | 2,154 | |||||||||||||||
| Balance, end of year |
$ | 25,496 | $ | 19,336 | $ | 19,148 | $ | 17,116 | $ | 16,384 | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses to loans |
1.36 | % | 1.11 | % | 1.24 | % | 1.26 | % | 1.30 | % | ||||||||||
| Net charge-offs (recoveries) to average loans |
0.21 | % | 0.05 | % | 0.01 | % | 0.03 | % | (0.06 | )% | ||||||||||
The following table shows an allocation among loan categories based upon analysis of the loan portfolio’s composition, historical loan loss experience and other factors, as well as, the ratio of the related outstanding loan balances to total loans as of December 31, (dollars in thousands).
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | % (1) | $ | % (1) | $ | % (1) | $ | % (1) | $ | % (1) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Commercial, financial and agriculture |
$ | 6,022 | 8.1 | % | $ | 4,567 | 8.0 | % | $ | 4,523 | 8.9 | % | $ | 4,320 | 9.3 | % | $ | 4,971 | 10.8 | % | ||||||||||
| Real estate construction |
$ | 14,161 | 21.5 | % | 10,740 | 22.7 | % | 10,635 | 20.9 | % | 9,229 | 20.1 | % | 7,998 | 17.5 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Real estate mortgage |
$ | 806 | 59.3 | % | 611 | 57.3 | % | 605 | 58.2 | % | 541 | 59.7 | % | 518 | 61.0 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Consumer & other |
$ | 4,507 | 11.1 | % | 3,418 | 12.0 | % | 3,385 | 11.9 | % | 3,026 | 10.9 | % | 2,897 | 10.7 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 25,496 | 100.0 | % | $ | 19,336 | 100.0 | % | $ | 19,148 | 100.0 | % | $ | 17,116 | 100.0 | % | $ | 16,384 | 100.0 | % | ||||||||||
| (1) | The percent represents the loan balance divided by total loans. |
33
The following table presents a five-year comparison of nonperforming assets as of December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | 2004 | ||||||||||||||||
| Nonaccrual loans |
$ | 14,412 | $ | 9,436 | $ | 10,873 | $ | 11,255 | $ | 11,169 | ||||||||||
| Foreclosed properties |
6,511 | 217 | — | — | 14 | |||||||||||||||
| Real estate investment |
629 | 476 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total nonperforming assets |
$ | 21,552 | $ | 10,129 | $ | 10,873 | $ | 11,255 | $ | 11,183 | ||||||||||
| Loans past due 90 days and accruing interest |
$ | 3,082 | $ | 905 | $ | 208 | $ | 150 | $ | 822 | ||||||||||
| Nonperforming assets to loans, foreclosed properties & real estate investments |
1.15 | % | 0.58 | % | 0.70 | % | 0.83 | % | 0.88 | % | ||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses to nonaccrual loans |
176.91 | % | 204.92 | % | 176.11 | % | 152.07 | % | 146.69 | % | ||||||||||
Securities Available for Sale
At December 31, 2008, the Company had securities available for sale, at fair value, in the amount of $309.7 million, or 12.1% of total assets, as compared to $282.7 million, or 12.3%, of total assets as of December 31, 2007. The Company seeks to diversify its portfolio to minimize risk and to maintain a large amount of securities issued by states and political subdivisions due to the tax benefits. It also focuses on purchasing mortgage-backed securities because of the reinvestment opportunities from the cash flows and the higher yield offered from these securities. All of the Company’s mortgage-backed securities are greater than or equivalent to investment grade. The investment portfolio has a high percentage of municipals and mortgage-backed securities; therefore a higher taxable equivalent yield exists on the portfolio compared to its peers. The Company does not engage in structured derivative or hedging activities. The following table sets forth a summary of the securities available for sale, at fair value as of December 31, (dollar in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
| U.S. government and agency securities |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 9,829 | |||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
120,257 | 112,596 | 104,222 | ||||||
| Corporate and other bonds |
12,136 | 15,996 | 27,202 | ||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
160,531 | 136,220 | 130,610 | ||||||
| Federal Reserve Bank stock |
3,383 | 3,337 | 3,097 | ||||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank stock |
13,171 | 13,800 | 7,554 | ||||||
| Other securities |
233 | 750 | 310 | ||||||
| Total securities available for sale, at fair value |
$ | 309,711 | $ | 282,699 | $ | 282,824 | |||
Management evaluates securities for other-than-temporary impairment at least on a quarterly basis and more frequently when economic or market concerns warrant such evaluation. Consideration is given to (i) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, (ii) the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and (iii) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value. The unrealized losses in the securities portfolio were attributable to changes in credit and market spreads, not in estimated cash flows or credit quality of the issuer, no other-than-temporary impairment was recorded at December 31, 2008. The Company did not own any the Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac preferred stock on which many institutions incurred significant writedowns.
Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties.
34
The following table summarizes the contractual maturity of securities available for sale, at fair value and their weighted average yields as of December 31, 2008 (dollar in thousands):
| 1 Year or Less | 1 - 5 Years | 5 - 10 Years | Over 10 Years and Equity Securities |
Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Mortgage backed securities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
$ | 916 | $ | 26,032 | $ | 44,608 | $ | 85,542 | $ | 157,098 | ||||||||||
| Fair value |
917 | 26,162 | 45,653 | 87,799 | 160,531 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted average yield (1) |
3.96 | % | 4.50 | % | 4.85 | % | 5.34 | % | 5.06 | % | ||||||||||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
$ | 3,630 | $ | 11,981 | $ | 38,442 | $ | 70,037 | $ | 124,090 | ||||||||||
| Fair value |
3,659 | 12,154 | 39,014 | 65,430 | 120,257 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted average yield (1) |
4.83 | % | 4.83 | % | 4.81 | % | 4.52 | % | 4.65 | % | ||||||||||
| Other securities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,353 | $ | 27,698 | $ | 31,051 | ||||||||||
| Fair value |
— | — | 2,810 | 26,113 | 28,923 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted average yield (1) |
— | — | 4.90 | % | 5.72 | % | 5.63 | % | ||||||||||||
| Total securities available for sale: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortized cost |
$ | 4,546 | $ | 38,013 | $ | 86,403 | $ | 183,277 | $ | 312,239 | ||||||||||
| Fair value |
4,576 | 38,316 | 87,477 | 179,342 | 309,711 | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted average yield (1) |
4.65 | % | 4.60 | % | 4.84 | % | 5.08 | % | 4.95 | % | ||||||||||
| (1) | Yields on tax-exempt securities have been computed on a tax-equivalent basis. |
Deposits
As of December 31, 2008, total deposits were $1.9 billion, increasing from $1.7 billion as of December 31, 2007. Total deposits consist of noninterest-bearing demand deposits of $274.8 million, or 14.3%, and interest-bearing deposits of $1.6 billion, or 85.7%. The Company issued brokered certificates of deposits during 2008, of which $66.7 million remained outstanding at December 31, 2008. When issued, the brokered CDs where at rates below the then-current retail market rates. It is anticipated that these brokered CDs will not be reissued as they mature in the first quarter of 2009. Money market account balances increased approximately $204.6 million, from $156.6 million a year ago, principally as a result of the Company’s successful marketing campaign targeting this product. The Company had no brokered certificates of deposit as of December 31, 2007.
The average deposits and rates paid for the past three years and maturities of certificates of deposit of $100,000 and over as of December 31, 2008 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Rate | Amount | Rate | Amount | Rate | |||||||||||||||
| Noninterest-bearing demand deposits |
$ | 272,764 | $ | 283,877 | $ | 284,094 | ||||||||||||||
| Interest-bearing deposits: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| NOW accounts |
218,349 | 0.62 | % | 206,748 | 0.64 | % | 204,023 | 0.45 | % | |||||||||||
| Money market accounts |
238,540 | 2.39 | % | 158,461 | 2.34 | % | 175,163 | 2.25 | % | |||||||||||
| Savings accounts |
100,782 | 0.58 | % | 104,507 | 0.78 | % | 116,569 | 0.91 | % | |||||||||||
| Time deposits of $100,000 and over |
435,807 | 3.98 | % | 446,662 | 4.93 | % | 387,023 | 4.55 | % | |||||||||||
| Brokered CDs |
57,100 | 3.59 | % | — | 0.00 | % | — | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||
| Other time deposits |
442,491 | 3.90 | % | 451,224 | 4.51 | % | 405,930 | 3.99 | % | |||||||||||
| Total interest-bearing |
1,493,069 | 2.97 | % | 1,367,602 | 3.53 | % | 1,288,708 | 3.08 | % | |||||||||||
| Total average deposits |
$ | 1,765,833 | $ | 1,651,478 | $ | 1,572,802 | ||||||||||||||
| Within 3 Months |
3 - 6 Months | 6 - 12 Months | Over 12 Months |
Total | Percent Of Total Deposits |
|||||||||||||||
| Maturities of time deposits of $100,000 and over |
$ | 82,401 | $ | 31,969 | $ | 143,534 | $ | 194,393 | $ | 452,297 | 23.47 | % | ||||||||
35
Capital Resources
Capital resources represent funds, earned or obtained, over which financial institutions can exercise greater or longer control in comparison with deposits and borrowed funds. The adequacy of the Company’s capital is reviewed by management on an ongoing basis with reference to size, composition, and quality of the Company’s resources and consistency with regulatory requirements and industry standards. Management seeks to maintain a capital structure that will assure an adequate level of capital to support anticipated asset growth and to absorb potential losses, yet allow management to effectively leverage its capital to maximize return to shareholders.
The Federal Reserve, along with the OCC and the FDIC, has adopted capital guidelines to supplement the existing definitions of capital for regulatory purposes and to establish minimum capital standards. Specifically, the guidelines categorize assets and off-balance sheet items into four risk-weighted categories. The minimum ratio of qualifying total assets is 8.0%, of which 4.0% must be Tier 1 capital, consisting of common equity, retained earnings and a limited amount of perpetual preferred stock, less certain intangible items. The Company had a ratio of total capital to risk-weighted assets of 14.56% and 11.67% on December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. The Company’s ratio of Tier 1 capital to risk-weighted assets was 13.31% and 10.65% at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively, allowing the Company to meet the definition of “well-capitalized” for regulatory purposes. Both of these ratios exceeded the fully phased-in capital requirements in 2008 and 2007. The Company’s equity to asset ratio at December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 were 10.73%, 9.22% and 9.53%, respectively.
In connection with its two most recent bank acquisitions, Prosperity and Guaranty, the Company has issued trust preferred capital notes to fund the cash portion of those acquisitions, collectively totaling $58.5 million. The total of the trust preferred capital notes currently qualify for Tier 1 capital of the Company for regulatory purposes. The Acquired Bank Branches were financed through normal operations.
On December 19, 2008, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement with the U. S Treasury pursuant to which it issued 59,000 shares of the Company’s Preferred Stock having a liquidation preference of $1,000 per share, for a total price of $59 million. The issuance was made pursuant to the Treasury’s Capital Purchase Plan under TARP. The Preferred Stock pays a cumulative dividend at a rate of 5% per year during the first five years and thereafter at 9% per year. The transaction closed on December 19, 2008. At the time of issuance, the Treasury also received a warrant to purchase 422,636 shares of the Company’s common stock at an initial per share exercise price of $20.94. The warrant expires ten years from the issuance date.
36
The following summarizes the Company’s regulatory capital and related ratios over the past three years ended December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Tier 1 capital: |
||||||||||||
| Preferred stock—par value |
$ | 590 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Common stock—par value |
18,055 | 17,879 | 17,716 | |||||||||
| Surplus |
101,719 | 40,758 | 38,047 | |||||||||
| Retained earnings |
155,140 | 152,238 | 142,168 | |||||||||
| Warrant |
2,808 | — | — | |||||||||
| Discount on preferred stock |
(2,790 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Total equity |
275,522 | 210,875 | 197,931 | |||||||||
| Plus: qualifying trust preferred capital notes |
58,500 | 58,500 | 58,500 | |||||||||
| Less: core deposit intangibles/goodwill |
65,896 | 68,024 | 62,390 | |||||||||
| Total Tier 1 capital |
268,126 | 201,351 | 194,041 | |||||||||
| Tier 2 capital: |
||||||||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
25,191 | 19,336 | 19,148 | |||||||||
| Total Tier 2 capital |
25,191 | 19,336 | 19,148 | |||||||||
| Total risk-based capital |
$ | 293,317 | $ | 220,687 | $ | 213,189 | ||||||
| Risk-weighted assets |
$ | 2,015,008 | $ | 1,890,569 | $ | 1,668,699 | ||||||
| Capital ratios: |
||||||||||||
| Tier 1 risk-based capital ratio |
13.31 | % | 10.65 | % | 11.63 | % | ||||||
| Total risk-based capital ratio |
14.56 | % | 11.67 | % | 12.78 | % | ||||||
| Leverage ratio (Tier 1 capital to average adjusted assets) |
11.14 | % | 9.20 | % | 9.57 | % | ||||||
| Equity to total assets |
10.73 | % | 9.22 | % | 9.53 | % | ||||||
Commitments and off-balance sheet obligations
In the normal course of business, the Company is a party to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk to meet the financing needs of its customers and to reduce its own exposure to fluctuations in interest rates. These financial instruments include commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit. These instruments involve elements of credit and interest rate risk in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheets. The contractual amounts of these instruments reflect the extent of the Company’s involvement in particular classes of financial instruments. For more information pertaining to these commitments, reference Note 11 “Financial Instruments with Off-Balance Sheet Risk” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.”
The Company’s exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the financial instruments for commitments to extend credit and letters of credit written is represented by the contractual amount of these instruments. The Company uses the same credit policies in making commitments and conditional obligations as it does for on-balance sheet instruments. Unless noted otherwise, the Company does not require collateral or other security to support off-balance sheet financial instruments with credit risk.
At December 31, 2008, Union Mortgage had rate lock commitments to originate mortgage loans amounting to $81.1 million and loans held for sale of $29.4 million. Union Mortgage has entered into corresponding mandatory commitments on a best-efforts basis to sell loans on a servicing released basis totaling approximately $110.5 million. These commitments to sell loans are designed to eliminate the mortgage company’s exposure to fluctuations in interest rates in connection with rate lock commitments and loans held for sale.
37
The following table represents the Company’s other commitments with balance sheet or off-balance sheet risk as of December 31, 2008 (dollars in thousands):
| Amount | |||
| Commitments with off-balance sheet risk: |
|||
| Commitments to extend credit (1) |
$ | 538,611 | |
| Standby letters of credit |
28,031 | ||
| Commitments to purchase securities |
— | ||
| Mortgage loan rate lock commitments |
81,146 | ||
| Total commitments with off-balance sheet risk |
$ | 647,788 | |
| Commitments with balance sheet risk: |
|||
| Loans held for sale |
$ | 29,424 | |
| Total commitments with balance sheet risk |
$ | 29,424 | |
| Total other commitments |
$ | 677,212 | |
| (1) | Includes unfunded overdraft protection. |
Liquidity
Liquidity represents an institution’s ability to meet present and future financial obligations through either the sale or maturity of existing assets or the acquisition of additional funds through liability management. Liquid assets include cash, interest-bearing deposits with banks, money market investments, Federal Funds sold, securities available for sale, loans held for sale and loans maturing or re-pricing within one year. Additional sources of liquidity available to the Company include its capacity to borrow additional funds when necessary through Federal Funds lines with several correspondent banks, a line of credit with the FHLB and a corporate line of credit with a large correspondent bank. During the last half of 2008, as the economic crisis continued to unfold, credit markets seized up and liquidity availability was uncertain, the Company borrowed $50 million at 3.52% in a one year FHLB advance under its commitment with the FHLB. Based on anticipated continued improvement in liquidity, it is anticipated that these funds will be fully repaid when they mature in September. As mentioned above, the Company also issued $59 million of Preferred Stock in 2008. These funds are available to meet the needs of our customers and provide additional liquidity for the Company as of December 31, 2008. Management considers the Company’s overall liquidity to be sufficient to satisfy its depositors’ requirements and to meet its customers’ credit needs.
At December 31, 2008, cash and cash equivalents and securities classified as available for sale comprised 18.0% of total assets, compared to 14.8% at December 31, 2007. Asset liquidity is also provided by managing loan and securities maturities and cash flows.
Additional sources of liquidity available to the Company include its capacity to borrow additional funds when necessary. The Community Banks maintain Federal Funds lines with several regional banks totaling $92.0 million as of December 31, 2008. No amounts were outstanding under these lines at December 31, 2008. The Company had outstanding borrowings pursuant to securities sold under agreements to repurchase transactions with a maturity of one day of $68.3 million as of December 31, 2008 compared to $82.0 million as of December 31, 2007. Lastly, the Company had a collateral dependent line of credit with the FHLB for up to $676 million as of December 31, 2008. There was approximately $205 million outstanding under this line at December 31, 2008.
38
NON GAAP MEASURES
SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations (“SFAS No. 141”), required that the purchase method of accounting be used for all business combinations initiated after June 30, 2001 through December 31, 2008. The acquisitions of Acquired Bank Branches, Prosperity and Guaranty are the three business combinations accounted for using the purchase method of accounting. At December 31, 2008, core deposit intangible assets and goodwill totaled $9.6 million and $56.5, respectively, compared to $11.6 million and $56.5 million, respectively, in 2007.
In reporting the results of 2008 and 2007, the Company has provided supplemental performance measures on an operating or tangible basis. Such measures exclude amortization expense related to intangible assets, such as core deposit intangibles. The Company believes these measures are useful to investors as they exclude non-operating adjustments resulting from acquisition activity and allow investors to see the combined economic results of the organization. Cash basis operating earnings per share was $1.16 for the year ended December 31, 2008 compared to $1.56 in 2007. Cash basis return on average tangible common equity and assets for the year ended December 31, 2008 was 10.69% and .68%, respectively, compared to 14.88% and 1.00%, respectively, in 2007.
These measures are a supplement to GAAP used to prepare the Company’s financial statements and should not be viewed as a substitute for GAAP measures. In addition, the Company’s non-GAAP measures may not be comparable to non-GAAP measures of other companies. The following table reconciles these non-GAAP measures from their respective GAAP basis measures for the years ended December 31, (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,514 | $ | 19,756 | ||||
| Plus: core deposit intangible amortization, net of tax |
1,259 | 1,214 | ||||||
| Cash basis operating earnings |
15,773 | 20,970 | ||||||
| Average assets |
2,379,403 | 2,167,123 | ||||||
| Less: average goodwill |
56,474 | 52,807 | ||||||
| Less: average core deposit intangibles |
10,568 | 11,835 | ||||||
| Average tangible assets |
2,312,361 | 2,102,481 | ||||||
| Average equity |
216,622 | 205,525 | ||||||
| Less: average goodwill |
56,474 | 52,807 | ||||||
| Less: average core deposit intangibles |
10,568 | 11,835 | ||||||
| Less: average preferred equity |
1,993 | — | ||||||
| Average tangible common equity |
$ | 147,587 | $ | 140,883 | ||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding, diluted |
13,542,948 | 13,422,139 | ||||||
| Cash basis earnings per share, diluted |
$ | 1.16 | $ | 1.56 | ||||
| Cash basis return on average tangible assets |
0.68 | % | 1.00 | % | ||||
| Cash basis return on average tangible common equity |
10.69 | % | 14.88 | % | ||||
39
QUARTERLY RESULTS
The following table presents the Company’s quarterly performance for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands, except per share amounts):
| Quarter | ||||||||||||||||
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | Total | ||||||||||||
| For the Year 2008 |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest and dividend income |
$ | 34,870 | $ | 33,308 | $ | 34,012 | $ | 32,905 | $ | 135,095 | ||||||
| Interest expense |
15,745 | 13,480 | 13,758 | 14,239 | 57,222 | |||||||||||
| Net interest income |
19,125 | 19,828 | 20,254 | 18,666 | 77,873 | |||||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
1,600 | 1,676 | 3,667 | 3,077 | 10,020 | |||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
17,525 | 18,152 | 16,587 | 15,589 | 67,853 | |||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
7,348 | 7,656 | 9,113 | 6,438 | 30,555 | |||||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
19,933 | 20,034 | 20,109 | 19,560 | 79,636 | |||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
4,940 | 5,774 | 5,591 | 2,467 | 18,772 | |||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
1,288 | 1,441 | 1,336 | 193 | 4,258 | |||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 3,652 | $ | 4,333 | $ | 4,255 | $ | 2,274 | $ | 14,514 | ||||||
| Earnings per share, basic |
$ | 0.27 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 1.08 | ||||||
| Earnings per share, diluted |
$ | 0.27 | $ | 0.32 | $ | 0.31 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 1.07 | ||||||
| For the Year 2007 |
||||||||||||||||
| Interest and dividend income |
$ | 33,627 | $ | 35,129 | $ | 36,251 | $ | 35,989 | $ | 140,996 | ||||||
| Interest expense |
15,467 | 15,908 | 16,903 | 16,973 | 65,251 | |||||||||||
| Net interest income |
18,160 | 19,221 | 19,348 | 19,016 | 75,745 | |||||||||||
| Provision for (recapture of) loan losses |
(735 | ) | 190 | 432 | 1,173 | 1,060 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
18,895 | 19,031 | 18,916 | 17,843 | 74,685 | |||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
6,209 | 6,212 | 6,282 | 6,402 | 25,105 | |||||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
17,959 | 17,666 | 17,978 | 19,947 | 73,550 | |||||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
7,145 | 7,577 | 7,220 | 4,298 | 26,240 | |||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
1,997 | 1,936 | 1,863 | 688 | 6,484 | |||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 5,148 | $ | 5,641 | $ | 5,357 | $ | 3,610 | $ | 19,756 | ||||||
| Earnings per share, basic |
$ | 0.39 | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 1.48 | ||||||
| Earnings per share, diluted |
$ | 0.38 | $ | 0.42 | $ | 0.40 | $ | 0.27 | $ | 1.47 | ||||||
ITEM 7A. – QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
This information is incorporated herein by reference from Item 7 “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” of this Form 10-K.
40
ITEM 8. – FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA.

REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Union Bankshares Corporation
Bowling Green, Virginia
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission, and our report dated February 26, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting.
Winchester, Virginia
February 26, 2009
41

REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
Union Bankshares Corporation
Bowling Green, Virginia
We have audited Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries’ management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (a) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (b) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (c) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
42
In our opinion, Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 and the related consolidated statements of income, changes in stockholders’ equity and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2008 of Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries and our report dated February 26, 2009 expressed an unqualified opinion.
 |
| Winchester, Virginia |
| February 26, 2009 |
43
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2008 AND 2007
(Dollars in thousands, except share amounts)
| 2008 | 2007 | ||||||
| ASSETS |
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents: |
|||||||
| Cash and due from banks |
$ | 144,625 | $ | 54,716 | |||
| Interest-bearing deposits in other banks |
903 | 662 | |||||
| Money market investments |
122 | 303 | |||||
| Other interest-bearing deposits |
2,598 | 2,598 | |||||
| Federal funds sold |
289 | — | |||||
| Total cash and cash equivalents |
148,537 | 58,279 | |||||
| Securities available for sale, at fair value |
309,711 | 282,699 | |||||
| Loans held for sale |
29,424 | 25,248 | |||||
| Loans, net of unearned income |
1,874,088 | 1,747,820 | |||||
| Less allowance for loan losses |
25,496 | 19,336 | |||||
| Net loans |
1,848,592 | 1,728,484 | |||||
| Bank premises and equipment, net |
77,425 | 75,741 | |||||
| Other real estate owned |
7,140 | 694 | |||||
| Core deposit intangibles, net |
9,613 | 11,550 | |||||
| Goodwill |
56,474 | 56,474 | |||||
| Other assets |
65,016 | 62,228 | |||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,551,932 | $ | 2,301,397 | |||
| LIABILITIES |
|||||||
| Noninterest-bearing demand deposits |
$ | 274,829 | $ | 281,405 | |||
| Interest-bearing deposits: |
|||||||
| NOW accounts |
201,317 | 217,809 | |||||
| Money market accounts |
361,138 | 156,576 | |||||
| Savings accounts |
93,559 | 100,885 | |||||
| Time deposits of $100,000 and over |
452,297 | 453,243 | |||||
| Other time deposits |
477,150 | 449,660 | |||||
| Brokered time deposits |
66,709 | — | |||||
| Total interest-bearing deposits |
1,652,170 | 1,378,173 | |||||
| Total deposits |
1,926,999 | 1,659,578 | |||||
| Securities sold under agreements to repurchase |
68,282 | 82,049 | |||||
| Other short-term borrowings |
55,000 | 200,837 | |||||
| Long-term borrowings |
150,000 | 69,500 | |||||
| Trust preferred capital notes |
60,310 | 60,310 | |||||
| Other liabilities |
17,543 | 17,041 | |||||
| Total liabilities |
2,278,134 | 2,089,315 | |||||
| Commitments and contingencies |
|||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|||||||
| Preferred stock, $10.00 par value, shares authorized 59,000; issued and outstanding, 59,000 shares at December 31, 2008 and none at December 31, 2007 |
590 | — | |||||
| Common stock, $1.33 par value, shares authorized 36,000,000; issued and outstanding, 13,570,970 shares at December 31, 2008 and 13,438,334 shares at December 31, 2007 |
18,055 | 17,879 | |||||
| Surplus |
101,719 | 40,758 | |||||
| Retained earnings |
155,140 | 152,238 | |||||
| Warrant |
2,808 | — | |||||
| Discount on preferred stock |
(2,790 | ) | — | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income |
(1,724 | ) | 1,207 | ||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
273,798 | 212,082 | |||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 2,551,932 | $ | 2,301,397 | |||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
44
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 AND 2006
(Dollars in thousands, except per share amounts)
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
| Interest and dividend income: |
|||||||||
| Interest and fees on loans |
$ | 120,642 | $ | 126,514 | $ | 113,392 | |||
| Interest on Federal funds sold |
98 | 614 | 1,438 | ||||||
| Interest on deposits in other banks |
39 | 57 | 57 | ||||||
| Interest on money market investments |
1 | 4 | 3 | ||||||
| Interest on other interest-bearing deposits |
49 | 135 | 129 | ||||||
| Interest and dividends on securities: |
|||||||||
| Taxable |
9,068 | 8,945 | 9,883 | ||||||
| Nontaxable |
5,198 | 4,727 | 4,254 | ||||||
| Total interest and dividend income |
135,095 | 140,996 | 129,156 | ||||||
| Interest expense: |
|||||||||
| Interest on deposits |
44,298 | 48,234 | 39,729 | ||||||
| Interest on Federal funds purchased |
380 | 1,224 | 1,256 | ||||||
| Interest on short-term borrowings |
4,407 | 6,618 | 4,168 | ||||||
| Interest on long-term borrowings |
8,137 | 9,175 | 7,288 | ||||||
| Total interest expense |
57,222 | 65,251 | 52,441 | ||||||
| Net interest income |
77,873 | 75,745 | 76,715 | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
10,020 | 1,060 | 1,450 | ||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
67,853 | 74,685 | 75,265 | ||||||
| Noninterest income: |
|||||||||
| Service charges on deposit accounts |
9,154 | 7,793 | 7,186 | ||||||
| Other service charges, commissions and fees |
6,637 | 6,157 | 6,009 | ||||||
| Gains on securities transactions, net |
29 | 586 | 688 | ||||||
| Gains on sales of loans |
11,120 | 8,817 | 11,277 | ||||||
| Gains on sales of other real estate owned and bank premises, net |
1,826 | 187 | 870 | ||||||
| Other operating income |
1,789 | 1,565 | 2,215 | ||||||
| Total noninterest income |
30,555 | 25,105 | 28,245 | ||||||
| Noninterest expenses: |
|||||||||
| Salaries and benefits |
43,126 | 38,765 | 37,635 | ||||||
| Occupancy expenses |
6,960 | 6,085 | 5,006 | ||||||
| Furniture and equipment expenses |
4,988 | 4,816 | 4,503 | ||||||
| Other operating expenses |
24,562 | 23,884 | 20,423 | ||||||
| Total noninterest expenses |
79,636 | 73,550 | 67,567 | ||||||
| Income before income taxes |
18,772 | 26,240 | 35,943 | ||||||
| Income tax expense |
4,258 | 6,484 | 9,951 | ||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,514 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | |||
| Amortization of discount on preferred stock |
18 | — | — | ||||||
| Net income available to common stockholders |
$ | 14,496 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | |||
| Earnings per common share, basic |
$ | 1.08 | $ | 1.48 | $ | 1.97 | |||
| Earnings per common share, diluted |
$ | 1.07 | $ | 1.47 | $ | 1.94 | |||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
45
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 AND 2006
(Dollars in thousands, except share amounts)
| Preferred Stock |
Common Stock |
Surplus | Retained Earnings |
Warrant | Discount on Preferred Stock |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2005 |
$ | — | $ | 17,595 | $ | 35,426 | $ | 124,531 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,806 | $ | 179,358 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
25,992 | $ | 25,992 | 25,992 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding gains arising during the period (net of tax, $68) |
126 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income (net of tax, $241) |
(447 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss (net of tax, $173) |
(321 | ) | (321 | ) | (321 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
$ | 25,671 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends common stock ($.63 per share) |
(8,345 | ) | (8,345 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock awards |
182 | 182 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash paid for fractional shares (206 shares) |
(10 | ) | (10 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Dividend Reinvestment Plan (33,194 shares) |
44 | 874 | 918 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Incentive Stock Option Plan (47,466 shares) |
63 | 653 | 716 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services rendered (18,302 shares) |
24 | 540 | 564 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| SFAS No. 123R implementation adjustment |
(10 | ) | 10 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
362 | 362 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2006 |
— | 17,716 | 38,047 | 142,168 | — | — | 1,485 | 199,416 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
19,756 | $ | 19,756 | 19,756 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding gains arising during the period (net of tax, $55) |
103 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income (net of tax, $205) |
(381 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss (net of tax, $150) |
(278 | ) | (278 | ) | (278 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
$ | 19,478 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends common stock ($.73 per share) |
(9,686 | ) | (9,686 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock awards |
22 | 22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Dividend Reinvestment Plan (47,769 shares) |
64 | 994 | 1,058 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Incentive Stock Option Plan (46,743 shares) |
62 | 582 | 644 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services rendered (27,933 shares) |
37 | 568 | 605 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
545 | 545 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2007 |
— | 17,879 | 40,758 | 152,238 | — | — | 1,207 | 212,082 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
14,514 | $ | 14,514 | 14,514 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized holding losses arising during the period (net of taxes, $1,568) |
(2,912 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reclassification adjustment for gains included in net income (net of taxes, $10) |
(19 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss (net of taxes, $1,578) |
(2,931 | ) | (2,931 | ) | (2,931 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
$ | 11,583 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash dividends common stock ($.74 per share) |
(9,990 | ) | (9,990 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock awards |
58 | 58 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cumulative-effect of a change in accounting principle |
(1,604 | ) | (1,604 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock |
590 | 58,334 | 2,808 | (2,808 | ) | 58,924 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of preferred stock discount |
(18 | ) | 18 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock purchased under stock repurchase plan (15,000 shares) |
(20 | ) | (234 | ) | (254 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Dividend Reinvestment Plan (57,747 shares) |
78 | 1,010 | 1,088 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock under Incentive Stock Option Plan (57,419 shares) |
77 | 698 | 775 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted stock under Incentive Stock Option Plan (3,282 shares) |
4 | (4 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common stock for services rendered (27,721 shares) |
37 | 521 | 558 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
578 | 578 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance - December 31, 2008 |
$ | 590 | $ | 18,055 | $ | 101,719 | $ | 155,140 | $ | 2,808 | $ | (2,790 | ) | $ | (1,724 | ) | $ | 273,798 | ||||||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
46
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 AND 2006
(Dollars in thousands)
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,514 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization of bank premises and equipment |
5,293 | 4,690 | 3,904 | |||||||||
| Amortization, net |
2,512 | 2,455 | 2,397 | |||||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
10,020 | 1,060 | 1,450 | |||||||||
| Gains on the sale of investment securities |
(29 | ) | (586 | ) | (688 | ) | ||||||
| Origination of loans held for sale |
(424,601 | ) | (371,873 | ) | (484,696 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sales of loans held for sale |
420,425 | 366,709 | 492,680 | |||||||||
| Gains on sales of other real estate owned and bank premises, net |
(1,826 | ) | (187 | ) | (870 | ) | ||||||
| Stock-based compensation expenses |
578 | 545 | 362 | |||||||||
| Issuance of common stock grants for services |
558 | 605 | 564 | |||||||||
| Increase in other assets |
(8,245 | ) | (7,480 | ) | (5,975 | ) | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in other liabilities |
(1,102 | ) | 1,330 | (807 | ) | |||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities |
18,097 | 17,024 | 34,313 | |||||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Purchases of securities available for sale |
(68,254 | ) | (55,080 | ) | (51,296 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sales of securities available for sale |
881 | 100 | 1,005 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from maturities, calls and paydowns of securities available for sale |
35,895 | 55,289 | 47,614 | |||||||||
| Net increase in loans |
(130,128 | ) | (199,247 | ) | (110,867 | ) | ||||||
| Net increase in bank premises and equipment |
(5,151 | ) | (14,573 | ) | (21,085 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from sales of other real estate owned |
— | — | 499 | |||||||||
| Cash paid in bank acquisition |
— | — | (35,955 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash acquired in bank and branch acquisitions |
— | 35,636 | 17,148 | |||||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in investing activities |
(166,757 | ) | (177,875 | ) | (152,937 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net decrease in noninterest-bearing deposits |
(6,576 | ) | (19,443 | ) | (18,254 | ) | ||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in interest-bearing deposits |
273,997 | (30,195 | ) | 116,205 | ||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in short-term borrowings |
(159,604 | ) | 220,190 | (45,400 | ) | |||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in long-term borrowings |
80,500 | (19,350 | ) | 41,850 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from trust preferred capital notes |
— | — | 37,114 | |||||||||
| Cash dividends paid |
(9,990 | ) | (9,686 | ) | (8,345 | ) | ||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of stock-based awards |
58 | 22 | 182 | |||||||||
| Cash paid for fractional shares |
— | — | (10 | ) | ||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock |
58,924 | — | — | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(254 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
1,863 | 1,702 | 1,634 | |||||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities |
238,918 | 143,240 | 124,976 | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
90,258 | (17,611 | ) | 6,352 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period |
58,279 | 75,890 | 69,538 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period |
$ | 148,537 | $ | 58,279 | $ | 75,890 | ||||||
| Supplemental Disclosure of Cash Flow Information |
||||||||||||
| Cash payments for: |
||||||||||||
| Interest |
$ | 57,520 | $ | 65,103 | $ | 51,312 | ||||||
| Income taxes |
7,470 | 7,909 | 9,935 | |||||||||
| Supplemental schedule of noncash investing and financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on securities available for sale |
$ | (4,509 | ) | $ | (378 | ) | $ | (417 | ) | |||
| Transfers from loans to other real estate owned |
6,376 | — | — | |||||||||
| Cumulative-effect of a change in accounting principle |
(1,604 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Transactions related to bank and branch acquisitions |
||||||||||||
| Increase in assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Loans |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 75,742 | ||||||
| Securities |
— | — | 34,003 | |||||||||
| Other assets |
— | 7,672 | 26,229 | |||||||||
| Noninterest bearing deposits |
— | 8,586 | 52,431 | |||||||||
| Interest bearing deposits |
— | 34,722 | 59,011 | |||||||||
| Borrowings |
— | — | 4,668 | |||||||||
| Other liabilities |
— | — | 1,057 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
47
UNION BANKSHARES CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006
1. SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accounting policies and practices of Union Bankshares Corporation and subsidiaries (the “Company”) conform to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and follow general practice within the banking industry. Major policies and practices are described below. In addition, share and per share amounts for all periods presented in the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the effect of the three-for-two stock split in October 2006.
(A) Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company, which is a bank holding company that owns all of the outstanding common stock of its banking subsidiaries, Union Bank and Trust Company (“Union Bank”), Northern Neck State Bank, Rappahannock National Bank, and of Union Investment Services Inc. Two affiliates, Prosperity Bank & Trust Company (“Prosperity”) and Bay Community Bank, were merged into the largest affiliate, Union Bank, in March and October 2008, respectively. Union Mortgage Group, Inc. (“Union Mortgage”) is a wholly owned subsidiary of Union Bank. Union Bank also has a non-controlling interest in Johnson Mortgage Company, LLC, which is accounted for under the equity method of accounting. The Company’s Statutory Trust I and II, wholly owned subsidiaries of the Company, were formed for the purpose of issuing redeemable Capital Securities in connection with the Company’s acquisitions of Guaranty Financial Corporation in May 2004 and its wholly owned subsidiary, Guaranty Bank (“Guaranty”) and Prosperity in April 2006. Statement of Financial Accounting Standard (“SFAS”) Interpretation No. 46R Consolidation of Variable Interest—an interpretation of ARB No. 51 (“FIN 46R”) precludes the Company from consolidating Statutory Trusts I and II. The subordinated debts payable to the trusts are reported as liabilities of the Company. All significant inter-company balances and transactions have been eliminated. The accompanying consolidated financial statements for prior periods reflect certain reclassifications in order to conform to the current presentation.
(B) Investment Securities
Debt securities that the Company has the positive intent and ability to hold to maturity are classified as held-to-maturity and reported at amortized cost. The Company has no securities in this category.
Securities classified as available for sale are those debt and equity securities that management intends to hold for an indefinite period of time, including securities used as part of the Company’s asset/liability strategy, and that may be sold in response to changes in interest rates, liquidity needs or other similar factors or called by the issuer under the terms of the debt. Securities available for sale are reported at fair value, with unrealized gains or losses, net of deferred taxes, included in accumulated other comprehensive income in stockholders’ equity.
Securities classified as held for trading are those debt and equity securities that are bought and held principally for the purpose of selling them in the near term and reported at fair value, with unrealized gains and losses included in earnings. The Company has no securities in this category.
Purchased premiums and discounts are recognized in interest income using the interest method over the terms of the securities. Declines in the fair value of held to maturity and available for sale securities below their cost that are deemed to be other than temporary are reflected in earnings as realized losses. In estimating other-than-temporary impairment losses, management considers (1) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, (2) the financial condition and near-term prospects
48
of the issuer, and (3) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value. The Company has recognized no other-than-temporary losses. Gains and losses on the sale of securities are recorded on the trade date and are determined using the specific identification method.
(C) Loans Held For Sale
Loans originated and intended for sale in the secondary market are sold servicing released and carried at the lower of cost or estimated fair value, which is determined in the aggregate based on sales commitments to permanent investors or on current market rates for loans of similar quality and type. In addition, the Company requires a firm purchase commitment from a permanent investor before a loan can be closed, thus limiting interest rate risk. As a result, loans held for sale are stated at fair value. Net unrealized losses, if any, are recognized through a valuation allowance by charges to income.
(D) Loans
The Company grants mortgage, commercial and consumer loans to customers. A substantial portion of the loan portfolio is represented by mortgage loans and commercial real estate (including acquisition and development and residential construction) loans throughout its market area. The ability of the Company’s debtors to honor their contracts is dependent upon the real estate and general economic conditions in this area.
Loans that management has the intent and ability to hold for the foreseeable future or until maturity or pay-offs generally are reported at their outstanding unpaid principal balances adjusted for charge-offs, the allowance for loan losses, and any deferred fees or costs on originated loans. Interest income is accrued on the unpaid principal balance. Loan origination fees, net of certain direct origination costs, are deferred and recognized as an adjustment of the related loan yield using the interest method.
The accrual of interest on mortgage and commercial loans is discontinued at the time the loan is 90 days delinquent unless the credit is well secured and in process of collection. Credit card loans and other personal loans are typically charged-off no later than 180 days past due. In all cases, loans are placed on non-accrual status or charged-off at an earlier date if collection of principal and interest is considered doubtful.
All interest accrued but not collected for loans that are placed on non-accrual status or charged-off is reversed against interest income. The interest on these loans is accounted for on the cash-basis or cost-recovery method, until qualifying for return to accrual. Loans are returned to accrual status when all the principal and interest amounts contractually due are brought current and future payments are reasonably assured.
(E) Allowance For Loan Losses
The provision for loan losses charged to operations is an amount sufficient to bring the allowance for loan losses to an estimated balance that management considers adequate to absorb potential losses in the portfolio. Loans are charged against the allowance when management believes the collectibility of the principal is unlikely. Recoveries of amounts previously charged-off are credited to the allowance. Management's determination of the adequacy of the allowance is based on an evaluation of the composition of the loan portfolio, the value and adequacy of collateral, current economic conditions, historical loan loss experience, and other risk factors. Management believes that the allowance for loan losses is adequate. While management uses available information to recognize losses on loans, future additions to the allowance may be necessary based on changes in economic conditions, particularly those affecting real estate values. In addition, regulatory agencies, as an integral part of their examination process, periodically review the Company’s allowance for loan losses. Such agencies may require the Company to recognize additions to the allowance based on their judgments about information available to them at the time of their examination.
49
The allowance consists of specific, general and unallocated components. The specific component relates to loans that classified as impaired, and on which an allowance is established when the discounted cash flows (or collateral value or observable market price) of the impaired loan is lower than the carrying value of that loan. The general component covers non-impaired loans and is based on historical loss experience adjusted for various qualitative and environmental factors. An unallocated component is maintained to cover uncertainties that could affect management’s estimate of probable losses. The unallocated component of the allowance reflects the margin of imprecision inherent in the underlying assumptions used in the methodologies for estimating specific and general losses in the portfolio. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, there were no amounts considered unallocated as part of the allowance for loan losses.
A loan is considered impaired when, based on current information and events, it is probable that the Company will be unable to collect the scheduled payments of principal or interest when due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement. Factors considered by management in determining impairment include payment status, collateral value, and the probability of collecting scheduled principal and interest payments when due. Loans that experience insignificant payment delays and payment shortfalls generally are not classified as impaired. Generally, a loan that is classified substandard or worse is considered impaired. Management determines the significance of payment delays and payment shortfalls on a case-by-case basis, taking into consideration all of the circumstances surrounding the loan and the borrower, including the length of the delay, the reasons for the delay, the borrower’s prior payment record, and the amount of the shortfall in relation to the principal and interest owed. Impairment is measured on a loan by loan basis by either the present value of expected future cash flows discounted at the loan’s effective interest rate, the loan’s obtainable market price, or the fair value of the collateral if the loan is collateral dependent.
Large groups of smaller balance homogeneous loans are collectively evaluated for impairment. Accordingly, the Company generally does not separately identify individual consumer and residential loans for impairment disclosures.
(F) Bank Premises and Equipment
Land is carried at cost. Bank premises and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation and amortization are computed using either the straight-line or accelerated method based on the type of asset involved. The Company’s policy is to capitalize additions and improvements and to depreciate the cost thereof over their estimated useful lives ranging from 3 to 40 years. Maintenance, repairs and renewals are expensed as they are incurred.
(G) Goodwill and Intangible Assets
SFAS No. 141, Business Combinations, required that the purchase method of accounting be used for all business combinations initiated after June 30, 2001 through December 31, 2008. For purchase acquisitions, the Company was required to record assets acquired, including identifiable intangible assets, and liabilities assumed at their fair value, which in many instances involved estimates based on third party valuations, such as appraisals, or internal valuations based on discounted cash flow analysis or other valuation techniques. Effective January 1, 2001, the Company adopted SFAS No. 142, Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets (“SFAS 142”), which prescribes the accounting for goodwill and intangible assets subsequent to initial recognition. The provisions of SFAS 142 discontinue the amortization of goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives but require at least an annual impairment review and more frequently if certain impairment indicators are in evidence. The Company adopted SFAS 147, Acquisitions of Certain Financial Institutions, on January 1, 2002 and determined that core deposit intangibles will continue to be amortized over the estimated useful life.
50
(H) Income Taxes
Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are determined using the liability (or balance sheet) method. Under this method, the net deferred tax asset or liability is determined based on the tax effects of the temporary differences between the book and tax bases of the various balance sheet assets and liabilities and gives current recognition to changes in tax rates and laws. Deferred taxes are reduced by a valuation allowance when, in the opinion of management, it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized.
When tax returns are filed, it is highly certain that some positions taken would be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, while others are subject to uncertainty about the merits of the position taken or the amount of the position that would be ultimately sustained. The benefit of a tax position is recognized in the financial statements in the period during which, based on all available evidence, management believes it is more likely than not that the position will be sustained upon examination, including the resolution of appeals or litigation processes, if any. Tax positions taken are not offset or aggregated with other positions. Tax positions that meet the more-likely-than-not recognition threshold are measured as the largest amount of tax benefit that is more than 50 percent likely of being realized upon settlement with the applicable taxing authority. The portion of the benefits associated with tax positions taken that exceeds the amount measured as described above is reflected as a liability for unrecognized tax benefits in the accompanying balance sheet along with any associated interest and penalties that would be payable to the taxing authorities upon examination.
Interest and penalties associated with unrecognized tax benefits are classified as additional income taxes in the statement of income. The Company did not have any of these for the period ending December 31, 2008.
(I) Other Real Estate Owned
Assets acquired through, or in lieu of, loan foreclosure are held for sale and are initially recorded at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value at the date of foreclosure, establishing a new cost basis. Subsequent to foreclosure, valuations are periodically performed by management and the assets are carried at the lower of carrying amount or fair value less cost to sell. Revenue and expenses from operations and changes in the valuation allowance are included in net expenses from foreclosed assets.
(J) Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
For purposes of reporting cash flows, the Company defines cash and cash equivalents as cash due from banks, interest-bearing deposits in other banks, money market investments, other interest-bearing deposits, and Federal Funds sold.
(K) Earnings Per Share
Basic earnings per share (“EPS”) is computed by dividing net income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the year. Diluted earnings per share reflects additional common shares that would have been outstanding if dilutive potential common shares had been issued, as well as any adjustment to income that would result from the assumed issuance. Potential common shares that may be issued by the Company relate solely to outstanding stock options, nonvested stock and warrants and are determined using the treasury stock method.
(L) Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) represents all changes in equity that result from recognized transactions and other economic events of the period. Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenues, expenses, gains and losses that under accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“U.S.”) are included in comprehensive income, but excluded from net income, such as unrealized gains and losses on certain investments in debt and equity securities.
51
(M) Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from these estimates. Material estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change in the near term relate to the determination of the allowance for loan losses, the valuation of goodwill and intangible assets, foreclosed real estate and deferred tax assets and liabilities.
(N) Advertising Costs
The Company follows a policy of charging the cost of advertising to expense as incurred. Total advertising costs included in other operating expenses for 2008, 2007, and 2006 were $1.2 million, $1.2 million, and $1.3 million, respectively.
(O) Off Balance Sheet Credit Related Financial Instruments
In the ordinary course of business, the Company has entered into commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit. Such financial instruments are recorded when they are funded.
(P) Rate Lock Commitments
The Company enters into commitments to originate mortgage loans whereby the interest rate on the loan is determined prior to funding (rate lock commitments). Rate lock commitments on mortgage loans that are intended to be sold are considered to be derivatives. The period of time between issuance of a loan commitment and closing and sale of the loan generally ranges from 30 to 120 days. The Company protects itself from changes in interest rates through the use of best efforts forward delivery commitments, whereby the Company commits to sell a loan at the time the borrower commits to an interest rate with the intent that the buyer has assumed interest rate risk on the loan. As a result, the Company is not exposed to losses and will not realize significant gains related to its rate lock commitments due to changes in interest rates. The correlation between the rate lock commitments and the best efforts contracts is very high due to their similarity.
The market value of rate lock commitments and best efforts contracts is not readily ascertainable with precision because rate lock commitments and best efforts contracts are not actively traded in stand-alone markets. The Company determines the fair value of rate lock commitments and best efforts contracts by measuring the change in the value of the underlying asset while taking into consideration the probability that the rate lock commitments will close. Because of the high correlation between rate lock commitments and best efforts contracts, no gain or loss occurs on the rate lock commitments.
(Q) Variable Interest Entities
In January 2003, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Interpretation No. 46, Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities—an interpretation of ARB No. 51 (“FIN 46”), which states that if a business enterprise is the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity, the assets, liabilities and results of the activities of the variable interest entity should be included in the consolidated financial statements of the business enterprise. This interpretation explains how to identify variable interest entities and how an enterprise assesses its interest in a variable interest entity to decide whether to consolidate the entity. FIN 46 also requires existing unconsolidated variable interest entities to be consolidated by their primary beneficiaries if the entities do not effectively disperse risks among parties involved. Variable interest entities that effectively disperse risks will be consolidated unless a single party holds an interest or combination of interests that effectively recombines risks that were previously dispersed. Due to the significant implementation concerns, the FASB revised FIN 46 (“FIN 46R”). Management has evaluated the Company’s investment in variable interest entities and potential variable interest entities or transactions, particularly in trust preferred securities structures, because these entities constitute the Company’s primary exposure.
52
Currently, other than the impact described above from the deconsolidation of the trust preferred capital notes, the adoption of FIN 46 and FIN 46R has not had a material impact on the financial condition or the operating results of the Company.
53
(R) Asset Prepayment Rates
The Company purchases amortizing loan pools and investment securities in which the underlying assets are residential mortgage loans subject to prepayments. The actual principal reduction on these assets varies from the expected contractual principal reduction due to principal prepayments resulting from the borrowers’ election to refinance the underlying mortgage based on market and other conditions. The purchase premiums and discounts associated with these assets are amortized or accreted to interest income over the estimated life of the related assets. The estimated life is calculated by projecting future prepayments and the resulting principal cash flows until maturity. Prepayment rate projections utilize actual prepayment speed experience and available market information on like-kind instruments. The prepayment rates form the basis for income recognition of premiums and discounts on the related assets. Changes in prepayment estimates may cause the earnings recognized on these assets to vary over the term that the assets are held, creating volatility in the net interest margin. Prepayment rate assumptions are monitored monthly and updated periodically to reflect actual activity and the most recent market projections.
(S) Concentrations of Credit Risk
Most of the Company’s activities are with customers located in portions of Central and Tidewater Virginia. Securities Available for Sale and Loans also represent concentrations of credit risk and are discussed in Note 2 “Securities Available for Sale” and Note 3 “Loans” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements,” respectively.
(T) Stock Compensation Plan
Effective January 1, 2006, the Company adopted SFAS 123R (Revised 2004), Share-Based Payment (“SFAS 123R”), which replaces SFAS 123, Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation (“SFAS 123”), and supersedes APB Opinion No. 25, Accounting for Stock Issued to Employees (“APB Opinion 25”). SFAS 123R requires the costs resulting from all share-based payments to employees be recognized in the financial statements. Stock-based compensation is estimated at the date of grant, using the Black-Scholes option valuation model for determining fair value. The model employs the following assumptions:
| • | Dividend yield - calculated as the ratio of historical dividends paid per share of common stock to the stock price on the date of grant; |
| • | Expected life (term of the option) - based on the average of the contractual life and vesting schedule for the respective option; |
| • | Expected volatility - based on the monthly historical volatility of the Company’s stock price over the expected life of the options; |
| • | Risk-free interest rate - based upon the U. S. Treasury bill yield curve, for periods within the contractual life of the option, in effect at the time of grant. |
Under APB Opinion 25, compensation expense was generally not recognized if the exercise price of the option equaled or exceeded the market price of the stock on the date of grant. For the year ended December 31, 2008, the Company recognized stock-based compensation expense of approximately $422 thousand, net of tax, or approximately $.03 per share, in accordance with SFAS 123R.
The Company has elected to adopt the modified prospective method which requires compensation expense to be recorded for the unvested portion of previously issued awards that remained outstanding as of January 1, 2006. In addition, compensation expense is recorded for any awards issued, modified, or settled after the effective date of this standard and prior periods are not restated. For awards granted prior to the effective date, the unvested portion of the awards are recognized in periods subsequent to the adoption based on the grant date fair value determined for pro forma disclosure purposes under SFAS 123R.
54
SFAS 123R requires the Company to estimate forfeitures when recognizing compensation expense and that this estimate of forfeitures be adjusted over the requisite service period or vesting schedule based on the extent to which actual forfeitures differ from such estimates. Changes in estimated forfeitures are recognized through a cumulative catch-up adjustment, which is recognized in the period of change, and also will impact the amount of estimated unamortized compensation expense to be recognized in future periods.
The Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan provides for the granting of incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, and nonvested stock awards to key employees of the Company and its subsidiaries. The Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan replaced the 1993 Stock Incentive Plan, and became effective on July 1, 2003, after shareholders approved the plan at the annual meeting of shareholders held in 2003. The Stock Incentive Plan makes available 525,000 shares (adjusted for the stock split), which may be awarded to employees of the Company and its subsidiaries in the form of incentive stock options intended to comply with the requirements of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 (“incentive stock options”), non-statutory stock options, and nonvested stock. Under the plan, the option price cannot be less than the fair market value of the stock on the grant date. The stock option’s maximum term is ten years from the date of grant and vests in equal annual installments of twenty percent over a five year vesting schedule. The Company issues new shares to satisfy share-based awards. As of December 31, 2008, approximately 310,630 shares were available for issuance under the Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan.
For more information and tables refer to Note 10 “Employee Benefits” within the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements.”
(U) Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In September 2006, the FASB reached a consensus on Emerging Issues Task Force (“EITF”) Issue 06-4, “Accounting for Deferred Compensation and Postretirement Benefit Aspects of Endorsement Split-Dollar Life Insurance Arrangements,” (EITF Issue 06-4). In March 2007, the FASB reached a consensus on EITF Issue 06-10, “Accounting for Collateral Assignment Split-Dollar Life Insurance Arrangements,” Both of these standards require a company to recognize an obligation over an employee’s service period based upon the substantive agreement with the employee such as the promise to maintain a life insurance policy or provide a death benefit postretirement. The Company adopted the provisions of these standards effective January 1, 2008. The adoption of these standards was not material to the consolidated financial statements.
In September 2006, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 157, “Fair Value Measurements” (“SFAS 157”). SFAS 157 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles, and expands disclosures about fair value measurements. SFAS 157 does not require any new fair value measurements, but rather, provides enhanced guidance to other pronouncements that require or permit assets or liabilities to be measured at fair value. This Statement is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2007 and interim periods within those years. The FASB has approved a one-year deferral for the implementation of the Statement for nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a nonrecurring basis. The Company adopted SFAS 157 effective January 1, 2008. The adoption of SFAS 157 was not material to the consolidated financial statements.
In February 2007, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial Assets and Financial Liabilities” (“SFAS 159”). This Statement permits entities to choose to measure many financial instruments and certain other items at fair value. The objective of this Statement is to improve financial reporting by providing entities with the opportunity to
55
mitigate volatility in reported earnings caused by measuring related assets and liabilities differently without having to apply complex hedge accounting provisions. The fair value option established by this Statement permits all entities to choose to measure eligible items at fair value at specified election dates. A business entity shall report unrealized gains and losses on items for which the fair value option has been elected in earnings at each subsequent reporting date. The fair value option may be applied instrument by instrument and is irrevocable. SFAS 159 is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after November 15, 2007, with early adoption available in certain circumstances. The Company adopted SFAS 159 effective January 1, 2008. The Company decided not to report any existing financial assets or liabilities at fair value that are not already reported, thus the adoption of this statement did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In December 2007, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 141(R), “Business Combinations” (“SFAS 141(R)”). The Standard will significantly change the financial accounting and reporting of business combination transactions. SFAS 141(R) establishes principles for how an acquirer recognizes and measures the identifiable assets acquired, liabilities assumed, and any noncontrolling interest in the acquiree; recognizes and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a bargain purchase; and determines what information to disclose to enable users of the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the business combination. SFAS 141(R) is effective for acquisition dates on or after the beginning of an entity’s first year that begins after December 15, 2008. The adoption of this statement will impact the Company’s accounting for and reporting of any acquisitions completed after January 1, 2009.
In December 2007, the FASB issued Statement of Financial Accounting Standards No. 160, “Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements an Amendment of ARB No. 51” (“SFAS 160”). The Standard will significantly change the financial accounting and reporting of noncontrolling (or minority) interests in consolidated financial statements. SFAS 160 is effective as of the beginning of an entity’s first fiscal year that begins after December 15, 2008, with early adoption prohibited. The Company does not expect the implementation of SFAS 160 to have a material impact on its consolidated financial statements.
In November 2007, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) issued Staff Accounting Bulletin No. 109, “Written Loan Commitments Recorded at Fair Value Through Earnings” (“SAB 109”). SAB 109 expresses the current view of the staff that the expected net future cash flows related to the associated servicing of the loan should be included in the measurement of all written loan commitments that are accounted for at fair value through earnings. SEC registrants are expected to apply the views in Question 1 of SAB 109 on a prospective basis to derivative loan commitments issued or modified in fiscal quarters beginning after December 15, 2007. Implementation of SAB 109 did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2008, the FASB issued FASB Staff Position (“FSP”) No. 142-3, “Determination of the Useful Life of Intangible Assets” (“FSP 142-3”). FSP 142-3 amends the factors an entity should consider in developing renewal or extension assumptions used in determining the useful life of recognized intangible assets under SFAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets” (“SFAS 142”). The intent of FSP 142-3 is to improve the consistency between the useful life of a recognized intangible asset under SFAS 142 and the period of expected cash flows used to measure the fair value of the assets under SFAS 141(R). FSP 142-3 is effective for the Company on January 1, 2009, and applies prospectively to intangible assets that are acquired individually or with a group of other assets in business combinations and asset acquisitions. The adoption of FSP 142-3 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
56
In May 2008, the FASB issued SFAS No. 162, “The Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting Principles,” (“SFAS 162”). SFAS 162 identifies the sources of accounting principles and the framework for selecting the principles to be used in the preparation of financial statements of nongovernmental entities that are presented in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles. SFAS 162 is effective 60 days following the SEC’s approval of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board amendments to AU Section 411, “The Meaning of Present Fairly in Conformity With Generally Accepted Accounting Principles.” The Company does not expect the adoption of the provision of SFAS 162 to have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
In October 2008, the FASB issued FSP FAS 157-3, “Determining the Fair Value of a Financial Asset When the Market for That Asset Is Not Active,” (“FSP 157-3”). FSP 157-3 clarifies the application of SFAS 157 in determining the fair value of a financial asset during periods of inactive markets. FSP 157-3 was effective as of September 30, 2008 and did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In December 2008, the FASB issued FSP FAS 140-4 and FIN 46(R)-8, “Disclosures by Public Entities (Enterprises) about Transfers of Financial Assets and Interests in Variable Interest Entities.” FSP FAS 140-4 and FIN 46(R)-8 requires enhanced disclosures about transfers of financial assets and interests in variable interest entities. The FSP is effective for interim and annual periods ending after December 15, 2008. Because the FSP requires only additional disclosures concerning transfers of financial assets and interest in variable interest entities, adoption of the FSP will not affect the Company’s financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
In January 2009, the FASB reached a consensus on EITF Issue 99-20-1. This FSP amends the impairment guidance in EITF Issue No. 99-20, “Recognition of Interest Income and Impairment on Purchased Beneficial Interests and Beneficial Interests That Continue to Be Held by a Transferor in Securitized Financial Assets,” to achieve more consistent determination of whether an other-than-temporary impairment has occurred. The FSP also retains and emphasizes the objective of an other-than-temporary impairment assessment and the related disclosure requirements in SFAS No. 115, “Accounting for Certain Investments in Debt and Equity Securities,” and other related guidance. The FSP is effective for interim and annual reporting periods ending after December 15, 2008 and shall be applied prospectively. The FSP was effective as of December 31, 2008 and did not have a material impact on the consolidated financial statements.
(V) Business Combinations
On September 7, 2007, the Company completed the acquisition of the deposits and facilities of six bank branches (“Acquired Bank Branches”) in Virginia. The branches are located in the communities of Charlottesville, Middleburg, Warrenton (two) and Winchester (two). They became part of two of the Company’s banking subsidiaries, Union Bank (Charlottesville branch) and Rappahannock National Bank (remaining five branches). The six bank branches had total deposits of approximately $43.3 million. This acquisition was financed through normal operations. As part of the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of the Acquired Bank Branches, the Company recorded approximately $1.1 million in core deposit intangible assets and $4.3 million in goodwill. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Acquired Bank Branches are being amortized over an average 8.1 years based on an independent core deposit study.
On April 1, 2006, the Company completed the acquisition of Prosperity in an all cash transaction valued at approximately $36 million. Prosperity, with nearly $130 million in assets, operates three offices in Springfield and Burke, Virginia, located in Fairfax County, a suburb of Washington, D.C. Prosperity operated as an independent bank subsidiary of the Company until March 2008 when it was merged into Union Bank. The acquisition was financed with proceeds from the issuance of trust preferred capital
57
notes. As part of the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of Prosperity, the Company recorded approximately $5.5 million in core deposit intangible assets and $20.6 million in goodwill. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Prosperity acquisition are being amortized over an average of 9.1 years based on an independent core deposit study.
On May 1, 2004, the Company completed its acquisition of Guaranty headquartered in Charlottesville, Virginia. This acquisition was accounted for using the purchase method of accounting. The total consideration paid to Guaranty stockholders in connection with the acquisition was approximately $54.9 million with approximately $23.2 million in cash and 1.5 million shares of the Company’s common stock. The Company operated Guaranty as a separate subsidiary until September 13, 2004, when it was merged into Union Bank. Guaranty transactions have been included in Union Bank’s financial results since May 1, 2004. Acquired assets on May 1, 2004 totaled $248 million, including $165 million in loans and $184 million in deposits. As part of the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of Guaranty, the Company recorded approximately $5.8 million in core deposit intangible assets and $30.1 million in goodwill, in 2004. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Guaranty acquisition are being amortized over an average of 8.7 years based on an independent core deposit study.
Prior to January 1, 2009, the Company accounted for acquisitions under the purchase method of accounting and accordingly was required to record the assets acquired, including identified intangible assets and liabilities assumed at their fair value, which often involved estimates based on third party valuations, such as appraisals, or internal valuations based on discounted cash flow analyses or other valuation techniques, which were inherently subjective. The amortization of identified intangible assets was based upon the estimated economic benefits to be received, which was also subjective. These estimates also included the establishment of various accruals and allowances based on planned facility dispositions and employee severance considerations, among other acquisition-related items. In addition, purchase acquisitions typically result in goodwill, which is subject to at least annual impairment testing, or more frequently if certain indicators are in evidence, based on the fair value of net assets acquired compared to the carrying value of goodwill.
The Company and the acquired entity also incur merger-related costs during an acquisition. The Company capitalized direct costs of the acquisition, such as investment banker and attorneys’ fees and included them as part of the purchase price. Other merger-related internal costs associated with acquisitions are expensed as incurred. Some examples of these merger-related costs include, but are not limited to, systems conversions, integration planning consultants and advertising fees. These merger-related costs are included within the Consolidated Statement of Income classified within the noninterest expense line. The acquired entity records merger-related costs which result from a plan to exit an activity, involuntarily terminate or relocate employees and are recognized as liabilities assumed as of the consummation date of the acquisition. After January 1, 2009, the Company will account for any future business combinations using SFAS 141(R). The acquired entities, Prosperity and Guaranty, recorded merger-related costs of approximately $849 thousand and $1.3 million principally related to employee severance and investment banker fees.
58
2. SECURITIES AVAILABLE FOR SALE
The amortized cost, gross unrealized gains and losses and estimated fair value of securities available for sale at December 31, 2008 and 2007 are summarized as follows (dollars in thousands):
| Gross Unrealized | |||||||||||||
| Amortized Cost |
Gains | (Losses) | Estimated Fair Value | ||||||||||
| December 31, 2008 |
|||||||||||||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
$ | 124,090 | $ | 1,331 | $ | (5,164 | ) | $ | 120,257 | ||||
| Corporate and other bonds |
14,242 | 8 | (2,114 | ) | 12,136 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
157,098 | 3,576 | (143 | ) | 160,531 | ||||||||
| Federal Reserve Bank stock - restricted |
3,383 | — | — | 3,383 | |||||||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank stock - restricted |
13,171 | — | — | 13,171 | |||||||||
| Other securities |
255 | — | (22 | ) | 233 | ||||||||
| $ | 312,239 | $ | 4,915 | $ | (7,443 | ) | $ | 309,711 | |||||
| December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
$ | 111,439 | $ | 1,840 | $ | (683 | ) | $ | 112,596 | ||||
| Corporate and other bonds |
15,435 | 653 | (92 | ) | 15,996 | ||||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
135,962 | 930 | (672 | ) | 136,220 | ||||||||
| Federal Reserve Bank stock - restricted |
3,337 | — | — | 3,337 | |||||||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank stock - restricted |
13,800 | — | — | 13,800 | |||||||||
| Other securities |
743 | 7 | — | 750 | |||||||||
| $ | 280,716 | $ | 3,430 | $ | (1,447 | ) | $ | 282,699 | |||||
The following table presents the amortized cost and estimated fair value of securities available for sale as of December 31, 2008, by contractual maturity (dollars in thousands). Expected maturities may differ from contractual maturities because borrowers may have the right to call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties.
| Amortized Cost |
Estimated Fair Value | |||||
| Due in one year or less |
$ | 4,546 | $ | 4,576 | ||
| Due after one year through five years |
38,013 | 38,316 | ||||
| Due after five years through ten years |
86,403 | 87,477 | ||||
| Due after ten years |
166,468 | 162,555 | ||||
| 295,430 | 292,924 | |||||
| Federal Reserve Bank stock - restricted |
3,383 | 3,383 | ||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank stock - restricted |
13,171 | 13,171 | ||||
| Other securities |
255 | 233 | ||||
| Total securities available for sale |
$ | 312,239 | $ | 309,711 | ||
Securities with an amortized cost of $129.6 million and $128.4 million as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 were pledged to secure public deposits, repurchase agreements and for other purposes.
59
Sales, call, maturities and paydowns of securities available for sale produced the following results for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sales |
$ | 881 | $ | 100 | $ | 1,005 | ||||
| Proceeds from calls, maturities and paydowns |
35,895 | 55,289 | 47,614 | |||||||
| Total proceeds |
$ | 36,776 | $ | 55,389 | $ | 48,619 | ||||
| Gross realized gains |
$ | 29 | $ | 587 | $ | 688 | ||||
| Gross realized losses |
— | (1 | ) | — | ||||||
| Net realized gains |
$ | 29 | $ | 586 | $ | 688 | ||||
Management evaluates securities for other-than-temporary impairment at least on a quarterly basis and more frequently when economic or market concerns warrant such evaluation. Consideration is given to (i) the length of time and the extent to which the fair value has been less than cost, (ii) the financial condition and near-term prospects of the issuer, and (iii) the intent and ability of the Company to retain its investment in the issuer for a period of time sufficient to allow for any anticipated recovery in fair value.
The primary purpose of the investment portfolio is to generate income and meet liquidity needs of the Company through readily saleable financial instruments. The portfolio includes fixed rate bonds, whose prices move inversely with rates. At the end of any accounting period, the investment portfolio has unrealized gains and losses. The Company monitors the portfolio, which is subject to liquidity needs, market rate changes and credit risk changes, to see if adjustments are needed. The primary cause of temporary impairments was the increase in spreads over comparable Treasury bonds. At December 31, 2008, there was $9.26 million of individual securities that had been in a continuous loss position for more than 12 months. Additionally, these securities had an unrealized loss of $876 thousand and primarily consisted of obligations of states and political subdivisions. Because the declines in fair value were attributable to changes in credit and market spreads, not in estimated cash flows or credit quality of the issuer, no other-than-temporary impairment was recorded at December 31, 2008.
The following tables present the gross unrealized losses and fair values as of December 31, 2008 and 2007, aggregated by investment category and length of time that the individual securities have been in a continuous unrealized loss position (dollars in thousands):
| Less than 12 months | More than 12 months | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| Fair value |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair value |
Unrealized Losses |
Fair value |
Unrealized Losses |
||||||||||||||||
| As of September 30, 2008 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
$ | 54,345 | $ | (4,497 | ) | $ | 5,057 | $ | (667 | ) | $ | 59,402 | $ | (5,164 | ) | ||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
25,481 | (116 | ) | 2,597 | (27 | ) | 28,078 | (143 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Corporate and other bonds |
9,464 | (1,954 | ) | 1,609 | (182 | ) | 11,073 | (2,136 | ) | ||||||||||||
| $ | 89,290 | $ | (6,567 | ) | $ | 9,263 | $ | (876 | ) | $ | 98,553 | $ | (7,443 | ) | |||||||
| As of December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
$ | 26,227 | $ | (564 | ) | $ | 4,055 | $ | (119 | ) | $ | 30,282 | $ | (683 | ) | ||||||
| Mortgage-backed securities |
10,891 | (16 | ) | 48,785 | (656 | ) | 59,676 | (672 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Corporate and other bonds |
— | — | 4,513 | (92 | ) | 4,513 | (92 | ) | |||||||||||||
| $ | 37,118 | $ | (580 | ) | $ | 57,353 | $ | (867 | ) | $ | 94,471 | $ | (1,447 | ) | |||||||
60
3. LOANS
Loans are stated at their face amount, net of unearned income, and consist of the following at December 31, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Mortgage loans on real estate: |
||||||
| Residential 1-4 family |
$ | 292,003 | $ | 281,847 | ||
| Commercial |
550,680 | 500,118 | ||||
| Construction |
403,502 | 396,928 | ||||
| Second mortgages |
38,060 | 37,875 | ||||
| Equity lines of credit |
162,740 | 128,897 | ||||
| Multifamily |
37,321 | 32,970 | ||||
| Agriculture |
30,727 | 18,958 | ||||
| Total real estate loans |
1,515,033 | 1,397,593 | ||||
| Commercial Loans |
146,827 | 136,317 | ||||
| Consumer installment loans |
||||||
| Personal |
160,161 | 173,650 | ||||
| Credit cards |
15,723 | 13,108 | ||||
| Total consumer installment loans |
175,884 | 186,758 | ||||
| All other loans |
36,344 | 27,152 | ||||
| Gross loans |
$ | 1,874,088 | $ | 1,747,820 | ||
At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the recorded investment in loans, which have been identified as impaired loans, in accordance with SFAS No. 114, Accounting by Creditors for Impairment of a Loan (“SFAS 114”), totaled $53.7 million and $9.4 million, respectively. The valuation allowance related to $24.1 million and $9.4 million of impaired loans at December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $3.8 million and $500 thousand, respectively. The remaining impaired loans of $29.6 million at December 31, 2008 did not require a valuation allowance. For the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, the average investment in impaired loans was $38.6 million, $8.9 million and $11.4 million, respectively. The interest income recorded on impaired loans was approximately $1.9 million in 2008 and zero in both 2007 and 2006.
Nonaccrual loans totaled $14.4 million and $9.4 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Had these loans performed in accordance with their original terms, interest income of approximately $560 thousand, $422 thousand and $752 thousand would have been recorded in 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. There were no non-accrual loans excluded from impaired loan disclosure at December 31, 2008 and 2007. Loans past due 90 days or more and accruing interest totaled $3.1 million and $905 thousand at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
61
4. ALLOWANCE FOR LOAN LOSSES
Activity in the allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 is summarized below (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of year |
$ | 19,336 | $ | 19,148 | $ | 17,116 | ||||||
| Allowance of acquired banks |
— | — | 785 | |||||||||
| Recoveries credited to allowance |
340 | 340 | 419 | |||||||||
| Loans charged off |
(4,200 | ) | (1,212 | ) | (622 | ) | ||||||
| Provision charged to operations |
10,020 | 1,060 | 1,450 | |||||||||
| Balance, end of year |
$ | 25,496 | $ | 19,336 | $ | 19,148 | ||||||
5. BANK PREMISES AND EQUIPMENT
Bank premises and equipment as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Land |
$ | 17,467 | $ | 16,238 | ||
| Land improvements and buildings |
56,508 | 52,372 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
1,739 | 1,962 | ||||
| Furniture and equipment |
27,921 | 26,722 | ||||
| Construction in progress |
7,126 | 6,724 | ||||
| Total |
110,761 | 104,018 | ||||
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization |
33,336 | 28,277 | ||||
| Bank premises and equipment, net |
$ | 77,425 | $ | 75,741 | ||
Depreciation expense for 2008, 2007 and 2006 was $5.3 million, $4.7 million, and $3.9 million, respectively. Future minimum rental payments required under non-cancelable operating leases for bank premises that have initial or remaining terms in excess of one year as of December 31, 2008 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 |
$ | 1,853 | |
| 2010 |
1,525 | ||
| 2011 |
1,343 | ||
| 2012 |
1,110 | ||
| 2013 |
583 | ||
| Thereafter |
3,051 | ||
| Total of future payments |
$ | 9,465 | |
The leases contain options to extend for periods up to 20 years. Rental expense for years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 totaled $2.3 million, $2.0 million, and $1.7 million, respectively.
6. GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
Effective January 1, 2001, the Company adopted SFAS No. 142, which prescribes the accounting for goodwill and intangible assets subsequent to initial recognition. The provisions of SFAS No. 142 discontinue the amortization of goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives but require at least an
62
annual impairment review and more frequently if certain impairment indicators are in evidence. Based on the testing for impairment of goodwill and intangible assets, there were no impairment charges for 2008, 2007 or 2006. Core deposit intangible assets are being amortized over the period of expected benefit, which ranges from 5 to 15 years.
As part of the purchase price allocation for the Acquired Bank Branches, the Company recorded approximately $1.1 million in core deposit intangible assets and $4.3 million in goodwill in 2007. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Acquired Bank Branch acquisition are being amortized over an average of 8.1 years.
As part of the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of Prosperity, the Company recorded approximately $5.5 million in core deposit intangible assets and $20.6 million in goodwill in 2006. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Prosperity acquisition are being amortized over an average of 9.1 years.
As part of the purchase price allocation for the acquisition of Guaranty, the Company recorded approximately $5.8 million in core deposit intangible assets and $30.1 million in goodwill in 2004. The core deposit intangible assets recorded in the Guaranty acquisition are being amortized over an average of 8.7 years.
Information concerning goodwill and intangible assets for years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 is presented in the following table (dollars in thousands):
| Gross Carrying Value |
Accumulated Amortization |
Net Carrying Value | |||||||
| December 31, 2008 |
|||||||||
| Amortizable core deposit intangibles |
$ | 20,215 | $ | 10,602 | $ | 9,613 | |||
| Unamortizable goodwill |
56,816 | 342 | 56,474 | ||||||
| December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||
| Amortizable core deposit intangibles |
$ | 20,215 | $ | 8,665 | $ | 11,550 | |||
| Unamortizable goodwill |
56,816 | 342 | 56,474 | ||||||
Amortization expense of core deposit intangibles for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 totaled $2.0 million, $1.9 million and $1.7 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2008, the estimated amortization expense of core deposit intangibles are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 |
$ | 1,924 | |
| 2010 |
1,924 | ||
| 2011 |
1,874 | ||
| 2012 |
1,687 | ||
| 2013 |
924 | ||
| Thereafter |
1,280 | ||
| Total estimated amortization expense |
$ | 9,613 | |
63
7. DEPOSITS
The aggregate amount of time deposits in denominations of $100,000 or more as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 was $452.3 million and $453.2 million, respectively. As of December 31, 2008, the scheduled maturities of time deposits are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 |
$ | 610,963 | |
| 2010 |
175,057 | ||
| 2011 |
156,300 | ||
| 2012 |
10,988 | ||
| 2013 |
40,059 | ||
| Thereafter |
2,789 | ||
| Total scheduled maturities of time deposits |
$ | 996,156 | |
8. BORROWINGS
Short-term borrowings consist of securities sold under agreements to repurchase, which are secured transactions with customers and generally mature the day following the date sold. Other short-term borrowings may include Federal Funds purchased, which are unsecured overnight borrowings from other financial institutions, and advances from the Federal Home Loan Bank of Atlanta (“FHLB”), which are secured by mortgage-related assets. The carrying value of the loans pledged as collateral for FHLB advances total $752.2 million as of December 31, 2008. Short-term borrowings consist of the following as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| Securities sold under agreements to repurchase |
$ | 68,282 | $ | 82,049 | ||||
| Federal Funds purchased |
— | 41,837 | ||||||
| Federal Home Loan Bank Advances |
55,000 | 159,000 | ||||||
| Total short-term borrowings |
$ | 123,282 | $ | 282,886 | ||||
| Maximum month-end outstanding balance |
$ | 267,311 | $ | 282,886 | ||||
| Average outstanding balance during the year |
188,442 | 178,603 | ||||||
| Average interest rate during the year |
2.54 | % | 4.39 | % | ||||
| Average interest rate at end of year |
1.73 | % | 4.21 | % | ||||
At December 31, 2008, the Company’s fixed-rate long-term debt totals $150.0 million, is made up of FHLB advances and matures on various dates through 2018 at interest rates that range from 3.60% to 6.26%. At December 31, 2007, the Company’s fixed-rate long-term debt totaled $20.0 million and matures on various dates through 2010.
64
As of December 31, 2008, the contractual maturities of long-term debt are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| Fixed Rate | Adjustable Rate |
Total | |||||||
| 2009 |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||
| 2010 |
10,000 | — | 10,000 | ||||||
| 2011 |
— | — | — | ||||||
| 2012 |
— | — | — | ||||||
| 2013 |
— | — | — | ||||||
| Thereafter |
140,000 | 60,310 | 200,310 | ||||||
| Total long-term debt |
$ | 150,000 | $ | 60,310 | $ | 210,310 | |||
During the first quarter of 2004, the Company’s Statutory Trust I, a wholly owned subsidiary, was formed for the purpose of issuing redeemable capital securities in connection with the acquisition of Guaranty Financial Corporation. A Trust Preferred Capital Note of $22.5 million was issued through a pooled underwriting. The securities have a LIBOR-indexed floating rate (three month LIBOR plus 2.75%) which adjusts and is payable quarterly. The interest rate at December 31, 2008 was 4.18%. The capital securities may be redeemed at par beginning on June 17, 2009 and each quarterly anniversary of such date until the securities mature on June 17, 2034. The principal asset of the Statutory Trust I is $23.2 million of the Company’s junior subordinated debt securities with like maturities and like interest rates to the capital notes, while $696 thousand is reflected as the Company’s investment in Statutory Trust I reported as “Other assets” within the consolidated balance sheet.
During the first quarter of 2006, the Company formed Statutory Trust II, a wholly owned subsidiary, for the purpose of issuing redeemable capital securities in connection with the acquisition of Prosperity that was completed on April 1, 2006. A Trust Preferred Capital Note of $36.0 million was issued through a pooled underwriting. The securities have a LIBOR-indexed floating rate (three month LIBOR plus 1.40%) which adjusts and is payable quarterly. The interest rate at December 31, 2008 was 2.83%. The redeemable securities may be called at par after five years on March 31, 2011 and each quarterly anniversary of such date until the securities mature in 30 years on March 31, 2036. The principal asset of the Statutory Trust II is $37.1 million of the Company’s junior subordinated debt securities with like maturities and like interest rates to the capital notes, while $1.1 million is reflected as the Company’s investment in Statutory Trust II reported as “Other assets” within the consolidated balance sheet.
The obligations of the Company with respect to the issuance of the capital securities constitute a full and unconditional guarantee by the Company of the trust’s obligations with respect to the capital securities. Subject to certain exceptions and limitations, the Company may elect from time to time to defer interest payments on the junior subordinated debt securities, which would result in a deferral of distribution payments on the related Capital Securities and require a deferral of common dividends.
The subsidiary banks maintain Federal Funds lines with several correspondent banks totaling $92.0 million and $49.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. Additionally, the Company had a collateral dependent line of credit with the FHLB of up to $752.2 million and $607.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
65
9. INCOME TAXES
The Company files income tax returns in the U. S. and the Commonwealth of Virginia. With few exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to U. S. federal, state and local income tax examinations by tax authorities for years prior to 2005.
The Company adopted the provisions of FIN 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in Income Taxes”, on January 1, 2007 with no impact on the financial statements.
Net deferred tax assets and liabilities consist of the following components as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||
| Allowance for loan losses |
$ | 9,044 | $ | 6,768 | ||
| Benefit plans |
891 | 853 | ||||
| Nonaccrual loans |
286 | 697 | ||||
| Conversion expenses |
— | 14 | ||||
| Securities available for sale |
911 | — | ||||
| Other |
400 | 555 | ||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
11,532 | 8,887 | ||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||
| Depreciation |
2,593 | 1,889 | ||||
| Purchase accounting intangibles |
2,364 | 2,798 | ||||
| Other |
550 | 399 | ||||
| Securities available for sale |
— | 667 | ||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
5,507 | 5,753 | ||||
| Net deferred tax asset |
$ | 6,025 | $ | 3,134 | ||
In assessing the ability to realize deferred tax assets, management considers the scheduled reversal of temporary differences, projected future taxable income, and tax planning strategies. Management believes it is more likely than not the Company will realize its deferred tax assets and, accordingly, no valuation allowance has been established.
The provision for income taxes charged to operations for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006 consists of the following (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||
| Current tax expense |
$ | 5,571 | $ | 6,246 | $ | 10,779 | |||||
| Deferred tax expense (benefit) |
(1,313 | ) | 238 | (828 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 4,258 | $ | 6,484 | $ | 9,951 | |||||
66
The income tax expense differs from the amount of income tax determined by applying the U. S. federal income tax rate to pretax income for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, due to the following (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Computed “expected” tax expense |
$ | 6,570 | $ | 9,184 | $ | 12,580 | ||||||
| (Decrease) in taxes resulting from: |
||||||||||||
| Tax-exempt interest income, net |
(1,978 | ) | (1,698 | ) | (1,565 | ) | ||||||
| Other, net |
(334 | ) | (1,002 | ) | (1,064 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 4,258 | $ | 6,484 | $ | 9,951 | ||||||
The effective tax rates were 22.7%, 24.7%, and 27.7% for years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively. Tax credits totaled $158 thousand, $172 thousand, and $201 thousand, for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
10. EMPLOYEE BENEFITS
The Company has a 401(k) Plan that allows employees to make pre-tax contributions for retirement. The 401(k) Plan provides for matching contributions by the Company for employee contributions up to 3% of each employee’s compensation. The Company also has an Employee Stock Ownership Plan (“ESOP”). The Company makes discretionary profit sharing contributions into the 401(k) Plan, ESOP and in cash. Company discretionary contributions to both the 401(k) Plan and the ESOP are allocated to participant accounts in proportion to each participant’s compensation and vested over a six year time interval. Employee contributions to the ESOP are not allowed. The 401(k) Plan does provide for limited investment in the Company’s stock. Company discretionary profit sharing payments made in 2008, 2007, and 2006 were as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
| 401(k) Plan |
$ | 1,355 | $ | 1,780 | $ | 1,429 | |||
| ESOP |
586 | 1,061 | 1,226 | ||||||
| Cash |
373 | 296 | 238 | ||||||
| Total |
$ | 2,314 | $ | 3,137 | $ | 2,893 | |||
The Company has an obligation to certain members of the subsidiary banks’ Boards of Directors under deferred compensation plans in the amount of $1.1 million on both December 31, 2008 and 2007. The expenses related to the deferred compensation plans were $85 thousand, $89 thousand, and $103 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. These benefits will be fully funded by life insurance proceeds.
In December 2001, the Company’s Board of Directors approved an annual incentive compensation plan as a means of attracting, rewarding and retaining management. Each annual plan, as it may be amended from time to time, is based on both corporate and individual objectives established annually for each participant. The corporate goals have been based on earnings per share and asset growth and growth relative to peer banks, while the individual goals are based on specific performance evaluation objectives. Each participant is evaluated within these two categories to determine eligibility and rate of incentive compensation based on performance. Salaries and benefits expense includes $366 thousand, $310 thousand, and $472 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively, for incentive compensation under this plan.
67
The Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan provides for the granting of incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, and nonvested stock awards to key employees of the Company. The Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan replaced the 1993 Stock Incentive Plan, and became effective on July 1, 2003 after shareholders approved the plan at the annual meeting of shareholders. The Stock Incentive Plan makes available 525,000 shares, which may be awarded to employees of the Company in the form of equity based awards intended to comply with the requirements of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986. Under the plan, the option price cannot be less than the fair market value of the stock on the grant date. The stock option’s maximum term is ten years from the date of grant and vests in equal annual installments of twenty percent over a five year vesting schedule. The Company issues new shares to satisfy stock-based awards. As of December 31, 2008, approximately 310,630 shares were available for issuance under the Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan.
Stock Options
The following table summarizes the stock option activity for the last three years:
| Number of Stock Options |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Options Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | ||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2005 |
328,294 | $ | 16.78 | 287,223 | $ | 16.44 | |||||
| Granted |
27,473 | 31.57 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(48,395 | ) | 15.35 | ||||||||
| Forfeited |
(2,836 | ) | 24.06 | ||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2006 |
304,536 | 18.28 | 247,438 | 16.71 | |||||||
| Granted |
22,400 | 27.62 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(46,743 | ) | 14.19 | ||||||||
| Forfeited |
(2,830 | ) | 26.65 | ||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2007 |
277,363 | 19.64 | 219,875 | 17.62 | |||||||
| Granted |
4,750 | 20.41 | |||||||||
| Exercised |
(59,461 | ) | 13.83 | ||||||||
| Forfeited |
(6,575 | ) | 22.41 | ||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 |
216,077 | 21.12 | 175,278 | 19.62 | |||||||
A summary of options outstanding at December 31, 2008 is as follows:
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Options Outstanding |
Options Exercisable | ||||||||||||||
| Number Outstanding |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Number Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price | ||||||||||||
| $ 8.54 | - | $ 8.67 | 14,298 | 1.72 yrs | $ | 8.59 | 14,298 | $ | 8.59 | |||||||
| 10.67 | 24,285 | 3.00 | 10.67 | 24,285 | 10.67 | |||||||||||
| 18.58 | 47,940 | 4.06 | 18.58 | 47,940 | 18.58 | |||||||||||
| 18.98 |
- | 20.41 | 10,000 | 6.87 | 20.17 | 5,250 | 19.94 | |||||||||
| 22.65 | 47,448 | 5.08 | 22.65 | 42,424 | 22.65 | |||||||||||
| 23.50 | 20,588 | 6.07 | 23.50 | 20,588 | 23.50 | |||||||||||
| 27.51 | 3,750 | 6.58 | 27.51 | 3,750 | 27.51 | |||||||||||
| 27.62 | 20,820 | 8.15 | 27.62 | 4,164 | 27.62 | |||||||||||
| 31.57 | 23,948 | 7.15 | 31.57 | 9,579 | 31.57 | |||||||||||
| 31.84 | 3,000 | 6.96 | 31.84 | 3,000 | 31.84 | |||||||||||
| $ 8.54 |
- | $ 31.84 | 216,077 | 5.15 yrs | $ | 21.12 | 175,278 | $ | 19.62 | |||||||
The fair value of each stock option grant was estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option valuation model that uses the assumptions noted in the following table for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006:
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Dividend yield (1) |
2.29 | % | 1.99 | % | 2.05 | % | ||||||
| Expected life in years (2) |
7.8 | 7.5 | 7.5 | |||||||||
| Expected volatility (3) |
29.89 | % | 25.23 | % | 29.53 | % | ||||||
| Risk-free interest rate (4) |
3.68 | % | 4.68 | % | 4.56 | % | ||||||
| Weighted average fair value per option granted |
$ | 6.15 | $ | 8.07 | $10.26 | |||||||
68
The following table summarizes information concerning stock options issued to the Company’s employees that are vested or are expected to vest and stock options exercisable as of December 31, 2008 (dollars in thousands, except share and per share amounts):
| Stock Options Vested or Expected to Vest |
Exercisable | |||||
| Stock options |
209,093 | 175,278 | ||||
| Weighted average remaining contractual life in years |
5.08 | 4.60 | ||||
| Weighted average exercise price on shares above water |
$ | 21.12 | $ | 19.62 | ||
| Aggregate intrinsic value |
$ | 1,043 | $ | 1,017 | ||
The total intrinsic value for stock options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2008 was $405 thousand. The total intrinsic values of stock options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2008 were both $1.0 million. The fair value of stock options vested during the year ended December 31, 2008 was approximately $237 thousand. Cash received from the exercise of stock options for the year ended December 31, 2008 was approximately $822 thousand. The tax benefits realized from tax deductions associated with options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2008 was $58 thousand.
Nonvested Stock
The 2003 plan permits the granting of nonvested stock, but is limited to one-third of the aggregate number of total awards granted. This equity component of compensation is divided between restricted (time-based) stock grants and performance-based stock grants. The restricted stock vests fifty percent on each of the third and fourth anniversaries of the date of the grant. The performance-based stock is subject to vesting on the fourth anniversary of the date of the grant based on the performance of the Company’s stock price. The value of the nonvested stock awards was calculated by multiplying the fair market value of the Company’s common stock on grant date by the number of shares awarded. Employees have the right to vote the shares and to receive cash or stock dividends (restricted stock), if any, except for the nonvested stock under the performance-based component (performance stock).
The following table summarizes nonvested stock activity for the year ended December 31, 2008:
| Restricted Stock | Performance Stock |
Total | Weighted Average Grant-Date Fair Value | |||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2007 |
28,343 | 30,281 | 58,624 | $ | 27.84 | |||||||
| Granted |
8,357 | — | 8,357 | 19.83 | ||||||||
| Vested |
(4,450 | ) | — | (4,450 | ) | 25.00 | ||||||
| Forfeited |
(1,228 | ) | (2,349 | ) | (3,577 | ) | 27.37 | |||||
| Balance, December 31, 2008 |
31,022 | 27,932 | 58,954 | 26.95 | ||||||||
69
The estimated unamortized compensation expense, net of estimated forfeitures, related to nonvested stock and stock options issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2008 will be recognized in future periods is as follows (dollars in thousands):
| Stock Options | Restricted Stock | Total | |||||||
| For year ended December 31, 2009 |
$ | 96 | $ | 307 | $ | 403 | |||
| For year ended December 31, 2010 |
93 | 191 | 284 | ||||||
| For year ended December 31, 2011 |
56 | 27 | 83 | ||||||
| For year ended December 31, 2012 |
17 | 9 | 26 | ||||||
| For year ended December 31, 2013 |
2 | — | 2 | ||||||
| Total |
$ | 264 | $ | 534 | $ | 798 | |||
At December 31, 2008, there was $798 thousand of total unrecognized compensation cost related to nonvested stock-based compensation arrangements granted under the plan. The cost is expected to be recognized through 2013.
11. FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS WITH OFF-BALANCE SHEET RISK
The Company is a party to financial instruments with off-balance sheet risk in the normal course of business to meet the financing needs of its customers and to reduce its own exposure to fluctuations in interest rates. These financial instruments include commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit. These instruments involve elements of credit and interest rate risk in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheets. The contractual amounts of these instruments reflect the extent of the Company’s involvement in particular classes of financial instruments.
The Company’s exposure to credit loss in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the financial instruments for commitments to extend credit and letters of credit written is represented by the contractual amount of these instruments. The Company uses the same credit policies in making commitments and conditional obligations as it does for on-balance sheet instruments. Unless noted otherwise, the Company does not require collateral or other security to support off-balance sheet financial instruments with credit risk.
Commitments to extend credit are agreements to lend to customers as long as there are no violations of any conditions established in the contracts. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee. Because many of the commitments may expire without being completely drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily represent future cash requirements. The Company evaluates each customer’s creditworthiness on a case by case basis. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the Company had outstanding loan commitments approximating $538.6 million and $704.6 million, respectively.
Letters of credit written are conditional commitments issued by the Company to guarantee the performance of customers to third parties. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit is essentially the same as that involved in extending loans to customers. The amount of standby letters of credit whose contract amounts represent credit risk totaled $28.0 million and $30.8 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively.
At December 31, 2008, Union Mortgage had rate lock commitments to originate mortgage loans amounting to $81.1 million and loans held for sale of $29.4 million. Union Mortgage has entered into corresponding mandatory commitments on a best-efforts basis to sell loans on a servicing released basis totaling approximately $110.5 million. These commitments to sell loans are designed to eliminate Union Mortgage’s exposure to fluctuations in interest rates in connection with rate lock commitments and loans held for sale.
70
12. RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The Company has entered into transactions with its directors, principal officers and affiliated companies in which they are principal stockholders. Such transactions were made in the ordinary course of business on substantially the same terms, including interest rates and collateral, as those prevailing at the same time for comparable transactions with other customers, and did not, in the opinion of management, involve more than normal credit risk or present other unfavorable features. The aggregate amount of loans to such related parties totaled $22.7 million and $39.6 million at December 31, 2008 and 2007, respectively. During 2008, new advances to such related parties amounted to $7.6 million and repayments amounted to $24.5 million.
13. EARNINGS PER SHARE
The basic EPS calculation was computed by dividing net income available to common shareholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted EPS is computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period, including the effect of dilutive potential common shares outstanding attributable to stock awards and warrant. Amortization of discount on the preferred stock is treated as a reduction of the numerator in calculating basis and diluted EPS.
There were approximately 131,301; 98,126 and 26,394 anti-dilutive options as of December 31, 2008, 2007, and 2006, respectively.
The following is a reconciliation of the denominators of the basic and diluted EPS computations for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 (in thousands except per share data):
| Net Income Available to Common Shareholders (Numerator) |
Weighted Average Shares (Denominator) |
Per Share Amount |
|||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
|||||||||
| Basic EPS |
$ | 14,496 | 13,478 | $ | 1.08 | ||||
| Effect of dilutive stock awards |
— | 52 | (0.01 | ) | |||||
| Effect of dilutive warrant |
— | 13 | — | ||||||
| Diluted EPS |
$ | 14,496 | 13,543 | $ | 1.07 | ||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||
| Basic EPS |
$ | 19,756 | 13,342 | $ | 1.48 | ||||
| Effect of dilutive stock awards |
— | 80 | (0.01 | ) | |||||
| Diluted EPS |
$ | 19,756 | 13,422 | $ | 1.47 | ||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2006 |
|||||||||
| Basic EPS |
$ | 25,992 | 13,233 | $ | 1.97 | ||||
| Effect of dilutive stock awards |
— | 129 | (0.03 | ) | |||||
| Diluted EPS |
$ | 25,992 | 13,362 | $ | 1.94 | ||||
14. COMMITMENTS AND LIABILITIES
In the ordinary course of its operations, the Company and its subsidiaries are parties to various legal proceedings. Based on the information presently available, and after consultation with legal counsel, management believes that the ultimate outcome in such proceedings, in the aggregate, will not have a material adverse effect on the business or the financial condition or results of operations of the Company.
71
The Company must maintain a reserve against its deposits in accordance with Regulation D of the Federal Reserve Act. For the final weekly reporting period in the years ended December 31, 2008 and 2007 the aggregate amount of daily average required reserves was approximately $6.8 million and $6.9 million, respectively. At December 2008, financial market uncertainty and the Federal Reserve Bank’s decision to pay interest on funds held at member reserve banks prompted the Company to maintain its excess cash at the Federal Reserve Bank instead of correspondent financial institutions in Federal Funds sold.
The Company has approximately $2.2 million in deposits in other financial institutions in excess of amounts insured by the FDIC at December 31, 2008.
15. REGULATORY MATTERS AND CAPITAL
The Company and its subsidiary banks are subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory—and possibly additional discretionary—actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct material effect on the Company’s and the Community Banks’ financial statements. Under capital adequacy guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Company and the Community Banks must meet specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of their assets, liabilities and certain off-balance sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting practices. The capital amounts and classification are also subject to qualitative judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings and other factors. Prompt corrective action provisions are not applicable to bank holding companies.
Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require the Company and Banks to maintain minimum amounts and ratios of Total to Risk-Weighted Assets (as defined) and Tier I capital (as defined) to Average Assets (as defined) and Risk-Weighted Assets. Management believes, as of December 31, 2008, that the Company met all capital adequacy requirements to which it is subject.
As of December 31, 2008, the most recent notification from their federal regulators categorized the subsidiary banks as well capitalized under the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action. To be categorized as well-capitalized, an institution must maintain minimum total risk-based, Tier I risk-based and Tier I leverage ratios as set forth in the following tables. There are no conditions or events since that notification that management believes have changed the subsidiary banks’ category.
On December 19, 2008, the Company entered into a Purchase Agreement with the U. S Treasury pursuant to which it issued 59,000 shares of the Company’s Preferred Stock having a liquidation preference of $1,000 per share, for a total price of $59 million. The issuance was made pursuant to the Treasury’s Capital Purchase Plan under TARP. The Preferred Stock pays a cumulative dividend at a rate of 5% per year during the first five years and thereafter at 9% per year. The transaction closed on December 19, 2008. At the time of issuance, the Treasury also received a warrant to purchase 422,636 shares of the Company’s common stock at an initial per share exercise price of $20.94. The warrant expires ten years from the issuance date. For the dilutive effects of the Preferred Stock and warrant, reference Note 13 “Earnings Per Share” in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements”.
72
The Company and its principal banking subsidiaries’ actual capital amounts and ratios are also presented in the following table at December 31, 2008 and 2007 (dollars in thousands):
| Actual | Required for Capital Adequacy Purposes |
Required in Order to Be Well Capitalized Under PCA |
||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||
| As of December 31, 2008 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total capital to risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
$ | 293,317 | 14.56 | % | $ | 161,201 | 8.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
185,582 | 11.26 | % | 131,806 | 8.00 | % | $ | 164,758 | 10.00 | % | ||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
30,428 | 12.29 | % | 19,808 | 8.00 | % | 24,760 | 10.00 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 capital to risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
268,126 | 13.31 | % | 80,600 | 4.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
164,964 | 10.01 | % | 65,903 | 4.00 | % | 98,855 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
28,428 | 11.48 | % | 9,904 | 4.00 | % | 14,856 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 capital to average adjusted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
268,126 | 11.14 | % | 96,294 | 4.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
164,964 | 8.87 | % | 74,426 | 4.00 | % | 93,032 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
28,428 | 8.24 | % | 13,807 | 4.00 | % | 17,258 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||
| As of December 31, 2007 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Total capital to risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
$ | 220,687 | 11.67 | % | $ | 151,246 | 8.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
143,203 | 10.58 | % | 108,288 | 8.00 | % | $ | 135,360 | 10.00 | % | ||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
28,017 | 11.29 | % | 19,851 | 8.00 | % | 24,814 | 10.00 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 capital to risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
201,351 | 10.65 | % | 75,623 | 4.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
128,525 | 9.50 | % | 54,144 | 4.00 | % | 81,216 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
25,911 | 10.44 | % | 9,925 | 4.00 | % | 14,888 | 6.00 | % | |||||||||
| Tier 1 capital to average adjusted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||
| UBSH Consolidated |
201,351 | 9.20 | % | 87,556 | 4.00 | % | NA | NA | ||||||||||
| Union Bank and Trust |
128,525 | 8.58 | % | 59,948 | 4.00 | % | 74,935 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||
| Northern Neck State Bank |
25,911 | 7.76 | % | 13,353 | 4.00 | % | 16,692 | 5.00 | % | |||||||||
16. FAIR VALUE MEASUREMENTS
The Company adopted SFAS No. 157 on January 1, 2008 to record fair value adjustments to certain assets and liabilities and to determine fair value disclosures. SFAS 157 clarifies that fair value of certain assets and liabilities is an exit price, representing the amount that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between willing market participants.
In February 2008, FASB issued Staff Position No. 157-2 (“FSP 157-2”) which delayed the effective date of SFAS 157 for certain nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities except for those items that are recognized or disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis. FSP 157-2 defers the effective date of SFAS 157 for such nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities to fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008, and interim periods within those fiscal years. Thus, the Company has only partially applied SFAS 157. Those items affected by FSP 157-2 include other real estate owned (OREO), goodwill and core deposit intangibles.
In October 2008, FASB issued Staff Position No. 157-3 (“FSP 157-3”) to clarify the application of SFAS 157 in a market that is not active and to provide key considerations in determining the fair value of a financial asset when the market for that financial asset is not active. FSP 157-3 was effective upon issuance.
SFAS 157 specifies a hierarchy of valuation techniques based on whether the inputs to those valuation techniques are observable or unobservable. Observable inputs reflect market data obtained from independent sources, while unobservable inputs reflect the Company’s market assumptions. The three levels of the fair value hierarchy under SFAS 157 based on these two types of inputs are as follows:
| Level 1 | Valuation is based on quoted prices in active markets for identical assets and liabilities. |
73
| Level 2 | Valuation is based on observable inputs including quoted prices in active markets for similar assets and liabilities, quoted prices for identical or similar assets and liabilities in less active markets, and model-based valuation techniques for which significant assumptions can be derived primarily from or corroborated by observable data in the market. | |||
| Level 3 | Valuation is based on model-based techniques that use one or more significant inputs or assumptions that are unobservable in the market. | |||
The following describes the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure certain financial assets and liabilities recorded at fair value on a recurring basis in the financial statements:
Securities available for sale
Securities available for sale are recorded at fair value on a recurring basis. Fair value measurement is based upon quoted market prices, when available (Level 1). If quoted market prices are not available, fair values are measured utilizing independent valuation techniques of identical or similar securities for which significant assumptions are derived primarily from or corroborated by observable market data. Third party vendors compile prices from various sources and may determine the fair value of identical or similar securities by using pricing models that considers observable market data (Level 2). If the inputs used to provide the evaluation for certain securities are unobservable and/or there is little, if any, market activity (Level 3). The carrying value of restricted Federal Reserve Bank and Federal Home Loan Bank stock approximates fair value based on the redemption provisions of each entity and is therefore excluded from the following table.
The following table presents the balances of financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2008 (dollars in thousands):
| Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2008 using | |||||||||||
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
Balance | ||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
| ASSETS |
|||||||||||
| Securities available for sale |
$ | 4,376 | $ | 288,781 | — | $ | 293,157 | ||||
| Total |
$ | 4,376 | $ | 288,781 | — | $ | 293,157 | ||||
Certain financial assets are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis in accordance with GAAP. Adjustments to the fair value of these assets usually result from the application of lower-of-cost-or-market accounting or write-downs of individual assets.
The following describes the valuation techniques used by the Company to measure certain financial assets recorded at fair value on a nonrecurring basis in the financial statements (dollars in thousands):
Loans held for sale
Loans held for sale are carried at the lower of cost or market value. These loans currently consist of residential loans originated for sale in the secondary market. Fair value is based on the price secondary markets are currently offering for similar loans using observable market data which is not materially different than cost due to the short duration between origination and sale (Level 2). As such, the Company records any fair value adjustments on a nonrecurring basis. No nonrecurring fair value adjustments were recorded on loans held for sale during the year ended December 31, 2008. Gains and losses on the sale of loans are recorded within income from mortgage segment on the Consolidated Statements of Income.
74
Impaired Loans
Loans are designated as impaired when, in the judgment of management, based on current information and events, it is probable that all amounts due according to the contractual terms of the loan agreement will not be collected. The measurement of loss associated with impaired loans can be based on either the observable market price of the loan or the fair value of the collateral. Fair value is measured based on the value of the collateral securing the loans. Collateral may be in the form of real estate or business assets including equipment, inventory, and accounts receivable. The vast majority of the Company’s collateral is real estate. The value of real estate collateral is determined utilizing an income or market valuation approach based on an appraisal conducted by an independent, licensed appraiser outside of the Company using observable market data (Level 2). However, if the collateral is a house or building in the process of construction or if an appraisal of the real estate property is over two years old, then the fair value is considered Level 3. The value of business equipment is based upon an outside appraisal if deemed significant, or the net book value on the applicable business’ financial statements if not considered significant using observable market data. Likewise, values for inventory and accounts receivables collateral are based on financial statement balances or aging reports (Level 3). Impaired loans allocated to the Allowance for Loan Losses are measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis. Any fair value adjustments are recorded in the period incurred as provision for loan losses on the Consolidated Statements of Income. At December 31, 2008 the Company’s Level 3 Impaired loans consisted of one credit relationship secured by real estate (two assisted living facilities). This relationship existed for all of 2008. In the table below, $24.1 million of impaired loans was reduced by a valuation allowance of $3.8 million, of which $500 thousand related to the Level 3 category.
The following table summarizes the Company’s financial assets that were measured at fair value on a nonrecurring basis during the period.
| Fair Value Measurements at December 31, 2008 using | ||||||||||||
| Quoted Prices in Active Markets for Identical Assets |
Significant Other Observable Inputs |
Significant Unobservable Inputs |
Balance | |||||||||
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | ||||||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
$ | — | $ | 29,424 | $ | — | $ | 29,424 | ||||
| Impaired loans |
— | 13,899 | 6,371 | 20,270 | ||||||||
| Total |
$ | — | $ | 43,323 | $ | 6,371 | $ | 49,694 | ||||
The fair value of a financial instrument is the current amount that would be exchanged between willing parties, other than in a forced liquidation. Fair value is best determined based on quoted market prices. However, in many instances, there are no quoted market prices for the Company’s various financial instruments. In cases where quoted market prices are not available, fair values are based on estimates using present value or other valuation techniques. Those techniques are significantly affected by the assumptions used, including the discount rate and estimates of future cash flows. Accordingly, the fair value estimates may not be realized in an immediate settlement of the instruments. SFAS No. 107,
75
Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments, excludes certain financial instruments and all non-financial instruments from its disclosure requirements. Accordingly, the aggregate fair value amounts presented may not necessarily represent the underlying fair value of the Company.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For those short-term instruments, the carrying amount is a reasonable estimate of fair value.
Loans
The fair value of performing loans is estimated by discounting the future cash flows using the current rates at which similar loans would be made to borrowers with similar credit ratings and for the same remaining maturities. Fair value for significant nonperforming loans is based on recent external appraisals. If appraisals are not available, estimated cash flows are discounted using a rate commensurate with the risk associated with the estimated cash flows.
Deposits
The fair value of demand deposits, savings accounts, and certain money market deposits is the amount payable on demand at the reporting date. The fair value of certificates of deposit is estimated by discounting the future cash flows using the rates currently offered for deposits of similar remaining maturities.
Borrowings
The carrying value of short-term borrowings is a reasonable estimate of fair value. The fair value of long-term borrowings is estimated based on interest rates currently available for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities.
Accrued Interest
The carrying amounts of accrued interest approximate fair value.
Commitments to Extend Credit and Standby Letters of Credit
The fair value of commitments is estimated using the fees currently charged to enter into similar agreements, taking into account the remaining terms of the agreements and the present creditworthiness of the counterparties. For fixed-rate loan commitments, fair value also considers the difference between current levels of interest rates and the committed rates. The fair value of letters of credit is based on fees currently charged for similar agreements or on the estimated cost to terminate them or otherwise settle the obligations with the counterparties at the reporting date. At December 31, 2008 and 2007, the carrying value and fair value of loan commitments and standby letters of credit was immaterial.
The carrying values and estimated fair values of the Company’s financial instruments as of December 31, 2008 and 2007 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||
| Carrying Amount |
Fair Value |
Carrying Amount |
Fair Value | |||||||||
| Financial assets: |
||||||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 148,537 | $ | 148,537 | $ | 58,279 | $ | 58,279 | ||||
| Securities available for sale |
309,711 | 309,711 | 282,699 | 282,699 | ||||||||
| Loans held for sale |
29,424 | 29,424 | 25,248 | 25,248 | ||||||||
| Net loans |
1,848,592 | 1,849,240 | 1,728,484 | 1,765,219 | ||||||||
| Accrued interest receivable |
10,230 | 10,230 | 11,303 | 11,303 | ||||||||
| Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Deposits |
1,926,999 | 1,953,527 | 1,659,578 | 1,669,232 | ||||||||
| Borrowings |
333,592 | 334,622 | 412,696 | 411,632 | ||||||||
| Accrued interest payable |
3,572 | 3,572 | 3,422 | 3,422 | ||||||||
76
The Company assumes interest rate risk (the risk that general interest rate levels will change) as a result of its normal operations. As a result, the fair values of the Company’s financial instruments will change when interest rate levels change and that change may be either favorable or unfavorable to the Company. Management attempts to match maturities of assets and liabilities to the extent believed necessary to minimize interest rate risk. However, borrowers with fixed rate obligations are less likely to prepay in a rising rate environment and more likely to prepay in a falling rate environment. Conversely, depositors who are receiving fixed rates are more likely to withdraw funds before maturity in a rising rate environment and less likely to do so in a falling rate environment. Management monitors rates and maturities of assets and liabilities and attempts to minimize interest rate risk by adjusting terms of new loans and deposits and by investing in securities with terms that mitigate the Company’s overall interest rate risk.
17. PARENT COMPANY FINANCIAL INFORMATION
The primary sources of funds for the dividends paid by Union Bankshares Corporation (the “Parent Company”) are dividends received from its subsidiary banks. The payments of dividends by the subsidiary banks to the Parent Company are subject to certain statutory limitations which contemplate that the current year earnings and earnings retained for the two preceding years may be paid to the Parent Company without regulatory approval. As of December 31, 2008, the aggregate amount of unrestricted funds, which could be transferred from the Company’s subsidiaries to the Parent Company, without prior regulatory approval, totaled approximately $27.0 million, or 9.9%, of the consolidated net assets.
Financial information for the Parent Company is as follows:
PARENT COMPANY
BALANCE SHEETS
AS OF DECEMBER 31, 2008 and 2007
(Dollars in thousands)
| 2008 | 2007 | ||||||
| ASSETS |
|||||||
| Cash |
$ | 50,465 | $ | 2,735 | |||
| Securities available for sale, at fair value |
100 | 100 | |||||
| Bank premises and equipment, net |
17,113 | 18,141 | |||||
| Other assets |
3,856 | 4,388 | |||||
| Investment in subsidiaries |
276,357 | 261,691 | |||||
| Total assets |
$ | 347,891 | $ | 287,055 | |||
| LIABILITIES & STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
|||||||
| Long-term borrowings |
$ | 11,875 | $ | 12,500 | |||
| Trust preferred capital notes |
60,310 | 60,310 | |||||
| Other liabilities |
1,908 | 2,163 | |||||
| Total liabilities |
74,093 | 74,973 | |||||
| Preferred stock |
590 | — | |||||
| Common stock |
18,055 | 17,879 | |||||
| Surplus |
101,719 | 40,758 | |||||
| Retained earnings |
155,140 | 152,238 | |||||
| Warrant |
2,808 | — | |||||
| Discount on preferred stock |
(2,790 | ) | — | ||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income |
(1,724 | ) | 1,207 | ||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
273,798 | 212,082 | |||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 347,891 | $ | 287,055 | |||
77
PARENT COMPANY
STATEMENTS OF INCOME
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006
(Dollars in thousands)
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||
| Income: |
||||||||||
| Interest and dividend income |
$ | 5 | $ | 6 | $ | 5 | ||||
| Management fee received from subsidiaries |
17,297 | 14,966 | 13,084 | |||||||
| Dividends received from subsidiaries |
9,876 | 20,618 | 12,031 | |||||||
| Equity in undistributed net income from subsidiaries |
7,358 | 2,594 | 17,003 | |||||||
| Gains on sale of securities, net |
— | 91 | 276 | |||||||
| Gains (losses) on sale of fixed assets, net |
(7 | ) | 307 | — | ||||||
| Other operating income |
8 | 38 | 67 | |||||||
| Total income |
34,537 | 38,620 | 42,466 | |||||||
| Expenses: |
||||||||||
| Interest expense |
3,855 | 4,821 | 3,618 | |||||||
| Salaries and benefits |
10,445 | 9,472 | 8,938 | |||||||
| Occupancy expenses |
955 | 643 | 306 | |||||||
| Furniture and equipment expenses |
1,479 | 1,423 | 1,245 | |||||||
| Other operating expenses |
3,289 | 2,505 | 2,367 | |||||||
| Total expenses |
20,023 | 18,864 | 16,474 | |||||||
| Net income |
14,514 | 19,756 | 25,992 | |||||||
| Amortization of discount on preferred stock |
18 | — | — | |||||||
| Net income available to common stockholders |
$ | 14,496 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | ||||
78
PARENT COMPANY
CONDENSED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
YEARS ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006
(Dollars in thousands)
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,514 | $ | 19,756 | $ | 25,992 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Equity in undistributed net income of subsidiaries |
(7,358 | ) | (2,594 | ) | (17,003 | ) | ||||||
| Gains on sale of investment securities |
— | (91 | ) | (276 | ) | |||||||
| Increase in other assets |
(2,782 | ) | (1,501 | ) | (1,869 | ) | ||||||
| Other, net |
848 | 1,961 | 3,515 | |||||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by operating activities |
5,222 | 17,531 | 10,359 | |||||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from sales of investment securities |
— | 123 | 559 | |||||||||
| Net increase in bank premises and equipment |
(160 | ) | (9,360 | ) | (6,653 | ) | ||||||
| Payments for investments in and advances to subsidiaries |
(7,308 | ) | (8,080 | ) | (41,415 | ) | ||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents used in investing activities |
(7,468 | ) | (17,317 | ) | (47,509 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in long-term borrowings |
(625 | ) | 10,150 | 2,350 | ||||||||
| Proceeds from trust preferred capital notes |
— | — | 37,114 | |||||||||
| Cash dividends paid |
(9,990 | ) | (9,686 | ) | (8,345 | ) | ||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise of equity-based awards |
58 | 22 | 182 | |||||||||
| Cash paid for fractional shares |
— | — | (10 | ) | ||||||||
| Issuance of preferred stock |
58,924 | — | — | |||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
(254 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Issuance of common stock |
1,863 | 1,702 | 1,634 | |||||||||
| Net cash and cash equivalents provided by financing activities |
49,976 | 2,188 | 32,925 | |||||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
47,730 | 2,402 | (4,225 | ) | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of the period |
2,735 | 333 | 4,558 | |||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of the period |
$ | 50,465 | $ | 2,735 | $ | 333 | ||||||
79
18. SEGMENT REPORTING
The Company has two reportable segments: traditional full service community banks and a mortgage loan origination business. The community bank business includes three banks, which provide loan, deposit, investment, and trust services to retail and commercial customers throughout their 59 retail locations in Virginia and the D.C. metro area. The mortgage segment provides a variety of mortgage loan products principally in Virginia and Maryland. These loans are originated and sold primarily in the secondary market through purchase commitments from investors, which subject the Company to only de minimus risk.
Profit and loss is measured by net income after taxes including realized gains and losses on the Company’s investment portfolio. The accounting policies of the reportable segments are the same as those described in the summary of significant accounting policies. Inter-segment transactions are recorded at cost and eliminated as part of the consolidation process.
Both of the Company’s reportable segments are service based. The mortgage business is a fee-based business while the banks are driven principally by net interest income. The banks provide a distribution and referral network through their customers for the mortgage loan origination business. The mortgage segment offers a more limited referral network for the banks, due largely to the minimal degree of overlapping geographic markets.
The community bank segment provides the mortgage segment with the short-term funds needed to originate mortgage loans through a warehouse line of credit and charges the mortgage banking segment interest at the three month LIBOR rate plus 25 basis points. These transactions are eliminated in the consolidation process. A management fee for operations and administrative support services is charged to all subsidiaries and eliminated in the consolidated totals.
80
Information about reportable segments and reconciliation of such information to the consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| Community Banks |
Mortgage | Eliminations | Consolidated Totals | |||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
$ | 77,248 | $ | 625 | $ | — | $ | 77,873 | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
10,020 | — | — | 10,020 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
67,228 | 625 | — | 67,853 | ||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
19,766 | 11,114 | (325 | ) | 30,555 | |||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
68,284 | 11,676 | (325 | ) | 79,636 | |||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
18,710 | 62 | — | 18,772 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
4,235 | 23 | — | 4,258 | ||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 14,475 | $ | 39 | $ | — | $ | 14,514 | ||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,546,330 | $ | 33,077 | $ | (27,475 | ) | $ | 2,551,932 | |||||
| Capital expenditures (1) |
$ | 5,033 | $ | 117 | $ | — | $ | 5,150 | ||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2007 |
||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
$ | 75,497 | $ | 248 | $ | — | $ | 75,745 | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
1,060 | — | — | 1,060 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
74,437 | 248 | — | 74,685 | ||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
16,586 | 8,797 | (278 | ) | 25,105 | |||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
63,437 | 10,391 | (278 | ) | 73,550 | |||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
27,586 | (1,346 | ) | — | 26,240 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
7,027 | (543 | ) | — | 6,484 | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 20,559 | $ | (803 | ) | $ | — | $ | 19,756 | |||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,300,528 | $ | 28,852 | $ | (27,983 | ) | $ | 2,301,397 | |||||
| Capital expenditures (1) |
$ | 14,573 | $ | 114 | $ | — | $ | 14,687 | ||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2006 |
||||||||||||||
| Net interest income |
$ | 76,490 | $ | 225 | $ | — | $ | 76,715 | ||||||
| Provision for loan losses |
1,450 | — | — | 1,450 | ||||||||||
| Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
75,040 | 225 | — | 75,265 | ||||||||||
| Noninterest income |
17,240 | 11,273 | (268 | ) | 28,245 | |||||||||
| Noninterest expenses |
56,571 | 11,264 | (268 | ) | 67,567 | |||||||||
| Income before income taxes |
35,709 | 234 | — | 35,943 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
9,855 | 96 | — | 9,951 | ||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 25,854 | $ | 138 | $ | — | $ | 25,992 | ||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 2,090,461 | $ | 23,763 | $ | (21,333 | ) | $ | 2,092,891 | |||||
| Capital expenditures (1) |
$ | 20,954 | $ | 130 | $ | — | $ | 21,084 | ||||||
| (1) | Capital expenditures include purchase of property, furniture and equipment. |
81
19. OTHER OPERATING EXPENSES
The following table presents the statement of income line “Other Operating Expenses” broken into greater detail for the years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006 (dollars in thousands):
| 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||
| Communication expenses |
$ | 6,822 | $ | 6,598 | $ | 5,046 | |||
| Professional services |
2,378 | 2,063 | 2,049 | ||||||
| Data processing fees |
1,340 | 1,366 | 1,367 | ||||||
| Marketing & advertising expense |
2,405 | 2,526 | 2,467 | ||||||
| Insurance expense |
1,245 | 333 | 281 | ||||||
| Other taxes |
1,662 | 1,692 | 1,321 | ||||||
| Loan & OREO expenses |
754 | 608 | 440 | ||||||
| Amortization of core deposit premuims |
1,957 | 1,889 | 1,697 | ||||||
| Other expenses (1) |
5,999 | 6,809 | 5,755 | ||||||
| Total other operating expenses |
$ | 24,562 | $ | 23,884 | $ | 20,423 | |||
| (1) | Includes internal conversion costs of $515 thousand, $211 thousand and $263 thousand for the years 2008, 2007 and 2006, respectively. |
20. STOCK SPLIT
On September 7, 2006, the Company’s Board of Directors declared a three-for-two stock split to shareholders of record as of the close of business on October 2, 2006. Shares resulting from the split were distributed by the Company’s transfer agent on October 13, 2006. Fractional shares were settled in cash based on the closing price of the Company’s shares reported by the NASDAQ Global Select Market as of October 13, 2006. Following the stock split, the number of outstanding shares increased to approximately 13.3 million shares. Accordingly, share and per share amounts for all periods presented in the consolidated financial statements and notes thereto have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the effect of the three-for-two split.
21. CUMULATIVE EFFECT OF A CHANGE IN ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLE
During the first quarter of 2008, Emerging Issues Task Force 06-4 “Accounting for Deferred Compensation and Postretirement Benefit Aspects of Endorsement Split-Dollar Life Insurance Arrangements” became effective. This statement requires the Company to recognize a liability (offset as a reduction to capital) and related compensation costs for endorsement split-dollar life insurance arrangements that provide benefits to employees during post-retirement periods. The Company recorded a reduction to retained earnings and corresponding increase to liabilities of $1.6 million. This reduction to retained earnings has been reflected in the Company’s Condensed Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity.
ITEM 9. – CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE.
During the past two years, there have been no changes in or reportable disagreement with the certifying accountants for the Company or any of its subsidiaries.
82
ITEM 9A. – CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. The Company maintains “disclosure controls and procedures,” as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”), that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized, and reported within the time periods specified in Securities and Exchange Commissions rules and forms, and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. In designing and evaluating its disclosure controls and procedures, management recognized that disclosure controls and procedures, no matter how well conceived and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance that the objectives of the disclosure controls and procedures are met. Additionally, in designing disclosure controls and procedures, management necessarily was required to apply its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible disclosure controls and procedures. The design of any disclosure controls and procedures also is based in part upon certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions.
Based on their evaluation as of the end of the period covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that the disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) of the Exchange Act. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Management assessed the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008. In making this assessment, management used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission in Internal Control—Integrated Framework. Based on the assessment using those criteria, management concluded that the internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2008.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2008 has been audited by Yount, Hyde & Barbour, P.C., the independent registered public accounting firm who also audited the Company’s consolidated financial statements included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Yount, Hyde & Barbour, P.C.’s attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting appears on pages 40 through 42 hereof.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting. There was no change in the internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the quarter ended December 31, 2008 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, the internal control over financial reporting.
Not applicable.
83
ITEM 10. – DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
Information regarding directors, executive officers, the Company’s audit committee and the audit committee financial expert is incorporated by reference from the Company’s definitive proxy statement for the Company’s 2009 Annual Meeting of Shareholders to be held April 21, 2009 (“Proxy Statement”), under the captions “Election of Directors,” “Corporate Governance,” and “Executive Officers.”
Information on Section 16(a) beneficial ownership reporting compliance for the directors and executive officers of the Company is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance.”
The Company has adopted a broad based code of ethics for all employees and directors. The Company has also adopted a code of ethics tailored for directors and senior officers who have financial responsibilities. A copy of the codes may be obtained without charge by request from the Company’s corporate secretary.
ITEM 11. – EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
This information is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the captions “Corporate Governance”, “Compensation Discussion and Analysis”, “Report of the Compensation Committee”, “Executive Compensation”, and “Director Compensation.”
ITEM 12. – SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS.
Other than as set forth below, this information is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Ownership of Company Common Stock” and from Note 10 “Employee Benefits” contained in the “Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements” of this 10-K.
The following table summarizes information, as of December 31, 2008, relating to the Company’s 2003 Stock Incentive Plan, pursuant to which grants of option to acquire shares of common stock may be awarded from time to time.
84
| Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
Weighted-average exercise |
Number of securities under equity compensation plans (excluding securities | |||||
| (A) | (B) | (C)1 | |||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
216,077 | $ | 21.12 | 310,630 | |||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
— | — | — | ||||
| Total |
216,077 | $ | 21.12 | 310,630 | |||
| 1 |
Consists of shares available for future issuance under the Union Bankshares Corporation 2003 Stock Incentive Plan. |
ITEM 13. – CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE.
This information is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the captions “Corporate Governance” and “Interest of Directors and Officers in Certain Transactions.”
ITEM 14. – PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES.
This information is incorporated by reference from the Proxy Statement under the caption “Principal Accounting Fees.”
ITEM 15. – EXHIBITS, FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
The following documents are filed as part of this report:
(a)(1) Financial Statements
The following consolidated financial statements and reports of independent registered public accountants of the Company are in Part II, Item 8:
| • | Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm; |
| • | Consolidated Balance Sheets - December 31, 2008 and 2007; |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Income - Years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006; |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Changes in Stockholders’ Equity - Years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006; |
| • | Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows - Years ended December 31, 2008, 2007 and 2006; |
| • | Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements. |
85
(a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules are omitted since they are not required, are not applicable, or the required information is shown in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
86
(a)(3) Exhibits
The following exhibits are filed as part of this Form 10-K and this list includes the Exhibit Index.
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 3.01 | Articles of Incorporation of Union Bankshares Corporation, as amended | |
| 3.02 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Union Bankshares Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.02 to Annual Report on Form 10-K filed on March 14, 2008) | |
| 4.01 | Warrant to Purchase up to 422,636 shares of Common Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 23, 2008) | |
| 10.01 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of G. William Beale | |
| 10.02 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement of G. William Beale | |
| 10.03 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of D. Anthony Peay | |
| 10.04 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of John C. Neal | |
| 10.05 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of N. Byrd Newton | |
| 10.06 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of Rawley H. Watson, III | |
| 10.07 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement (formerly referred to as Change in Control Employment Agreement) of Janis Orfe | |
| 10.08 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement of John C. Neal | |
| 10.09 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement of D. Anthony Peay | |
| 10.10 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement of Michael T. Leake | |
| 10.11 | Amended and Restated Management Continuity Agreement of Robert L. Bailey | |
| 10.12 | Union Bankshares Corporation 2003 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Form S-8 Registration Statement; SEC file no. 333-113839) | |
| 10.13 | Union Bankshares Corporation Non-Employee Directors’ Stock Plan (incorporated by reference to Form S-8 Registration Statement; SEC file no. 333-113842) | |
| 10.14 | Letter Agreement, dated December 19, 2008, including the Securities Purchase Agreement – Standard Terms incorporated by reference therein, between Union Bankshares Corporation and the United States Department of the Treasury (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 23, 2008) | |
| 11.03 | Statement re: Computation of Per Share Earnings (incorporated by reference to Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements included in this Annual Report) | |
| 21.01 | Subsidiaries of the Registrant | |
| 23.01 | Consent of Yount, Hyde & Barbour, P.C. | |
| 31.01 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 31.02 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 32.01 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
87
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Union Bankshares Corporation | ||||
| By: | /s/ G. William Beale |
Date: March 16, 2009 | ||
| G. William Beale | ||||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities indicated on March 16, 2009.
| Signature |
Title | |
| /s/ G. William Beale G. William Beale |
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (principal executive officer) | |
| /s/ Douglas E. Caton Douglas E. Caton |
Director | |
| /s/ Daniel I. Hansen Daniel I. Hansen |
Director | |
| /s/ Ronald L. Hicks Ronald L. Hicks |
Chairman of the Board of Directors | |
| /s/ Patrick J. McCann Patrick J. McCann |
Director | |
| /s/ Hullihen W. Moore Hullihen W. Moore |
Director | |
| /s/ R. Hunter Morin R. Hunter Morin |
Director | |
| /s/ W. Tayloe Murphy, Jr. W. Tayloe Murphy, Jr. |
Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors | |
| /s/ D. Anthony Peay D. Anthony Peay |
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer (principal financial and accounting officer) | |
| /s/ Ronald L. Tillett Ronald L. Tillett |
Director | |
| /s/ A. D. Whittaker A. D. Whittaker |
Director | |
88